Altyn-Tagh
| Altyn-Tagh | |
|---|---|
| Altunshan, Astyn-Tagh, Altun Mountains, Pinyin: Altun Shan, A-erh-chin, Wade–Giles:A-erh-chin shan, Aerjin Shan, (Chinese: 阿尔金山) | |
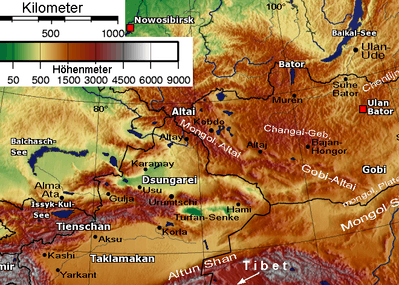 Eastern part of Altun Shan at bottom of elevation map | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Sulamutag Feng (Xinjiang) |
| Elevation | 6,245 m (20,489 ft) |
| Coordinates | 37°55′N 87°23′E / 37.917°N 87.383°E |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 805 km (500 mi) WSW-ENE[1] |
| Geography | |
| Country | China |
| Province | Xinjiang, Qinghai and Gansu |
| Range coordinates | 38°36′N 89°0′E / 38.600°N 89.000°ECoordinates: 38°36′N 89°0′E / 38.600°N 89.000°E [1] |
| Borders on | Kunlun Mountains and Qilian Mountains |
| Biome | Desert |
- For neighborhoods in Turkish cities, see Altındağ, İzmir and Altındağ, Ankara
Altyn-Tagh, (Astyn-Tagh, Altun Mountains, Pinyin: Altun Shan, A-erh-chin, Wade–Giles:A-erh-chin shan, Aerjin Shan, (Chinese: 阿尔金山))[2] is a part of the range south of Lop Nor), and is a mountain range in northwestern China that separates the eastern Tarim Basin from the Tibetan Plateau. The western third is in Xinjiang while the eastern part forms the border between Qinghai to the south and Xinjiang and Gansu to the north.
Altun Shan is also the name of a 5,830 metres (19,130 ft) mountain near the eastern end of the range, the highest point in Gansu.
Etymology
Altyn Tag means Gold Mountain in Turkic, and Shan is Chinese for mountain.
Geography
A series of mountain ranges run along the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. In the west are the Kunlun Mountains. About halfway across the south side of the Tarim Basin, the Altyn-Tagh Range diverges northeast while the Kunluns continue directly east, forming a relatively narrow "V".[nb 1] Inside the "V" are a number of endorheic basins. The eastern end of the Altyn-Shan is near the Dangjin Pass on the Dunhuang-Golmud road in far western Gansu. East of the Altyn-Tagh the border range rises to the Qilian Mountains. The range separates the Tarim Basin, to the north, and Lake Ayakkum, to the south. The range can be divided into three portions. The southwest portion borders the Kunlun Mountains, is very rugged, with peaks reaching more than 6,100 metres (20,000 ft) and many perennial snow fields. The central portion is lower in elevation, around 4,000 metres (13,000 ft). The eastern portion is higher in elevation, about 5,000 metres (16,000 ft) and consists of a group of smaller ranges oriented in a south-east to north-west trend.[2]
Along the northern side of the mountains ran the main Silk road trade route from China proper to the Tarim Basin and westward. The Altyn-Tagh and Qilians were sometimes called the Nan Shan ('south mountains') because they were south of the main route. Near the east end of the Altyn-Shan, the Gansu or Hexi Corridor ends and the Silk Road splits. One branch follows the Altyn-Tagh along the south side of the Tarim Basin while the other follows the north side.
The southwestern part of the Altyn-Tagh range reaches snowy peaks of up to 6,295 metres (20,653 ft), although it descends to an average of 4,000 metres (13,000 ft) in the narrow middle and eventually rises up to average 5,000 metres (16,000 ft) as it meets the Qilian Mountains.
There are a dearth of rivers and streams in these mountains, due to the aridity of the region. The western portion has some small streams that either head north into the desert or south into Lake Ayakkum. The remainder of the range is lacking in rivers.[2]
Intermontane endorheic basins
Inside the "V" shaped area between the Altyn-Tagh and the main Kunlun range (which in this area is called Arka-Tagh) a number of endorheic basins are located.
Within southeastern Xinjiang, the main of these basins is the Kumkol Basin (Chinese: 库木库里盆地; pinyin: Kùmùkùlǐ Péndì)[nb 2]
The two main lakes in this basin are the saline Lake Aqqikkol (also Ajig Kum Kul,[6] Achak-kum; Chinese: 阿其克库勒湖; pinyin: Āqíkèkùlè Hú; 37°05′N,88°25′E, 4,250 metres (13,940 ft) elevation)[7] and Lake Ayakum (Chinese: 阿牙克库木湖; pinyin: Āyákèkùmù hú; 37°30′N,89°30′E; elevation 3,876 metres (12,717 ft)).[8] These lakes are two of the few noticeable bodies of water in this extremely arid area; the area around them is officially protected as the Altun Shan Nature Reserve.[8]
Farther east, in northwestern Qinghai, the much larger Qaidam Basin starts between the Altyn-Tagh and the Kunlun and extends almost to the east side of the plateau; the Altyn-Tagh separates the west side of this basin from the Kumtagh Desert.
Major Peaks
The five highest peaks are Sulamutag Feng (6,245 metres (20,489 ft)), Yusupu Aleketag Shan (6,065 metres (19,898 ft)), Altun Shan (5,830 metres (19,130 ft)), Muzluktag (5,766 metres (18,917 ft)) and Kogantag (4,800 metres (15,700 ft)).[9][10]
Economic development
China National Highway 315 crosses the Altyn-Tagh on its way between Qinghai and Xinjiang.
As of the late 2013, preliminary planning is conducted for the Kurla-Golmud Railway, which, if constructed, will cross the Altyn-Tagh as well.
Notes
- ↑ See e.g. the map in Fig. 1 in Meng & Fang's Cenozoic tectonic development of the Qaidam Basin in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[3]
- ↑ The Chinese-based spelling (pinyin) for this place name, "Kumukuli Basin" is often used in English. When trying to produce a Turkic-like spelling for this name, authors occasionally transcribe it as "Kumukol Basin", as in the map in Fig. 2 in Meng & Fang's Cenozoic tectonic development of the Qaidam Basin in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau,[4] but more often as "Kumkol",[5] or "Kumkuli".
Footnotes
- 1 2 Cohen 1998, p. 86
- 1 2 3 Hoiberg 2010, p. 1
- ↑ Meng & Fang 2008, p. 2
- ↑ Meng & Fang 2008, p. 3
- ↑ Zheng 1997, p. 229
- ↑ Holdich 2006, p. 288
- ↑ Anon 2013
- 1 2 Li 2000, pp. 230–231
- ↑ Anon 2004
- ↑ de Ferranti, Jurgalski & Maizlish 2011
References
- Cohen, Saul B., ed. (1998) [1952]. "Altunshan". The Columbia Gazetteer of the World. New York, NY: Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-11040-5.
- de Ferranti, Jonathan; Jurgalski, Eberhard; Maizlish, Aaron (2011). "Sinkiang - Xinjiang". www.peaklist.com. Archived from the original on 23 August 2010. Retrieved 6 Feb 2014.
- Hoiberg, Dale H., ed. (2010). "A-erh-chin Mountains". Encyclopædia Britannica. I: A-Ak - Bayes (15th ed.). Chicago, Illinois: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. ISBN 978-1-59339-837-8.
- Holdich, Sir Thomas (2006) [1906]. Keltie, J. Scott, ed. Tibet, the Mysterious. Elibron Classic Series. Adamant Media Corporation. ISBN 1-4212-8483-9.
- Li, Bosheng (2000). "Nature Conservation". In Du Zheng, Qingsong Zhang; Wu, Shaohong. Mountain Geoecology and Sustainable Development of the Tibetan Plateau. GeoJournal library. 57. Springer Science + Business Media Dordrecht. ISBN 978-94-010-3800-3. doi:10.1007/978-94-010-0965-2.
- Meng, Qing-Ren; Fang, Xiang (2008). Burchfield, B. C.; Wang, Erchie, eds. "Cenozoic Tectonic Development of the Qaidam Basin in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau". Special Paper - Geological Society Of America. Geological Society of America. 444: 1–24. doi:10.1130/2008.2444(01).
- Anon (2013). "阿其克库勒湖(A lake whose Ke Kule)". Retrieved 6 Feb 2014.
- Anon (2004). "Altun Shan". Retrieved 6 Feb 2014.
- Zheng, Mianping (1997). An introduction to saline lakes on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Monographiae Biologicae. 76. Springer. ISBN 978-0792340980.
Further reading
- National Geographic Atlas of China. Washington, DC: National Geographic. 2009. ISBN 978-1426203275.
External links
- www.baike.com (2013). 阿牙克库木湖 "Ayakkum Lake" Check
|url=value (help). www.baike.com. - NASA photos of Ayakkum Lake and surrounding area
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Altyn-Tagh". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Altyn-Tagh". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.