Alkali metal nitrate

- Do not confuse with alkali metal nitrite or alkali metal nitride.
Alkali metal nitrates are chemical compounds consisting of an alkali metal (lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium and caesium) and the nitrate ion. Only two are of major commercial value, the sodium and potassium salts.[1][2] They are white, water-soluble salts with relatively similar melting points.[3]
| Compound | Chemical Formula | Molar Mass | Melting Point | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium nitrate | LiNO3 | 68.946 g/mol | 255 °C (491 °F; 528 K) | 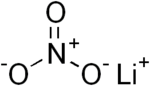 |
| Sodium nitrate | NaNO3 | 84.9947 g/mol | 308 °C (586 °F; 581° K ) |  |
| Potassium nitrate | KNO3 | 101.1032 g/mol | 334 °C (633 °F; 607 K) |  |
| Rubidium nitrate | RbNO3 | 147.473 g/mol | 310 °C (590 °F; 583 K) |  |
| Caesium nitrate | CsNO3 | 194.91 g/mol | 414 °C (777 °F; 687 K) | 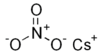 |
Applications
The main uses of alkali metal nitrates are in fertilizers in the case of the sodium and potassium derivatives. They are also commonly used in explosives and pyrotechnic compositions;[1] they are strong oxidizers. Other uses are for coloring in fireworks: caesium nitrate produces an indigo color, potassium nitrate and rubidium nitrate produce violet colors, lithium nitrate produces a red color, and sodium nitrate produces a yellow color.[4]
Sodium and potassium nitrate are also commonly used as fertilisers.
See also
References
- 1 2 Wolfgang Laue, Michael Thiemann, Erich Scheibler, Karl Wilhelm Wiegand "Nitrates and Nitrites" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_265
- ↑ webmaster@chemicalelements.com, Yinon Bentor -. "Chemical Elements.com - Alkali Metals". www.chemicalelements.com. Retrieved 2016-09-26.
- ↑ "THERMODYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF MOLTEN NITRATE SALTS" (PDF).
- ↑ "Phantom Fireworks : Fireworks University : Pyrotechnic Compounds". Phantom Fireworks. Retrieved 2016-10-16.