Lord Alfred Douglas
| Lord Alfred Douglas | |
|---|---|
.jpg) Alfred Douglas in 1903 (by George Charles Beresford) | |
| Born |
22 October 1870 Powick, Worcestershire, England |
| Died |
20 March 1945 (aged 74) Lancing, Sussex, England |
| Resting place | Friary Church of St Francis and St Anthony, Crawley |
| Occupation | Poet |
| Nationality | British |
| Education | Winchester College, Wixenford School |
| Alma mater | Magdalen College, Oxford |
| Spouse | Olive Custance (1902–1944) |
Lord Alfred Bruce Douglas (22 October 1870 – 20 March 1945), nicknamed Bosie, was a British author, poet, translator, and political commentator, better known as the friend and lover of Oscar Wilde. Much of his early poetry was Uranian in theme, though he tended, later in life, to distance himself from both Wilde's influence and his own role as a Uranian poet. Politically he would describe himself as "a strong Conservative of the 'Diehard' variety".[1]
Early life and background
Douglas was born at Ham Hill House in Powick, Worcestershire, the third son of John Douglas, 9th Marquess of Queensberry and his first wife Sibyl Montgomery. He was his mother's favourite child; she called him Bosie (a derivative of "boysie", as in boy), a nickname which stuck for the rest of his life.[2] His mother successfully sued for divorce in 1887 on the grounds of his father's adultery.[3] The Marquess married Ethel Weeden in 1893 but the marriage was annulled the following year.
Douglas was educated at Wixenford School,[4] Winchester College (1884–88) and Magdalen College, Oxford (1889–93), which he left without obtaining a degree. At Oxford, he edited an undergraduate journal, The Spirit Lamp (1892–3), an activity that intensified the constant conflict between him and his father. Their relationship had always been a strained one and during the Queensberry-Wilde feud, Douglas sided with Wilde, even encouraging Wilde to prosecute the Marquess for libel. In 1893, Douglas had a brief affair with George Ives.
In 1858, before Douglas's birth, his grandfather, the 8th Marquess of Queensberry, had died in what was reported as a shooting accident, but was widely believed to have been suicide.[5][6] In 1862, his widowed grandmother, Lady Queensberry, converted to Roman Catholicism and took her children to live in Paris.[7]
One of his uncles, Lord James Douglas, was deeply attached to his twin sister "Florrie" (Lady Florence Douglas) and was heartbroken when she married. In 1885, he tried to abduct a young girl, and after that became ever more manic. In 1888, Lord James married, but this proved disastrous.[8] Separated from Florrie, James drank himself into a deep depression,[8] and in 1891 committed suicide by cutting his throat.[7] Another of his uncles, Lord Francis Douglas (1847–1865) had died in a climbing accident on the Matterhorn. His uncle Lord Archibald Edward Douglas (1850–1938), on the other hand, became a clergyman.[7][9] Alfred Douglas's aunt, Lord James's twin Lady Florence Douglas (1855–1905), was an author, war correspondent for the Morning Post during the First Boer War, and a feminist.[10] In 1890, she published a novel, Gloriana, or the Revolution of 1900, in which women's suffrage is achieved after a woman posing as a man named Hector D'Estrange is elected to the House of Commons. The character D'Estrange is clearly based on Oscar Wilde.[11]
Relationship with Wilde

In 1891, Douglas met Oscar Wilde; although the playwright was married with two sons, they soon began an affair.[12][13] In 1894, the Robert Hichens novel The Green Carnation was published. Said to be a roman à clef based on the relationship of Wilde and Douglas, it would be one of the texts used against Wilde during his trials in 1895.
Douglas has been described as spoiled, reckless, insolent and extravagant. He would spend money on men and gambling and expected Wilde to contribute to his tastes. They often argued and broke up, but would also always reconcile.
Douglas had praised Wilde's play Salome in the Oxford magazine, The Spirit Lamp, of which he was editor (and used as a covert means of gaining acceptance for homosexuality). Wilde had originally written Salomé in French, and in 1893 he commissioned Douglas to translate it into English. Douglas's French was very poor and his translation was highly criticised; for example, a passage that runs "On ne doit regarder que dans les miroirs" ("One should only look in mirrors") he rendered "One must not look at mirrors". Douglas was angered at Wilde's criticism, and claimed that the errors were in fact in Wilde's original play. This led to a hiatus in the relationship and a row between the two men, with angry messages being exchanged and even the involvement of the publisher John Lane and the illustrator Aubrey Beardsley when they themselves objected to Douglas's work. Beardsley complained to Robbie Ross: "For one week the numbers of telegraph and messenger boys who came to the door was simply scandalous". Wilde redid much of the translation himself, but, in a gesture of reconciliation, suggested that Douglas be dedicated as the translator rather than credited, along with him, on the title-page. Accepting this, Douglas, somewhat vainly, likened a dedication to sharing the title-page as "the difference between a tribute of admiration from an artist and a receipt from a tradesman."[14]
On another occasion, while staying together in Brighton, Douglas fell ill with influenza and was nursed by Wilde, but failed to return the favour when Wilde himself fell ill in consequence. Instead Douglas moved to the Grand Hotel and, on Wilde's 40th birthday, sent him a letter saying that he had charged him the bill. Douglas also gave his old clothes to male prostitutes, but failed to remove from the pockets incriminating letters exchanged between him and Wilde, which were then used for blackmail.[14]
Alfred's father, the Marquess of Queensberry, suspected the liaison to be more than a friendship. He sent his son a letter, attacking him for leaving Oxford without a degree and failing to take up a proper career. He threatened to "disown [Alfred] and stop all money supplies". Alfred responded with a telegram stating: "What a funny little man you are".
Queensberry's next letter threatened his son with a "thrashing" and accused him of being "crazy". He also threatened to "make a public scandal in a way you little dream of" if he continued his relationship with Wilde.
Queensberry was well known for his temper and threatening to beat people with a horsewhip. Alfred sent his father a postcard stating "I detest you" and making it clear that he would take Wilde's side in a fight between him and the Marquess, "with a loaded revolver".
In answer Queensberry wrote to Alfred (whom he addressed as "You miserable creature") that he had divorced Alfred's mother in order not to "run the risk of bringing more creatures into the world like yourself" and that, when Alfred was a baby, "I cried over you the bitterest tears a man ever shed, that I had brought such a creature into the world, and unwittingly committed such a crime... You must be demented".
When Douglas's eldest brother Francis Viscount Drumlanrig died in a suspicious hunting accident in October 1894, rumours circulated that he had been having a homosexual relationship with the Prime Minister, Lord Rosebery, and that the cause of death was suicide. The Marquess of Queensberry thus embarked on a campaign to save his other son, and began a public persecution of Wilde. Wilde had been openly flamboyant, and his actions made the public suspicious even before the trial.[15] He and a minder confronted the playwright in his own home; later, Queensberry planned to throw rotten vegetables at Wilde during the premiere of The Importance of Being Earnest, but, forewarned of this, the playwright was able to deny him access to the theatre.
Queensberry then publicly insulted Wilde by leaving, at the latter's club, a visiting card on which he had written: "For Oscar Wilde posing as a somdomite (sic)". The wording is in dispute – the handwriting is unclear – although Hyde reports it as this. According to Merlin Holland, Wilde's grandson, it is more likely "Posing somdomite," while Queensberry himself claimed it to be "Posing as somdomite". Holland suggests that this wording ("posing [as] ...") would have been easier to defend in court.
The 1895 trials
In response to this card, and with Douglas's avid support, but against the advice of friends such as Robbie Ross, Frank Harris, and George Bernard Shaw, Wilde had Queensberry arrested and charged with criminal libel in a private prosecution; as sodomy was then a criminal offence. According to libel laws of the time, since his authorship of the charge of sodomy was not in question, Queensberry could avoid conviction only by demonstrating in court that the charge he had made was not only factually true, but that there was also some public interest in having made the charge publicly. Edward Carson, Queensberry's lawyer, therefore portrayed Wilde as a vicious older man who habitually preyed upon naive young boys and seduced them into a life of homosexuality with extravagant gifts and promises of a glamorous lifestyle. Several highly suggestive erotic letters that Wilde had written to Douglas were introduced into evidence; he claimed that they were works of art. Wilde was closely questioned about the homoerotic themes in The Picture of Dorian Gray and in The Chameleon, a single-issue magazine published by Douglas to which he had contributed a short article.
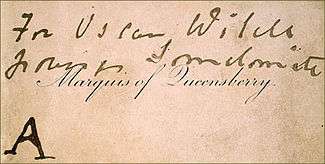
Queensberry's attorney announced in court that he had located several male prostitutes who were to testify that they had had sex with Wilde. Wilde's lawyers advised him that this would make a conviction on the libel charge very unlikely; he then dropped the libel charge, on his lawyers' advice, to avoid further pointless scandal. Without a conviction, the libel law of the time left Wilde liable to pay Queensberry's considerable legal costs, which left him bankrupt.
Based on the evidence raised during the case, Wilde was arrested the next day and charged with committing criminal sodomy and "gross indecency", a charge only capable of being committed by two men and which covered sexual acts other than sodomy.
Douglas's 1892 poem Two Loves, which was used against Wilde at the latter's trial, ends with the famous line that refers to homosexuality as the love that dare not speak its name, a quote often falsely attributed to Wilde. Wilde gave an eloquent but counterproductive explanation of the nature of this love on the witness stand. The trial resulted in a hung jury.
In 1895, when during his trials Wilde was released on bail, Douglas's cousin Sholto Johnstone Douglas stood surety for £500 of the bail money.[16] The prosecutor opted to retry the case. Wilde was convicted on 25 May 1895 and sentenced to two years' hard labour, first at Pentonville, then Wandsworth, then famously in Reading Gaol. Douglas was forced into exile in Europe.
While in prison, Wilde wrote Douglas a long and critical letter titled De Profundis, describing exactly what he felt about him, which Wilde was not permitted to send, but which may or may not have been sent to Douglas after Wilde's release: it was given to Robbie Ross, with the instructions to make a copy and send the original to Lord Alfred Douglas. Lord Alfred Douglas later said that he received only a letter from Ross with a few choice quotes, and didn't know there was a letter until it was referenced in a biography of Wilde's that Ross consulted on. Following Wilde's release (on 19 May 1897), the two reunited in August at Rouen, but stayed together only a few months owing to personal differences and the various pressures on them.
Naples and Paris
The meeting in Rouen was disapproved of by the friends and families of both men. During the later part of 1897, Wilde and Douglas lived together in Naples, but because of financial pressures and for other personal reasons, they separated. Wilde lived the remainder of his life primarily in Paris, and Douglas returned to England in late 1898.
The period when the two men lived in Naples would later become controversial. Wilde claimed that Douglas had offered a home, but had no funds or ideas. When Douglas eventually did gain funds from his late father's estate, he refused to grant Wilde a permanent allowance, although he did give him occasional handouts. When Wilde died in 1900, he was still bankrupt. Douglas served as chief mourner, although there reportedly was an altercation at the grave between him and Robbie Ross. This struggle would preview the later litigations between the two former lovers of Wilde.
Marriage

After Wilde's death, Douglas established a close friendship with Olive Eleanor Custance, an heiress, poet and bisexual. She briefly lived in Paris and sent him letters asking if he wanted to engage in threesomes with her girlfriend at the time. They married on 4 March 1902 and had one son, Raymond Wilfred Sholto Douglas, born on 17 November 1902.
The marriage was stormy after Douglas became a Roman Catholic in 1911. They separated in 1913, lived together for a time in the 1920s after Olive also converted, and then lived apart after she gave up Catholicism. The health of their only child further strained the marriage, which by the end of the 1920s was all but over, although they never divorced.
Repudiation of Wilde
In 1911, Douglas embraced Roman Catholicism, as Wilde had done earlier. More than a decade after Wilde's death, with the release of suppressed portions of Wilde's De Profundis letter in 1912, Douglas turned against his former friend, whose homosexuality he grew to condemn. He was a defence witness in the libel case brought by Maud Allan against Noel Pemberton Billing in 1918. Billing had accused Allan, who was performing Wilde's play Salome, of being part of a homosexual conspiracy to undermine the war effort.
Douglas also contributed to Billing's journal Vigilante as part of his campaign against Robbie Ross. He had written a poem referring to Margot Asquith "bound with Lesbian fillets" while her husband Herbert, the Prime Minister, gave money to Ross.[17] During the trial he described Wilde as "the greatest force for evil that has appeared in Europe during the last three hundred and fifty years."
Douglas added that he intensely regretted having met Wilde, and having helped him with the translation of Salome, which he described as "a most pernicious and abominable piece of work".
Plain English
In 1920 Douglas founded a right-wing, Catholic, and "deeply anti-Jewish"[18] weekly magazine called Plain English, on which he collaborated with Harold Sherwood Spencer, and to begin with Thomas William Hodgson Crosland. It regarded itself as the successor to The Academy, to which Douglas had been a contributing editor. Plain English ran until the end of 1922. Douglas would later admit that its policy was "strongly anti-Semitic".[19]
From August 1920 (issue No 8) Plain English began publishing a long running series of articles called "The Jewish Peril" by Major-General Count Cherep-Spiridovitch the title of which was taken from the fore-title of George Shanks's version of The Protocols of the Elders of Zion. Plain English advertised (from issue 20) The Britons' second edition of Shank's version the Protocols. Douglas challenged the Jewish Guardian, published by the League of British Jews, to take him to court suggesting they would not as they were "well aware of the absolute truth of the allegations which we have made."[20] The magazine would suggest in 1921 that "we need a Klu Klux Klan in this country",[21] but a promotion for Ostara magazine was generally not well received by readers.
Other regular targets of the magazine included David Lloyd George, Alfred Viscount Northcliffe, H.G. Wells, Frank Harris, and Sinn Féin. In December 1920 the magazine would be the first to publish the secret constitution of the Irish Republican Brotherhood.
From 25 December 1920 onwards it would begin publishing regularly its most notorious series of articles alleging that a "powerful individual in the Admiralty" had alerted the Germans at the Battle of Jutland that the British had broken their code, and that Winston Churchill had falsified a report in return for a large sum of money from Ernest Cassel who thereby profited; in May 1921 Douglas would also insinuate that Herbert Earl Kitchener had been murdered by the Jews.[22]
Douglas would cease to be editor after issue 67 in 1921 after a row with Spencer.[23] He then produced a short lived, almost identical, rival magazine called Plain Speech in 1921 with Herbert Moore Pim. Its first issue would contain a letter from a correspondent in Germany telling the British about a "Herr Hittler" (as spelt in original) and "The German White Labour Party".
Douglas's view of a Jewish plot was nuanced. In 1920 he would, whilst recognizing "the Jewish Peril", noted that "Christian Charity forbids us to join in wholesale and indiscriminate abuse and vilification of an entire race".[24] In 1921 he would state it was not acceptable to "shift responsibility" on to the Jews.[25] In his Autobiography in 1929 he would write "I feel now that it is ridiculous to make accusations against the Jews, attributing them qualities and methods which are really much more typically English than Jewish" , and then indicate the country only had itself to blame if the Jews came in and trampled on it.[26]
The historian Colin Holmes indicated that while "Douglas had been to the forefront of anti-semitism in the early 1920s, he was quite unable to come to terms with the vicious racist anti-semitism in Germany" under the Nazis.[27]
Libel actions
Douglas started his "litigious and libellous career"[28] by obtaining an apology and fifty guineas each from the Oxford and Cambridge university magazines Isis and Cambridge for defamatory references to him in an article on Wilde.
He was a plaintiff and defendant in several trials for civil or criminal libel. In 1913 he was charged with libelling his father-in-law. Also in 1913 he accused Arthur Ransome of libelling him in his book Oscar Wilde: A Critical Study. He saw this trial as a weapon against his enemy Ross, not understanding that Ross would not be called to give evidence. The court found in Ransome's favour. Douglas was bankrupted by the failed libel suit.[29] Ransome did, however, remove the offending passages from the 2nd edition of his book.[30]
In the most noted case, brought by the Crown on Winston Churchill's behalf in 1923, Douglas was found guilty of libelling Churchill and was sentenced to six months in prison. Churchill had been accused as cabinet minister, of falsifying an official report on the Battle of Jutland in 1916 when, although suffering losses, the Royal Navy drove the German battle fleet off the high seas. Churchill was said to have reported that the British navy had in fact, been defeated; the motive was supposed to be that when this news was flashed, the prices of British securities would tumble on the world's stock exchanges, allowing a group of named Jewish financiers to snap them up cheaply. Churchill's reward was a houseful of furniture, valued at £40,000.
The allegations were made by Douglas in his journal Plain English and later at a public meeting in London. A false report of a crushing British naval defeat had indeed been planted in the New York press by German interests but, by this time (following the failure of his Dardanelles Campaign), Churchill was not connected with the Admiralty. As the attorney-general claimed in court, on Churchill's behalf, there was "no plot, no phoney communiqué, no stock market raid and no present of fine furniture."[31][32]
In 1924, while in prison, Douglas, in an echo of Wilde's composition of De Profundis (Latin for "From the Depths") during his incarceration, wrote his last major poetic work, In Excelsis (literally, "In the Highest"), which contains 17 cantos. Since the prison authorities would not allow Douglas to take the manuscript with him when he was released, he had to rewrite the work from memory. Douglas maintained that his health never recovered from his harsh prison ordeal, which included sleeping on a plank bed without a mattress.
Later life
Following his own incarceration in 1924, Douglas's feelings toward Wilde began to soften considerably. He said in Oscar Wilde: A Summing Up that "Sometimes a sin is also a crime (for example, a murder or theft) but this is not the case with homosexuality, any more than with adultery."[33]
Throughout the 1930s and until his death, Douglas maintained correspondences with many people, including Marie Stopes and George Bernard Shaw. Anthony Wynn wrote the play Bernard and Bosie: A Most Unlikely Friendship based on the letters between Shaw and Douglas. One of Douglas's final public appearances was his well-received lecture to the Royal Society of Literature on 2 September 1943, entitled The Principles of Poetry, which was published in an edition of 1,000 copies. He attacked the poetry of T. S. Eliot, and the talk was praised by Arthur Quiller-Couch and Augustus John.[34]
Douglas's only child, Raymond, was diagnosed with schizoaffective disorder in 1927, at the age of 24, and entered St Andrew's Hospital, a mental institution. He was decertified and discharged after five years, but suffered a subsequent breakdown and returned to the hospital. In February 1944, when his mother died of a cerebral haemorrhage at the age of 70, Raymond was able to attend her funeral and in June he was again decertified. However, his conduct rapidly deteriorated and he returned to St Andrew's in November where he stayed until his death on 10 October 1964. He had never married.[35]
Death

Douglas died of congestive heart failure in Lancing, Sussex, on 20 March 1945 at the age of 74. He was buried on 23 March at the Franciscan Friary, Crawley,[36] where he is interred alongside his mother, who had died on 31 October 1935 at the age of 91. A single gravestone covers them both.
The elderly Douglas, living in reduced circumstances in Hove in the 1940s, is mentioned in the diaries of Henry Channon and in the first autobiography of Donald Sinden, who, according to his son Marc, was one of only two people to attend his funeral.[37][38]
He died at the home of Edward and Sheila Colman. The couple were the main beneficiaries in his will, inheriting the copyright to Douglas's work. She endowed a memorial prize at Oxford in Douglas's name for the best Petrarchan sonnet.[39]
Writings
Douglas published several volumes of poetry; two books about his relationship with Wilde, Oscar Wilde and Myself (1914; largely ghostwritten by T. W. H. Crosland, the assistant editor of The Academy and later repudiated by Douglas), Oscar Wilde: A Summing Up (1940); and two memoirs, The Autobiography of Lord Alfred Douglas (1929) and Without Apology (1938).
Douglas also was the editor of a literary journal, The Academy, from 1907 to 1910, and during this time he had an affair with artist Romaine Brooks, who was also bisexual (the main love of her life, Natalie Clifford Barney, also had an affair with Wilde's niece Dorothy and even, in 1901, with Douglas's future wife Olive Custance, the year before the couple married). In 1920 he would edit, and write many articles for, the political paper Plain English, a journal which he regarded as the 'apple of his eye'.[40]
There are six biographies of Douglas. The earlier ones by Braybrooke and Freeman were not allowed to quote from Douglas's copyright work, and De Profundis was unpublished. Later biographies were by Rupert Croft-Cooke, H. Montgomery Hyde (who also wrote about Wilde), Douglas Murray (who describes Braybrooke's biography as "a rehash and exaggeration of Douglas's book", i.e. his autobiography). The most recent is Alfred Douglas: A Poet's Life and His Finest Work by Caspar Wintermans, from Peter Owen Publishers in 2007.
Poetry
- Poems (1896)
- Tails with a Twist 'by a Belgian Hare' (1898)
- The City of the Soul (1899)
- The Duke of Berwick (1899)
- The Placid Pug (1906)
- The Pongo Papers and the Duke of Berwick (1907)
- Sonnets (1909)
- The Collected Poems of Lord Alfred Douglas (1919)
- In Excelsis (1924)
- The Complete Poems of Lord Alfred Douglas (1928)
- Sonnets (1935)
- Lyrics (1935)
- The Sonnets of Lord Alfred Douglas (1943)
Non-fiction
- Oscar Wilde and Myself (1914) (ghost-written by T. W. H. Crosland[41])
- Foreword to New Preface to the 'Life and Confessions of Oscar Wilde' by Frank Harris (1925)
- Introduction to Songs of Cell by Horatio Bottomley (1928)
- The Autobiography of Lord Alfred Douglas (1929; 2nd ed. 1931)
- My Friendship with Oscar Wilde (1932; retitled American version of his memoir)
- The True History of Shakespeare's Sonnets (1933)
- Introduction to The Pantomime Man by Richard Middleton (1933)
- Preface to Bernard Shaw, Frank Harris, and Oscar Wilde by Robert Harborough Sherard (1937)
- Without Apology (1938)
- Preface to Oscar Wilde: A Play by Leslie Stokes and Sewell Stokes (1938)
- Introduction to Brighton Aquatints by John Piper (1939)
- Ireland and the War Against Hitler (1940)
- Oscar Wilde: A Summing Up (1940)
- Introduction to Oscar Wilde and the Yellow Nineties by Frances Winwar (1941)
- The Principles of Poetry (1943)
- Preface to Wartime Harvest by Marie Carmichael Stopes (1944)
On film
In the films Oscar Wilde and The Trials of Oscar Wilde, both released in 1960, Douglas was portrayed by John Neville and John Fraser respectively. In the 1997 British film Wilde, Douglas was portrayed by Jude Law. In the upcoming 2017 film The Happy Prince, he will be portrayed by Colin Morgan.
Notes
- ↑ The Autobiography of Lord Alfred Douglas (1929) p220
- ↑ "Douglas, Lord Alfred Bruce (1870–1945)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/32869. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ↑ "The Queensberry Divorce Case", The Times, 24 January 1887, p. 4
- ↑ Rupert Croft-Cooke, Bosie: The Story of Lord Alfred Douglas, His Friends and Enemies (1963), p. 33
- ↑ Linda Stratmann, The Marquess of Queensberry: Wilde's Nemesis, Yale University Press 2013 p.25
- ↑ Neil McKenna, The Secret Life Of Oscar Wilde, Random House 2011 p.427
- 1 2 3 Lady Florence Dixie Archived 20 March 2008 at the Wayback Machine. at spartacus.schoolnet.co.uk (accessed 8 March 2008)
- 1 2 Douglas, Murray, Bosie: A Biography of Lord Alfred Douglas, Chapter One online at nytimes.com (accessed 8 March 2008)
- ↑ G.E. Cokayne et al., eds., The Complete Peerage of England, Scotland, Ireland, Great Britain and the United Kingdom, Extant, Extinct or Dormant, new edition, 13 volumes in 14 (1910–1959; new edition, 2000), volume X, page 694
- ↑ Dixie, Lady Florence, poet, novelist, writer; explorer and a keen champion of Woman's Rights in Who Was Who online at 7345683 at xreferplus.com (subscription required), accessed 11 March 2008
- ↑ Heilmann, Ann, Wilde's New Women: the New Woman on Wilde in Uwe Böker, Richard Corballis, Julie A. Hibbard, The Importance of Reinventing Oscar: Versions of Wilde During the Last 100 Years (Rodopi, 2002) pp. 135–147, in particular p. 139
- ↑ H. Montgomery Hyde, The Love That Dared not Speak its Name; p.144
- ↑ Ellmann (1988:98)
- 1 2 Oscar Wilde by Richard Ellman, published in 1987
- ↑ Ellmann (1988:101)
- ↑ Borland, Maureen, Wilde's Devoted Friend: A Life of Robert Ross, 1869–1918 (Lennard Publishing, 1990) p. 206 at books.google.com, accessed 22 January 2009
- ↑ Philip Hoare. (1999). Oscar Wilde’s Last Stand: Decadence, Conspiracy, and the Most Outrageous Trial of the Century. Arcade Publishing, p. 110.
- ↑ Toczek, Nick Haters, Baiters and Would-Be Dictators: Anti-Semitism and the UK Far Right Routledge (2016) p239
- ↑ The Autobiography of Lord Alfred Douglas (1929) p302
- ↑ The "Jewish Guardian" Again, Plain English No 21, 27 November 1920
- ↑ Lies, Plain English No 66, 8 October 1921
- ↑ Heathorn, Stephen Haig and Kitchener in Twentieth-Century Britain: Remembrance, Representation and Appropriation Routledge (2016) pp. 68-72.
- ↑ Toczek, Nick Haters, Baiters and Would-Be Dictators: Anti-Semitism and the UK Far Right Routledge (2016) p34
- ↑ Christian Charity and the Jews, Plain English No 4, 31 July 1920, p78
- ↑ The Jews, "The Britons" and the "Morning Post", Plain Speech No 10, 24 December 1921, p149
- ↑ The Autobiography of Lord Alfred Douglas (1929) pp303-304
- ↑ Holmes, Colin Anti-Semitism in British Society, 1876-1939 Routledge (1979)p218
- ↑ (Murray p152)
- ↑ The Edinburgh Gazette Publication date:17 January 1913 Issue: 12530, Page 77
- ↑ Ransome, Arthur, Oscar Wilde – A Critical Study, 2nd edition, Methuen, 1913
- ↑ http://content.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,727630,00.html accessed 10/2/2017
- ↑ http://www.jta.org/1923/12/13/archive/churchill-wins-libel-suit-against-douglas accessed 10/2/2017
- ↑ (Murray p309-310)
- ↑ (Murray pages 318–319)
- ↑ "Timeline to the Life of Lord Alfred 'Bosie' Douglas" anthonywynn.com Retrieved 24 August 2011
- ↑ Bastable, Roger (1983). Crawley: A Pictorial History. Chichester: Phillimore & Co. §147. ISBN 0-85033-503-5.
- ↑ Libby Purvis interviews Freddie Fox. The Times Page 8. 17 January 2013
- ↑ "Sir Donald Sinden: Legendary actor dies aged 90". BBC News. 12 Sep 2014. Retrieved 12 Sep 2014.
- ↑ A. N. Wilson in The Telegraph 26 November 2001
- ↑ Brown, William Sorley The Life and Genius of T.W.H. Crosland (1928) p394
- ↑ Jonathan Fryer (2000). Robbie Ross: Oscar Wilde's Devoted Friend. Carrol & Graf, New York and Constable & Robinson, London. p. 224. ISBN 0-7867-0781-X.
References
- Braybrooke, Patrick. Lord Alfred Douglas: His Life and Work (1931)
- Ellmann, Richard (1988). Oscar Wilde. New York: Vintage Books. ISBN 978-0-394-75984-5.
- Freeman, William. Lord Alfred Douglas: Spoilt Child of Genius (1948)
- Queensberry, Marquess of [Francis Douglas] and Percy Colson. Oscar Wilde and the Black Douglas (1949)
- Croft-Cooke, Rupert. Bosie: Lord Alfred Douglas, His Friends and Enemies (1963)
- Roberts, Brian. The Mad Bad Line: The Family of Lord Alfred Douglas (1981)
- Hyde, Mary, ed. Bernard Shaw and Alfred Douglas: A Correspondence (1982)
- Hyde, H. Montgomery. Lord Alfred Douglas: A Biography (1985) ISBN 0-413-50790-4
- Murray, Douglas. Bosie: A Biography of Lord Alfred Douglas (2000) ISBN 0-340-76771-5
- Fisher, Trevor. Oscar and Bosie: A Fatal Passion (2002) ISBN 0-7509-2459-4
- Fleming, Justin. The Cobra, a play, published by Xlibris in Coup d'État & Other Plays (2004) by Justin Fleming
- Michael Matthew Kaylor, Secreted Desires: The Major Uranians: Hopkins, Pater and Wilde (2006), a 500-page scholarly volume that considers the Victorian writers of Uranian poetry and prose, such as Douglas
- Smith, Timothy d'Arch. Love in Earnest. Some Notes on the Lives and Writings of English 'Uranian' Poets from 1889 to 1930. (1970) ISBN 0-7100-6730-5
- Wintermans, Caspar. Alfred Douglas: A Poet's Life and His Finest Work (2007) ISBN 978-0-7206-1270-7
- Whittington-Egan, Molly. "Such White Lilies: Frank Miles & Oscar Wilde" Rivendale Press Jan. 2008
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Alfred Douglas. |
- Unofficial website of Lord Alfred 'Bosie' Douglas
- Works by Lord Alfred Douglas at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about Lord Alfred Douglas at Internet Archive
- Works by Lord Alfred Douglas at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)

- Lord Alfred Douglas at Find a Grave
- "Archival material relating to Lord Alfred Douglas". UK National Archives.
- Numerous archival resources relating to Lord Alfred Douglas are listed in ArchiveGrid