American black duck
| American black duck | |
|---|---|
 | |
| American black duck in flight | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Anseriformes |
| Family: | Anatidae |
| Genus: | Anas |
| Species: | A. rubripes |
| Binomial name | |
| Anas rubripes (Brewster, 1902) | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Anas obscura Gmelin, 1789 | |
The American black duck (Anas rubripes) is a large dabbling duck in the family Anatidae. It was described by William Brewter in his landmark article An Undescribed form of the Black Duck (Anas obscura), in The Auk's 19th volume. It has the highest body mass in the Anas genus, weighing 720–1,640 g (1.59–3.62 lb) on average and measuring 54–59 cm (21–23 in) in length with a 88–95 cm (35–37 in) wingspan. It somewhat resembles the female mallard in coloration, but has a darker plumage. The male and the female of this species are generally similar in appearance, but the male's bill is yellow while the female's is dull green with dark marks on the upper mandible. It is native to eastern North America. During the breeding season, it is usually found in coastal and freshwater wetlands in northern Saskatchewan, Manitoba, across Ontario, Quebec as well as the Atlantic Canadian Provinces, including the Great Lakes and the Adirondacks in the United States. It is a partially migratory species, mostly wintering in the east-central United States, especially coastal areas.
It interbreeds regularly and extensively with the mallard, to which it are closely related. The female lays six to fourteen oval eggs, which have smooth shells and come in varied shades of white, cream white and buff-green color. Hatching takes 30 days on average. Incubation usually takes 25 to 26 days, with both sexes share duties, although the male usually defends the territory until the female reaches the middle of her incubation period. It takes about 6 weeks to fledge. Once the eggs hatch, the hen leads the brood to rearing areas with abundant invertebrates and vegetation.
The American black duck is considered to be a species of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). It has long been valued as a game bird. Habitat loss due drainage, global warming, filling of wetlands due to urbanization and rising sea levels are major reasons for the declining population of the American black duck. The United States Fish and Wildlife Service has been purchasing and managing the habitat of this species in many areas supporting the migratory stopover, wintering and breeding populations. The Atlantic Coast Joint Venture has also been protecting the habitat of the American black duck, through habitat restoration and land acquisition projects, mostly within their wintering and breeding areas.
Taxonomy and etymology
American ornithologist William Brewter described the American black duck as Anas obscura rubripes, for "red-legged black duck".[2] This was in his landmark article An Undescribed form of the Black Duck (Anas obscura), in The Auk's 19th volume, in 1902, to present out the differences between the two kinds of black ducks found in New England. One of them was described as being comparatively small, with brownish legs and olivaceous or dusky bill, and the other as being comparatively larger, with a lighter skin tone, bright red legs and a clear yellow bill.[2] The larger of the two was described as Anas obscura, by the German naturalist Johann Friedrich Gmelin in 1789,[1] in the 13th edition of the Systema Naturae part 2, and he based it on the "Ducky Duck" of Welsh naturalist Thomas Pennant.[2] The current scientific name, Anas rubripes, is derived from Latin, with Anas meaning "duck", and rubripes coming from ruber, "red", and pes, "foot".[3]
Pennant, in Arctic Zoology's volume 2, described this duck as coming "from the province of New York" and having "a long and narrow dusky bill, tinged with blue: chin white: neck pale brown, streaked downwards with dusky lines".[2] In a typical obscura, characteristics such as greenish black, olive green or dusky olive bill; olivaceous brown legs with at most one reddish tinge; the nape and pileum nearly uniformly dark; spotless chin and throat; fine linear and dusky markings on the neck and sides of the head, rather than blackish, do not vary with age or season.[2]
Description


The American black duck weighs 720–1,640 g (1.59–3.62 lb) and measures 54–59 cm (21–23 in) in length with a 88–95 cm (35–37 in) wingspan.[4] This species has the highest mean body mass in the Anas genus, with a sample of 376 males averaging 1.4 kg (3.1 lb) and 176 females averaging 1.1 kg (2.4 lb).[5][6] The American black duck somewhat resembles the female mallard in coloration, although the black duck's plumage is darker.[7] The male and the female of this species are generally similar in appearance, but the male's bill is yellow while the female's is dull green with dark marks on the upper mandible[8] and is occasionally flecked with black.[9][10] The head is a slightly lighter brown than the dark brown body. The cheeks and throat are streaked brown and there is a dark streak going through the crown and dark eye.[7] The speculums are iridescent violet-blue with predominantly black margins.[8] The black duck has fleshy orange feet with dark webs.[11]
In flight, the white lining of the underwings can be seen in contrast to the blackish underbody and upperside.[7][12] The purple speculum lacks white bands at the front and rear, and rarely has a white trailing edge. A dark crescent is visible on the median underwing primary coverts.[12]
Juveniles resemble adult females, but has broken narrow pale edges at underpart feathers, which gives a slightly streaked rather than scalloped appearance, and whole appearance browner rather than uniformly blackish. Juvenile males have brownish-orange feet and juvenile females have brownish feet and dusky greyish-green bill.[12]
Distribution and habitat

The American black duck is endemic to eastern North America.[13] The range extends from northeastern Saskatchewan to Newfoundland and Labrador, in Canada.[7] In the United States, it is found in northern Illinois, Michigan, New Jersey, Ohio, Connecticut, Vermont, southern to northern South Dakota, central West Virginia, Maine and on the Atlantic coast to North Carolina.[14][7]
The American black duck is a habitat generalist species as it is associated to tidal marshes and present throughout the year in northeastern salt marshes from the Gulf of Maine to coastal Virginia.[15] It usually prefers freshwater and coastal wetlands throughout northeastern America, including brackish marshes,estuaries and edges of backwater ponds and rivers, lined by speckled alder.[14][7] They also inhabit beaver ponds, shallow lakes with sedges and reeds, bogs in open boreal and mixed hardwood forests, and forested swamps.[14] The American black duck population of Vermont have also been found in glacial kettle ponds surrounded by bog mats.[14] During winter, the American black duck mostly inhabits brackish marshes bordering bays, agricultural marshes, flooded timber, agricultural fields, estuaries and riverine areas.[14] They usually take shelter from hunting and other disturbances, by moving to brackish and fresh impoundments on conservation land.[4]
Behavior
Feeding
The American black duck is an omnivorous species[16] and has a diverse diet.[17] It feeds by dabbling in shallow water and grazing on land.[16] Its plant diet primarily includes a wide variety of wetland grasses and sedges, seeds, stems, leaves and roots-stalks of aquatic plants,[8] while their animal diet includes mollusks, snails, amphipods, insects, mussels and small fishes.[16][17] It also forages on aquatic plants, such as eelgrass, pondweed and smartweed.[7]
During the breeding season, the American black duck consumes about 80% plant food and 20% animal food, which increases to 85% during winter.[16] During nesting, the proportion of invertebrates increases.[8] Ducklings mostly eat water invertebrates for the first 12 days after hatching, including aquatic snowbugs, snails, mayflies, dragonflies, beetles, flies, caddisflies and larvae. After this, they shift to seeds and other plant food.[16]
Breeding
The breeding habitat includes alkaline marshes, acid bogs, lakes, ponds, rivers, marshes, brackish marshes and the margins of estuaries and other aquatic environments in northern Saskatchewan, Manitoba, across Ontario, Quebec as well as the Atlantic Canadian Provinces, including the Great Lakes and the Adirondacks in the United States.[18] It is partially migratory, and many winter in the east-central United States, especially coastal areas; some remain year-round in the Great Lakes region.[19]
Nest sites are well-concealed on the ground, often on uplands.[20] Egg clutches number six to fourteen eight oval eggs,[11] which have smooth shells and come in varied shades of white, cream white and buff-green color.[18] On an average, they measure 59.4 mm (2.34 in) long, 43.2 mm (1.70 in) wide and weigh 56.6 g (0.125 lb).[18] Hatching takes 30 days on average .[11] The incubation period is of varied lengths,[18] but usually takes 25 to 26 days.[20] Both sexes share duties, although the male usually defends the territory until the female reaches the middle of her incubation period.[20] It takes about 6 weeks to fledge.[20] Once the eggs hatch, the hen leads the brood to rearing areas with abundant invertebrates and vegetation.[20]
The American black duck interbreeds regularly and extensively with the mallard, to which it is closely related.[21] Some authorities even consider the black duck to be a subspecies of the mallard instead of a separate species. Mank et al. argue that this is in error as the extent of hybridization alone is not a valid means to delimitate Anas species.[22]
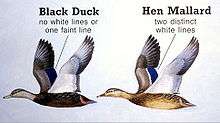
In the past, it has been proposed that the American black duck and the mallard were formerly separated by habitat preference, with the American black duck’s dark plumage giving it a selective advantage in shaded forest pools in eastern North America, and the mallard’s lighter plumage giving it an advantage in the brighter, more open prairie and plains lakes.[23] In recent times, according to this view, deforestation in the east and tree planting on the plains, has broken down this habitat separation, leading to the high levels of hybridization now observed.[24] However, rates of past hybridization are unknown in this and most other avian hybrid zones, and it is merely presumed in the case of the American black duck, that past hybridization rates were lower than those seen today. Also, many avian hybrid zones are known to be stable and longstanding despite the occurrence of extensive interbreeding.[21] The American black duck and the local mallard are now very hard to distinguish by means of microsatellite comparisons, even if many specimens are sampled [25] Contrary to this study's claims, the question whether the American haplotype is an original mallard lineage is far from resolved. Their statement, "[N]orthern black ducks are now no more distinct from mallards than their southern conspecifics" only holds true in regard to the molecular markers tested.[22] As birds indistinguishable according to the set of microsatellite markers still can look different, there are other genetic differences that were simply not tested in the study.[22]
It has been revealed in captivity studies that most of the hybrids do not follow Haldane's Rule, but sometimes hybrid females die before they reach sexual maturity. This underscores the case for the American black duck being a distinct species.[21][26] This duck is a rare vagrant to Great Britain and Ireland, where over the years several birds have settled in and bred with the local mallard.[27] The resulting hybrid can present considerable identification difficulties.[27]
Nest predators and hazards
The apex nest predators of the American black duck includes American crows, gulls and raccoons, especially in tree nests.[16] Great horned owls are also a major predator of the adult species. Bullfrogs and snapping turtles are know to take away many ducklings.[16] Ducklings often catch diseases caused by protozoan blood parasites which transmit by bites of insects such as blackflies.[16] They are also vulnerable to lead shot poisoning, known as plumbism, due to their bottom-foraging food habits.[16]
Status and conservation
Since 1988, the American black duck has been rated as least concern on the IUCN Red List of Endangered species.[1] This is because the range of this species is extremely large, which is not near the threshold of vulnerable species.[1] In addition, the population of the American black duck is much larger, and the population decline is also not as rapid to rate this species as vulnerable.[1] It has long been valued as a game bird, being extremely wary and fast on wings.[28] Habitat loss due drainage, filling of wetlands due to urbanization, global warming and rising sea levels, are major reasons for the declining population of the American black duck.[13] Some conservationists consider hybridization and competition with the mallard an additional source of concern should this decline continue.[29][30] Hybridization itself is not a major problem; natural selection makes sure that the best-adapted individuals have the most offspring.[31] However, the reduced viability of female hybrids causes some broods to fail in the long run, due to the death of the offspring before reproducing themselves.[32] While this is not a problem in the plentiful mallard, it might place an additional strain on the American black duck's population. Recent research conducted for the Delta Waterfowl Foundation suggests that hybrids are a result of forced copulations and not a normal pairing choice by black hens.[33]
The United States Fist and Wildlife Service has continued to purchase and manage the habitat in many areas supporting the migratory stopover, wintering and breeding populations of the American black duck.[13] In addition, the Montezuma National Wildlife Refuge has purchased and restored over 1,000 acres of wetlands in order to provide the stopover habitat for over 10,000 American black ducks during fall migration.[13] Also, the Atlantic Coast Joint Venture has been protecting the habitat of the American black duck through habitat restoration and land acquisition projects, mostly within their wintering and breeding areas.[13] In 2003, a Boreal Forest Conservation Framework was adopted by conservation organizations, industries and First Nations, to protect the Canadian boreal forests, including the American black duck's eastern Canadian breeding range, where large numbers of it breed.[13]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 BirdLife International (2012). "Anas rubripes". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Archived from the original on 2016-04-25. Retrieved 2013-11-26.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Union., American Ornithologists' (1902). "The Auk.". v. 19 1902. ISSN 0004-8038.
- ↑ Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 46, 340. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- 1 2 "American Black Duck". www.allaboutbirds.org. 2011. Archived from the original on 2017-02-17. Retrieved 2017-06-29.
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses by John B. Dunning Jr. (Editor). CRC Press (1992), ISBN 978-0-8493-4258-5.
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses, 2nd Edition by John B. Dunning Jr. (Editor). CRC Press (2008), ISBN 978-1-4200-6444-5.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Smith, Christopher (2000). Field Guide to Upland Birds and Waterfowl. United States: Wilderness Adventures Press. p. 60. ISBN 9781885106209.
- 1 2 3 4 Kear, Janet (2005). Ducks, Geese and Swans: Species accounts (Cairina to Mergus). United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. p. 509. ISBN 9780198610090.
- ↑ Potter, Eloise F.; Parnell, James F.; Teulings, Robert P.; Davis, Ricky (2015). Birds of the Carolinas. United States: The University of North Carolina Press. p. 47. ISBN 9781469625652.
- ↑ Dunn, Jon Lloyd; Alderfer, Jonathan K. (2006). National Geographic Field Guide to the Birds of North America. United States: National Geographic Books. p. 30. ISBN 9780792253143.
- 1 2 3 Ryan, James M. (2009). Adirondack Wildlife: A Field Guide. United States: University Press of New England. p. 118. ISBN 9781584657491.
- 1 2 3 Beaman, Mark; Madge, Steve (2010). The Handbook of Bird Identification: For Europe and the Western Palearctic. United Kingdom: A&C Black. p. 163. ISBN 9781408135235.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Wells, Jeffrey V. (2010). Birder's Conservation Handbook: 100 North American Birds at Risk. United States: Princeton University Press. pp. 56–57. ISBN 1400831512.
- 1 2 3 4 5 U.S Department of the Interior, National Park Service (2007). Cape Cod National Seashore (N.S.), Hunting Program: Environmental Impact Statement. United States. pp. 83–84.
- ↑ Roman, Charles T. (2012). Tidal Marsh Restoration: A Synthesis of Science and Management. United States: Island Press. p. 132. ISBN 9781610912297.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Eastman, John Andrew (1999). Birds of Lake, Pond, and Marsh: Water and Wetland Birds of Eastern North America. United States: Stackpole Books. pp. 57–58. ISBN 9780811726818.
- 1 2 Maehr, David S.; II, Herbert W. Kale (2005). Florida's Birds: A Field Guide and Reference. United States: Pineapple Press Inc. p. 56. ISBN 9781561643356.
- 1 2 3 4 Baldassarre, Guy A. (2014). Ducks, Geese, and Swans of North America. United States: Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 353–356. ISBN 9781421407517.
- ↑ Jerry R., Longcore; McAuley, Daniel G.; Hepp, Gary R.; Rhymer, Judith M. (2000). "American Black Duck: Anas rubripes". Archived from the original on 2016-03-25. Retrieved 2017-06-30.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Schwartz, Nancy A. (2010). Wildlife Rehabilitation: Basic Life Support. United Kingdom: Xlibris Corporation. ISBN 9781453531921.
- 1 2 3 McCarthy, Eugene M. (2006). "Handbook of Avian Hybrids of the World". Oxford University Press.
- 1 2 3 Mank, Judith E.; Carlson, John E.; Brittingham, Margaret C. (2004). "A century of hybridization: Decreasing genetic distance between American black ducks and mallards.". Conservation Genetics. 5 (3): 395–403. doi:10.1023/B:COGE.0000031139.55389.b1.
- ↑ Armistead, George L.; Sullivan, Brian L. (2015). Better Birding: Tips, Tools, and Concepts for the Field. United States: Princeton University Press. p. 13. ISBN 9780691129662.
- ↑ Johnsgard, Paul A. (1967). "Sympatry Changes and Hybridization Incidence in Mallards and Black Ducks". American Midland Naturalist. 77 (1): 51–63. JSTOR 2423425. doi:10.2307/2423425.
- ↑ Avise, John C.; Ankney, C. Davison; Nelson, William S. (1990). "Mitochondrial Gene Trees and the Evolutionary Relationship of Mallard and Black Ducks". Evolution. 44 (4): 1109–1119. doi:10.2307/2409570.
- ↑ Kirby, Ronald E.; Sargeant, Glen A.; Shutler, Dave (2004). "Haldane’s rule and American black duck × mallard hybridization". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 82 (11): 1827–1831. doi:10.1139/z04-169.
- 1 2 Evans, Lee G. R. (1994). Rare Birds in Britain 1800-1990. LGRE Productions Incorporated. pp. 13–14. ISBN 9781898918004.
- ↑ Anonymous (2007). Lake Umbagog National Wildlife Refuge (N.W.R.), Conservation Plan: Environmental Impact Statement. United States. pp. 142–143.
- ↑ Rhymer, Judith M. (2006). "Extinction by hybridization and introgression in anatine ducks". Acta Zoologica Sinica. 52 (Supplement): 583–585. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-12-03.
- ↑ Rhymer, Judith M.; Simberloff, Daniel (1996). "Extinction by hybridization and introgression". Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 27: 83–109. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.27.1.83.
- ↑ Ashton, Mike (2014). Domestic Duck. United Kingdom: Crowood Press. p. 7. ISBN 9781847979704.
- ↑ Newton, Ian (2003). Speciation and Biogeography of Birds. United States: Academic Press. p. 417. ISBN 9780080924991.
- ↑ Wintersteen, Kyle (2013-03-01). "Black Ducks in Peril". American Hunter. Archived from the original on 2016-03-26. Retrieved 2013-03-02.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to American Black Duck. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Anas rubripes |
- American Black Duck Species Account – Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- "American Black Duck media". Internet Bird Collection.
- American Black Duck photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Interactive range map of Anas rubripes at IUCN Red List maps
