Oromo language
| Oromo | |
|---|---|
| Afaan Oromoo | |
| Native to | Ethiopia, Kenya |
| Region | Oromia |
| Ethnicity | Oromo |
Native speakers |
25 million people in Ethiopia (2015 census)[1] 500,000 in Kenya (2015 census), 42,000 in Somalia (2015 census)[1] |
| Latin (Qubee), formerly also Ge'ez script | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 |
om |
| ISO 639-2 |
orm |
| ISO 639-3 |
orm – inclusive codeIndividual codes: gax – Borana–Arsi–Guji–Walagaa Oromohae – Eastern Oromoorc – Ormagaz – West Central Oromossn – Waata |
| Glottolog |
nucl1736[2] |
|
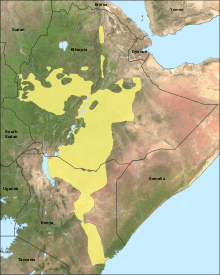
Areas in East Africa where Oromo is spoken | |
Oromo (pron. /ˈɒrəmoʊ/[3] or /ɔːˈroʊmoʊ/[4][5]) is an Afroasiatic language. It is the most widely spoken tongue in the family's Cushitic branch. Forms of Oromo are spoken as a first language by more than 24.6 million Oromo people and neighbouring peoples in Ethiopia and by an additional half million in parts of northern and eastern Kenya.[6] It is also spoken by smaller numbers of emigrants in other African countries such as South Africa, Libya, Egypt and Sudan. Oromo is a dialect continuum; not all varieties are mutually intelligible.
The native name for the Oromo language is Afaan Oromo, which translates to "mouth (language) of Oromo". It was formerly known as "Galla", a term now considered pejorative but still found in older literature.
Varieties

Ethnologue (2015) divides the Oromo macrolanguage into four languages
- Boranaa–Arsii–Gujii Oromo (Southern Oromo, incl. Gabra and Sakuye dialects), ISO code [gax]
- Eastern Oromo (Harar), ISO code [hae]
- Orma (Munyo, Orma, Waata/Sanye), ISO code [orc]
- West–Central Oromo (Western Oromo and Central Oromo, incl. Mecha/Wollega, Raya, Wello(Kemise), Tulema/Shewa) ISO code [gaz]
It is divided into five languages in the ISO 639-3 listing:
- [gax] – Borana–Arsi–Guji–Walagaa Oromo
- [hae] – Eastern Oromo
- [orc] – Orma
- [gaz] – West Central Oromo
- [ssn] – Waata
Blench (2006) concurs, dividing Oromo into four languages:
- Western Oromo (Maca)
- Shewa (Tuulama, Arsi)
- Eastern Oromo (Harar)
- Southern Oromo (Ajuran, Borana, Gabra, Garreh, Munyo, Orma, Sakuye, Waata)
Speakers
About 85 percent of Oromo speakers live in Ethiopia, mainly in Oromia Region. In addition, in Somalia there are also some speakers of the language.[7] In Kenya, the Ethnologue also lists 722,000 speakers of Borana and Orma, two languages closely related to Ethiopian Oromo.[8] Within Ethiopia, Oromo is the language with the largest number of native speakers.
Within Africa, Oromo is the language with the fourth most speakers, after Arabic (if one counts the mutually unintelligible spoken forms of Arabic as a single language and assumes the same for the varieties of Oromo), Swahili, and Hausa.
Besides first language speakers, a number of members of other ethnicities who are in contact with the Oromo speak it as a second language. See, for example, the Omotic-speaking Bambassi and the Nilo-Saharan-speaking Kwama in northwestern Oromiyaa.[9]
Language policy
Before the Ethiopian Revolution of 1974, publishing or broadcasting in Oromo was very limited. The few works that had been published, most notably Onesimos Nesib's and Aster Ganno's translation of the Bible from the late nineteenth century, were written in the Ge'ez alphabet, as was the 1875 New Testament produced by Krapf. Following the 1974 Revolution, the government undertook a literacy campaign in several languages, including Oromo, and publishing and radio broadcasts began in the language. All Oromo materials printed in Ethiopia at that time, such as the newspaper Bariisaa, Urjii and many others, were written in the traditional script.
Plans to introduce Oromo language instruction in the schools, however, were not realized until the government of Mengistu Haile Mariam was overthrown in 1991, except in regions controlled by the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF). With the creation of the regional state of Oromia under the new system of Ethnic federalism in Ethiopia, it has been possible to introduce Oromo as the medium of instruction in elementary schools throughout the region (including areas where other ethnic groups live speaking their languages) and as a language of administration within the region. Since the OLF left the transitional Ethiopian government in the early 1990s, the Oromo Peoples' Democratic Organization (OPDO) continued developing Oromo in Ethiopia.
Oromo is written with a Latin alphabet called Qubee which was formally adopted in 1991.[10] Various versions of the Latin-based orthography had been used previously, mostly by Oromos outside of Ethiopia and by the OLF by the late 1970s (Heine 1986).[11] With the adoption of Qubee, it is believed more texts were written in the Oromo language between 1991 and 1997 than in the previous 100 years. In Kenya, the Borana and Waata also use Roman letters but with different systems.
The Sapalo script was an indigenous Oromo script invented by Sheikh Bakri Sapalo (also known by his birth name, Abubaker Usman Odaa) in the years following Italian invasion of Ethiopia, and used underground afterwards.[12][13] The Arabic script has also been used intermittently in areas with Muslim populations.
Within Kenya there has been radio broadcasting in Oromo (in the Borana dialect) on the Voice of Kenya since at least the 1980s.[14] The Borana Bible in Kenya was printed in 1995 using the Latin alphabet, but not using the same spelling rules as in Ethiopian Qubee. The first comprehensive online Afaon Oromo dictionary was developed by the Jimma Times Oromiffa Group (JTOG) in cooperation with SelamSoft.[15] Voice of America also broadcasts in Oromo alongside its other horn of Africa programs. Oromo and Qubee are currently utilized by the Ethiopian government's state radios, TV stations and regional government newspaper.
Phonology and orthography
Consonant and vowel phonemes
Like most other Ethiopian languages, whether Semitic, Cushitic, or Omotic, Oromo has a set of ejective consonants, that is, voiceless stops or affricates that are accompanied by glottalization and an explosive burst of air. Oromo has another glottalized phone that is more unusual, an implosive retroflex stop, "dh" in Oromo orthography, a sound that is like an English "d" produced with the tongue curled back slightly and with the air drawn in so that a glottal stop is heard before the following vowel begins. It is retroflex in most dialects, though it is not strongly implosive and may reduce to a flap between vowels.[16] One source describes it as voiceless [ᶑ̥].[17]
Oromo has the typical Eastern Cushitic set of five short and five long vowels, indicated in the orthography by doubling the five vowel letters. The difference in length is contrastive, for example, hara 'lake', haaraa 'new'. Gemination is also significant in Oromo. That is, consonant length can distinguish words from one another, for example, badaa 'bad', baddaa 'highland'.
In the Qubee alphabet, letters include the digraphs ch, dh, ny, ph, sh. Gemination is not obligatorily marked for digraphs, though some writers indicate it by doubling the first element: qopphaa'uu 'be prepared'. In the charts below, the International Phonetic Alphabet symbol for a phoneme is shown in brackets where it differs from the Oromo letter. The phonemes /p v z/ appear in parentheses because they are only found in recently adopted words. Note that there have been minor changes in the orthography since it was first adopted: ⟨x⟩ ([tʼ]) was originally rendered ⟨th⟩, and there has been some confusion among authors in the use of ⟨c⟩ and ⟨ch⟩ in representing the phonemes /tʃʼ/ and /tʃ/, with some early works using ⟨c⟩ for /tʃ/ and ⟨ch⟩ for /tʃʼ/ and even ⟨c⟩ for different phonemes depending on where it appears in a word. This article uses ⟨c⟩ consistently for /tʃʼ/ and ⟨ch⟩ for /tʃ/.
| Bilabial/ Labiodental |
Alveolar/ Retroflex |
Palato-alveolar/ Palatal |
Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stops and affricates |
Voiceless | (p) | t | ch /tʃ/ | k | ' /ʔ/ |
| Voiced | b | d | j /dʒ/ | g /ɡ/ | ||
| Ejective | ph /pʼ/ | x /tʼ/ | c /tʃʼ/ | q /kʼ/ | ||
| Implosive | dh /ᶑ/ | |||||
| Fricatives | Voiceless | f | s | sh /ʃ/ | h | |
| Voiced | (v) | (z) | ||||
| Nasals | m | n | ny /ɲ/ | |||
| Approximants | w | l | y /j/ | |||
| Rhotic | r | |||||
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i /ɪ/, ii /iː/ | u /ʊ/, uu /uː/ | |
| Mid | e /ɛ/, ee /eː/ | o /ɔ/, oo /oː/ | |
| Open | a /ɐ/ | aa /ɑː/ |
Tone and stress
Only the penultimate or final syllable of a root can have a high tone, and if the penultimate is high, the final must also be high;[18] this implies that Oromo has a pitch-accent system (in which the tone need be specified only on one syllable, the others being predictable) rather than a tone system (in which each syllable must have its tone specified),[19] although the rules are complex (each morpheme can contribute its own tone pattern to the word), so that "one can call Oromo a pitch-accent system in terms of the basic lexical representation of pitch, and a tone system in terms of its surface realization."[20] The stressed syllable is perceived as the first syllable of a word with high pitch.[21]
Grammar
Nouns
Gender
Like most other Afroasiatic languages, Oromo has two grammatical genders, masculine and feminine, and all nouns belong to either one or the other. Grammatical gender in Oromo enters into the grammar in the following ways:
- Verbs (except for the copula be) agree with their subjects in gender when the subject is third person singular (he or she).
- Third person singular personal pronouns (he, she, it, etc., in English) have the gender of the noun they refer to.
- Adjectives agree with the nouns they modify in gender.
- Some possessive adjectives ("my", "your") agree with the nouns they modify in some dialects.
Except in some southern dialects, there is nothing in the form of most nouns that indicates their gender. A small number of nouns pairs for people, however, end in -eessa (m.) and -eettii (f.), as do adjectives when they are used as nouns: obboleessa 'brother', obboleettii 'sister', dureessa 'the rich one (m.)', hiyyeettii 'the poor one (f.)'. Grammatical gender normally agrees with natural gender for people and animals; thus nouns such as abbaa 'father', ilma 'son', and sangaa 'ox' are masculine, while nouns such as haadha 'mother' and intala 'girl, daughter' are feminine. However, most names for animals do not specify biological gender.
Names of astronomical bodies are feminine: aduu 'sun', urjii 'star'. The gender of other inanimate nouns varies somewhat among dialects.
Number
Oromo has singular and plural number, but nouns that refer to multiple entities are not obligatorily plural. That is, if the context is clear, a formally singular noun may refer to multiple entities: nama "man" or "people", nama shan "five men" or "five people". Another way of looking at this is to treat the "singular" form as unspecified for number.
When it is important to make the plurality of a referent clear, the plural form of a noun is used. Noun plurals are formed through the addition of suffixes. The most common plural suffix is -oota; a final vowel is dropped before the suffix, and in the western dialects, the suffix becomes -ota following a syllable with a long vowel: mana 'house', manoota 'houses', hiriyaa 'friend', hiriyoota 'friends', barsiisaa 'teacher', barsiiso(o)ta 'teachers'. Among the other common plural suffixes are -(w)wan, -een, and -(a)an; the latter two may cause a preceding consonant to be doubled: waggaa 'year', waggaawwan 'years', laga 'river', laggeen 'rivers', ilma 'son', ilmaan 'sons'.
Definiteness
Oromo has no indefinite articles (corresponding to English a, some), but (except in the southern dialects) it indicates definiteness (English the) with suffixes on the noun: -(t)icha for masculine nouns (the ch is geminated though this is not normally indicated in writing) and -(t)ittii for feminine nouns. Vowel endings of nouns are dropped before these suffixes: karaa 'road', karicha 'the road', nama 'man', namicha/namticha 'the man', haroo 'lake', harittii 'the lake'. Note that for animate nouns that can take either gender, the definite suffix may indicate the intended gender: qaalluu 'priest', qaallicha 'the priest (m.)', qallittii 'the priest (f.)'. The definite suffixes appear to be used less often than the in English, and they seem not to co-occur with the plural suffixes.
Case
Oromo noun has a citation form or base form that is used when the noun is the object of a verb, the object of a preposition or postposition, or a nominal predicative.
- mana 'house', mana binne 'we bought a house'
- hamma 'until', dhuma 'end', hamma dhuma 'until (the) end'
- mana keessa, 'inside (a/the) house'
- inni 'he', barsiisaa 'teacher'
- inni barsiisaa (dha) 'he is a teacher'
A noun may also appear in one of six other grammatical cases, each indicated by a suffix or the lengthening of the noun's final vowel. The case endings follow plural or definite suffixes if these appear. For some of the cases, there is a range of forms possible, some covering more than one case, and the differences in meaning among these alternatives may be quite subtle.
- Nominative
- The nominative is used for nouns that are the subjects of clauses.
- Ibsaa (a name), Ibsaan 'Ibsaa (nom.)', konkolaataa '(a) car', qaba 'he has':
- Ibsaan konkolaataa qaba 'Ibsaa has a car'.
- Most nouns ending in short vowels with a preceding single consonant drop the final vowel and add -ni to form the nominative. Following certain consonants, assimilation changes either the n or that consonant (the details depend on the dialect).
- nama 'man', namni 'man (nom.)'
- namoota 'men'; namootni, namoonni 'men (nom.)' (t + n may assimilate to nn)
- If a final short vowel is preceded by two consonants or a geminated consonant, -i is suffixed.
- ibsa 'statement', ibsi 'statement (nom.)'
- namicha 'the man', namichi 'the man (nom.)' (the ch in the definite suffix -icha is actually geminated, though not normally written as such)
- If the noun ends in a long vowel, -n is suffixed to this. This pattern applies to infinitives, which end in -uu.
- maqaa 'name', maqaan 'name (nom.)'
- nyachuu 'to eat, eating', nyachuun 'to eat, eating (nom.)'
- If the noun ends in n, the nominative is identical to the base form.
- afaan 'mouth, language (base form or nom.)'
- Some feminine nouns ending in a short vowel add -ti. Again assimilation occurs in some cases.
- haadha 'mother', haati (dh + t assimilates to t)
- lafa 'earth', lafti
- Genitive
- The genitive is used for possession or "belonging"; it corresponds roughly to English of or -'s. The genitive is usually formed by lengthening a final short vowel, by adding -ii to a final consonant, and by leaving a final long vowel unchanged. The possessor noun follows the possessed noun in a genitive phrase. Many such phrases with specific technical meanings have been added to the Oromo lexicon in recent years.
- obboleetti 'sister', namicha 'the man', obboleetti namichaa 'the man's sister'
- hojii 'job', Caaltuu, woman's name, hojii Caaltuu, 'Caaltuu's job'
- barumsa 'field of study', afaan 'mouth, language', barumsa afaanii 'linguistics'
- In place of the genitive it is also possible to use the relative marker kan (m.) / tan (f.) preceding the possessor.
- obboleetti kan namicha 'the man's sister'
- Dative
- The dative is used for nouns that represent the recipient (to) or the benefactor (for) of an event. The dative form of a verb infinitive (which acts like a noun in Oromo) indicates purpose. The dative takes one of the following forms:
- Lengthening of a final short vowel (ambiguously also signifying the genitive)
- namicha 'the man', namichaa 'to the man, of the man'
- -f following a long vowel or a lengthened short vowel; -iif following a consonant
- intala 'girl, daughter', intalaaf 'to a girl, daughter'
- saree 'dog', sareef 'to a dog'
- baruu 'to learn', baruuf 'in order to learn'
- bishaan 'water', bishaaniif 'for water'
- -dhaa or -dhaaf following a long vowel
- saree 'dog'; sareedhaa, sareedhaaf 'to a dog'
- -tti (with no change to a preceding vowel), especially with verbs of speaking
- Caaltuu woman's name, himi 'tell, say (imperative)', Caaltuutti himi 'tell Caaltuu'
- Instrumental
- The instrumental is used for nouns that represent the instrument ("with"), the means ("by"), the agent ("by"), the reason, or the time of an event. The formation of the instrumental parallels that of the dative to some extent:
- -n following a long vowel or a lengthened short vowel; -iin following a consonant
- harka 'hand', harkaan 'by hand, with a hand'
- halkan 'night', halkaniin 'at night'
- -tiin following a long vowel or a lengthened short vowel
- Afaan Oromo 'Oromo (language)', Afaan Oromotiin 'in Oromo'
- -dhaan following a long vowel
- yeroo 'time', yeroodhaan 'on time'
- bawuu 'to come out, coming out', bawuudhaan 'by coming out'
- Locative
- The locative is used for nouns that represent general locations of events or states, roughly at. For more specific locations, Oromo uses prepositions or postpositions. Postpositions may also take the locative suffix. The locative also seems to overlap somewhat with the instrumental, sometimes having a temporal function. The locative is formed with the suffix -tti.
- Arsiitti 'in Arsii'
- harka 'hand', harkatti 'in hand'
- guyyaa 'day', guyyaatti 'per day'
- jala, jalatti 'under'
- Ablative
- The ablative is used to represent the source of an event; it corresponds closely to English from. The ablative, applied to postpositions and locative adverbs as well as nouns proper, is formed in the following ways:
- When the word ends in a short vowel, this vowel is lengthened (as for the genitive).
- biyya 'country', biyyaa 'from country'
- keessa 'inside, in', keessaa 'from inside'
- When the word ends in a long vowel, -dhaa is added (as for one alternative for the dative).
- Finfinneedhaa 'from Finfinnee (Addis Ababa)'
- gabaa 'market', gabaadhaa 'from market'
- When the word ends in a consonant, -ii is added (as for the genitive).
- Hararii 'from Harar'
- Following a noun in the genitive, -tii is added.
- mana 'house', buna 'coffee', mana bunaa 'cafe', mana bunaatii 'from cafe'
- An alternative to the ablative is the postposition irraa 'from' whose initial vowel may be dropped in the process:
- gabaa 'market', gabaa irraa, gabaarraa 'from market'
Pronouns
Personal pronouns
In most languages, there is a small number of basic distinctions of person, number, and often gender that play a role within the grammar of the language. Oromo and English are such languages. We see these distinctions within the basic set of independent personal pronouns, for example, English I, Oromo ani; English they, Oromo isaani and the set of possessive adjectives and pronouns, for example, English my, Oromo koo; English mine, Oromo kan koo. In Oromo, the same distinctions are also reflected in subject–verb agreement: Oromo verbs (with a few exceptions) agree with their subjects; that is, the person, number, and (singular third person) gender of the subject of the verb are marked by suffixes on the verb. Because these suffixes vary greatly with the particular verb tense/aspect/mood, they are normally not considered to be pronouns and are discussed elsewhere in this article under verb conjugation.
In all of these areas of the grammar—independent pronouns, possessive adjectives, possessive pronouns, and subject–verb agreement—Oromo distinguishes seven combinations of person, number, and gender. For first and second persons, there is a two-way distinction between singular ('I', 'you sg.') and plural ('we', 'you pl.'), whereas for third person, there is a two-way distinction in the singular ('he', 'she') and a single form for the plural ('they'). Because Oromo has only two genders, there is no pronoun corresponding to English it; the masculine or feminine pronoun is used according to the gender of the noun referred to.
Oromo is a subject pro-drop language. That is, neutral sentences in which the subject is not emphasized do not require independent subject pronouns: kaleessa dhufne 'we came yesterday'. The Oromo word that translates 'we' does not appear in this sentence, though the person and number are marked on the verb dhufne ('we came') by the suffix -ne. When the subject in such sentences needs to be given prominence for some reason, an independent pronoun can be used: nuti kaleessa dhufne 'we came yesterday'.
The table below gives forms of the personal pronouns in the different cases, as well as the possessive adjectives. For the first person plural and third person singular feminine categories, there is considerable variation across dialects; only some of the possibilities are shown.
The possessive adjectives, treated as separate words here, are sometimes written as noun suffixes. In most dialects there is a distinction between masculine and feminine possessive adjectives for first and second person (the form agreeing with the gender of the modified noun). However, in the western dialects, the masculine forms (those beginning with k-) are used in all cases. Possessive adjectives may take the case endings for the nouns they modify: ganda kootti 'to my village' (-tti: locative case).
| English | Base | Subject | Dative | Instrumental | Locative | Ablative | Possessive adjectives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | ana, na | ani, an | naa, naaf, natti | naan | natti | narraa | koo, kiyya [too, tiyya (f.)] |
| you (sg.) | si | ati | sii, siif, sitti | siin | sitti | sirraa | kee [tee (f.)] |
| he | isa | inni | isaa, isaa(tii)f, isatti | isaatiin | isatti | isarraa | (i)saa |
| she | isii, ishii, isee, ishee | isiin, etc. | ishii, ishiif, ishiitti, etc. | ishiin, etc. | ishiitti, etc. | ishiirraa, etc. | (i)sii, (i)shii |
| we | nu | nuti, nu'i, nuy, nu | nuu, nuuf, nutti | nuun | nutti | nurraa | keenna, keenya [teenna, teenya (f.)] |
| you (pl.) | isin | isini | isinii, isiniif, isinitti | isiniin | isinitti | isinirraa | keessan(i) [teessan(i) (f.)] |
| they | isaan | isaani | isaanii, isaaniif, isaanitti | isaaniitiin | isaanitti | isaanirraa | (i)saani |
As in languages such as French, Russian, and Turkish, the Oromo second person plural is also used as a polite singular form, for reference to people that the speaker wishes to show respect towards. This usage is an example of the so-called T-V distinction that is made in many languages. In addition, the third person plural may be used for polite reference to a single third person (either 'he' or 'she').
For possessive pronouns ('mine', 'yours', etc.), Oromo adds the possessive adjectives to kan 'of': kan koo 'mine', kan kee 'yours', etc.
Reflexive and reciprocal pronouns
Oromo has two ways of expressing reflexive pronouns ('myself', 'yourself', etc.). One is to use the noun meaning 'self': of(i) or if(i). This noun is inflected for case but, unless it is being emphasized, not for person, number, or gender: isheen of laalti 'she looks at herself' (base form of of), isheen ofiif makiinaa bitte 'she bought herself a car' (dative of of).
The other possibility is to use the noun meaning 'head', mataa, with possessive suffixes: mataa koo 'myself', mataa kee 'yourself (s.)', etc.
Oromo has a reciprocal pronoun wal (English 'each other') that is used like of/if. That is, it is inflected for case but not person, number, or gender: wal jaalatu 'they like each other' (base form of wal), kennaa walii bitan 'they bought each other gifts' (dative of wal).
Demonstrative pronouns
Like English, Oromo makes a two-way distinction between proximal ('this, these') and distal ('that, those') demonstrative pronouns and adjectives. Some dialects distinguish masculine and feminine for the proximal pronouns; in the western dialects the masculine forms (beginning with k-) are used for both genders. Unlike in English, singular and plural demonstratives are not distinguished, but, as for nouns and personal pronouns in the language, case is distinguished. Only the base and nominative forms are shown in the table below; the other cases are formed from the base form as for nouns, for example, sanatti 'at/on/in that' (locative case).
| Case | Proximal ('this, these') |
Distal ('that, those') |
|---|---|---|
| Base | kana [tana (f.)] |
san |
| Nominative | kuni [tuni (f.)] |
suni |
Verbs
An Oromo verb consists minimally of a stem, representing the lexical meaning of the verb, and a suffix, representing tense or aspect and subject agreement. For example, in dhufne 'we came', dhuf- is the stem ('come') and -ne indicates that the tense is past and that the subject of the verb is first person plural.
As in many other Afroasiatic languages, Oromo makes a basic two-way distinction in its verb system between the two tensed forms, past (or "perfect") and present (or "imperfect" or "non-past"). Each of these has its own set of tense/agreement suffixes. There is a third conjugation based on the present which has three functions: it is used in place of the present in subordinate clauses, for the jussive ('let me/us/him, etc. V', together with the particle haa), and for the negative of the present (together with the particle hin). For example, deemne 'we went', deemna 'we go', akka deemnu 'that we go', haa deemnu 'let's go', hin deemnu 'we don't go'. There is also a separate imperative form: deemi 'go (sg.)!'.
Conjugation
The table below shows the conjugation in the affirmative and negative of the verb beek- 'know'. The first person singular present and past affirmative forms require the suffix -n to appear on the word preceding the verb or the word nan before the verb. The negative particle hin, shown as a separate word in the table, is sometimes written as a prefix on the verb.
| Past | Present | Jussive, Imperative | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main clause | Subordinate clause | |||||||
| Affirmative | Negative | Affirmative | Negative | Affirmative | Negative | Affirmative | Negative | |
| I | -n beeke | hin beekne | -n beeka | hin beeku | -n beeku | hin beekne | haa beeku | hin beekin |
| you (sg.) | beekte | beekta | hin beektu | beektu | beeki | hin beek(i)in | ||
| he | beeke | beeka | hin beeku | beeku | haa beeku | hin beekin | ||
| she | beekte | beekti | hin beektu | beektu | haa beektu | |||
| we | beekne | beekna | hin beeknu | beeknu | haa beeknu | |||
| you (pl.) | beektani | beektu, beektan(i) | hin beektan | beektani | beekaa | hin beek(i)inaa | ||
| they | beekani | beeku, beekan(i) | hin beekan | beekani | haa beekanu | hin beekin | ||
For verbs with stems ending in certain consonants and suffixes beginning with consonants (that is, t or n), there are predictable changes to one or the other of the consonants. The dialects vary a lot in the details, but the following changes are common.
| b- + -t → bd | qabda 'you (sg.) have' |
| g- + -t → gd | dhugda 'you (sg.) drink' |
| r- + -n → rr | barra 'we learn' |
| l- + -n → ll | galla 'we enter' |
| q- + -t → qx | dhaqxa 'you (sg.) go' |
| s- + -t → ft | baas- 'take out', baafta 'you (sg.) take out' |
| s- + -n → fn | baas- 'take out', baafna 'we take out' |
| t-/d-/dh-/x- + -n → nn | biti 'buy', binna 'we buy'; nyaadhaa 'eat', nyaanna 'we eat' |
| d- + -t → dd | fid- 'bring', fidda 'you (sg.) bring' |
| dh- + -t → tt | taphadh- 'play', taphatta 'you (sg.) play' |
| x- + -t → xx | fix- 'finish', fixxa 'you (sg.) finish' |
Verbs whose stems end in two consonants and whose suffix begins with a consonant must insert a vowel to break up the consonants since the language does not permit sequences of three consonants. There are two ways this can happen: either the vowel i is inserted between the stem and the suffix, or the final stem consonants are switched (an example of metathesis) and the vowel a is inserted between them. For example, arg- 'see', arga 'he sees', argina or agarra (from agar-na) 'we see'; kolf- 'laugh', kolfe 'he laughed', kolfite or kofalte 'you (sg.) laughed'.
Verbs whose stems end in the consonant ' (which may appear as h, w, or y in some words, depending on the dialect) belong to three different conjugation classes; the class is not predictable from the verb stem. It is the forms that precede suffixes beginning with consonants (t and n) that differ from the usual pattern. The third person masculine singular, second person singular, and first person plural present forms are shown for an example verb in each class.
- du'- 'die': du'a 'he dies', duuta 'you (sg.) die', duuna 'we die'
- beela'-, 'be hungry': beela'a 'he is hungry', beelofta 'you (sg.) are hungry', beelofna 'we are hungry'
- dhaga'- 'hear': dhaga'a 'he hears', dhageessa 'you (sg.) hear', dhageenya 'we hear' (note that the suffix consonants change)
The common verbs fedh- 'want' and godh- 'do' deviate from the basic conjugation pattern in that long vowels replace the geminated consonants that would result when suffixes beginning with t or n are added: fedha 'he wants', feeta 'you (sg.) want', feena 'we want', feetu 'you (pl.) want', hin feene 'didn't want', etc.
The verb dhuf- 'come' has the irregular imperatives koottu, koottaa. The verb deem- 'go' has, alongside regular imperative forms, the irregular imperatives beenu, beenaa.
Derivation
An Oromo verb root can be the basis for three derived voices, passive, causative, and autobenefactive, each formed with addition of a suffix to the root, yielding the stem that the inflectional suffixes are added to.
- Passive voice
- The Oromo passive corresponds closely to the English passive in function. It is formed by adding -am to the verb root. The resulting stem is conjugated regularly. Examples: beek- 'know', beekam- 'be known', beekamani 'they were known'; jedh- 'say', jedham- 'be said', jedhama 'it is said'
- Causative voice
- The Oromo causative of a verb V corresponds to English expressions such as 'cause V', 'make V', 'let V'. With intransitive verbs, it has a transitivizing function. It is formed by adding -s, -sis, or -siis to the verb root, except that roots ending in -l add -ch. Verbs whose roots end in ' drop this consonant and may lengthen the preceding vowel before adding -s. Examples: beek- 'know', beeksis- 'cause to know, inform', beeksifne 'we informed'; ka'- 'go up, get up', kaas- 'pick up', kaasi 'pick up (sing.)!'; gal- 'enter', galch- 'put in', galchiti 'she puts in'; bar- 'learn', barsiis- 'teach', nan barsiisa 'I teach'.
- Autobenefactive voice
- The Oromo autobenefactive (or "middle" or "reflexive-middle") voice of a verb V corresponds roughly to English expressions such as 'V for oneself' or 'V on one's own', though the precise meaning may be somewhat unpredictable for many verbs. It is formed by adding -adh to the verb root. The conjugation of a middle verb is irregular in the third person singular masculine of the present and past (-dh in the stem changes to -t) and in the singular imperative (the suffix is -u rather than -i). Examples: bit- 'buy', bitadh- 'buy for oneself', bitate 'he bought (something) for himself', bitadhu 'buy for yourself (sing.)!'; qab- 'have', qabadh- 'seize, hold (for oneself)', qabanna 'we hold'. Some autobenefactives are derived from nouns rather than verbs, for example, hojjadh- 'work' from the noun hojii 'work'.
The voice suffixes can be combined in various ways. Two causative suffixes are possible: ka'- 'go up', kaas- 'pick up', kaasis- 'cause to pick up'. The causative may be followed by the passive or the autobenefactive; in this case the s of the causative is replaced by f: deebi'- 'return (intransitive)', deebis- 'return (transitive), answer', deebifam- 'be returned, be answered', deebifadh- 'get back for oneself'.
Another derived verbal aspect is the frequentative or "intensive," formed by copying the first consonant and vowel of the verb root and geminating the second occurrence of the initial consonant. The resulting stem indicates the repetition or intensive performance of the action of the verb. Examples: bul- 'spend the night', bubbul- 'spend several nights', cab- 'break', caccab- 'break to pieces, break completely'; dhiib- 'push, apply pressure', dhiddhiib- 'massage'.
The infinitive is formed from a verb stem with the addition of the suffix -uu. Verbs whose stems end in -dh (in particular all autobenefactive verbs) change this to ch before the suffix. Examples: dhug- 'drink', dhuguu 'to drink'; ga'- 'reach', ga'uu 'to reach'; jedh- 'say', jechu 'to say'. The verb fedh- is exceptional; its infinitive is fedhuu rather than the expected fechuu. The infinitive behaves like a noun; that is, it can take any of the case suffixes. Examples: ga'uu 'to reach', ga'uuf 'in order to reach' (dative case); dhug- 'drink', dhugam- 'be drunk', dhugamuu to be drunk', dhugamuudhaan 'by being drunk' (instrumental case).
Notes
- 1 2 Oromo at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Borana–Arsi–Guji–Walagaa Oromo at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Eastern Oromo at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Orma at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
West Central Oromo at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Waata at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) - ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Nuclear Oromo". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Laurie Bauer, 2007, The Linguistics Student’s Handbook, Edinburgh
- ↑ Dictionary Reference: Oromo
- ↑ The Free Dictionary: Oromo
- ↑ https://www.ethnologue.com/subgroups/oromo-1
- ↑ "Languages of Somalia". ethnologue.com. Retrieved 15 October 2010.
- ↑ "Languages of Kenya". ethnologue.com. Retrieved 15 October 2010.
- ↑ Ethnologue (1999-02-19). "Languages of Ethiopia". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2013-08-10.
- ↑ "Afaan Oromo". University of Pennsylvania, School of African Studies.
- ↑ "Letter from the Oromo Communities in North America to H.E. Mr. Kofi Anan, Secretary-General of the United Nations". April 17, 2000. Retrieved 15 October 2010.
- ↑ R. J. Hayward and Mohammed Hassan (1981). "The Oromo Orthography of Shaykh Bakri Saṗalō". 44 (3). Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies: 550–566.
- ↑ "The Oromo Orthography of Shaykh Bakri Sapalo". Retrieved 15 October 2010.
- ↑ Stroomer, p. 4.
- ↑ "Online Afaan Oromoo–English Dictionary". Jimmatimes.com. Retrieved 2013-08-10.
- ↑ Lloret 1997:500
- ↑ Dissassa 1980: 10–11
- ↑ Jonathan Owens, A Grammar of Harar Oromo (Buske Verlag, 1985; ISBN 3-87118-717-8), p. 29.
- ↑ Owens, A Grammar of Harar Oromo, p. 35.
- ↑ Owens, A Grammar of Harar Oromo, pp. 36-37.
- ↑ Owens, A Grammar of Harar Oromo, p. 37.
Bibliography
Grammar
- Ali, Mohamed; Zaborski, A. (1990). Handbook of the Oromo Language. Wroclaw, Poland: Polska Akademia Nauk. ISBN 83-04-03316-X.
- Griefenow-Mewis, Catherine; Tamene Bitima (1994). Lehrbuch des Oromo. Köln: Rüdiger Köppe Verlag. ISBN 3-927620-05-X.
- Griefenow-Mewis, Catherine (2001). A Grammatical Sketch of Written Oromo (Language and dialect atlas of Kenya, 4.). Köln, Germany: Rüdiger Köppe Verlag. ISBN 3-89645-039-5.
- Heine, Bernd (1981). The Waata Dialect of Oromo: Grammatical Sketch and Vocabulary. Berlin: Dietrich Reimer. ISBN 3-496-00174-7.
- Hodson, Arnold Weinholt (1922). An elementary and practical grammar of the Galla or Oromo language. London: Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge.
- Owens, Jonathan (1985). A Grammar of Harar Oromo. Hamburg: Buske. ISBN 3-87118-717-8.
- Praetorius, Franz (1973) [1872]. Zur Grammatik der Gallasprache. Hildesheim; New York: G. Olms. ISBN 3-487-06556-8.
- Roba, Taha M. (2004). Modern Afaan Oromo grammar : qaanqee galma Afaan Oromo. Bloomington, IN: Authorhouse. ISBN 1-4184-7480-0.
- Stroomer, Harry (1987). A comparative study of three Southern Oromo dialects in Kenya. Hamburg: Helmut Buske Verlag. ISBN 3-87118-846-8.
Dictionaries
- Bramly, A. Jennings (1909). English-Oromo-Amharic Vocabulary. [Typescript in Khartoum University Library].
- Foot, Edwin C. (1968) [1913]. An Oromo-English, English-Oromo dictionary. Cambridge University Press (repr. Farnborough, Gregg). ISBN 0-576-11622-X.
- Gragg, Gene B. et al. (ed., 1982) Oromo Dictionary. Monograph (Michigan State University. Committee on Northeast African Studies) no. 12. East Lansing, Mich. : African Studies Center, Michigan State Univ.
- Mayer, Johannes (1878). Kurze Wörter-Sammlung in Englisch, Deutsch, Amharisch, Oromonisch, Guragesch, hrsg. von L. Krapf. Basel: Pilgermissions-Buchsdruckerei St. Chrischona.
- Tamene Bitima (2000). A dictionary of Oromo technical terms. Oromo – English. Köln: Rüdiger Köppe Verlag. ISBN 3-89645-062-X.
- Stroomer, Harry (2001). A concise vocabulary of Orma Oromo (Kenya) : Orma-English, English-Orma. Köln: Rudiger Köppe.
- Tilahun Gamta (1989). Oromo-English dictionary. Addis Ababa: University Printing Press.
External links
| Oromo edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Oromo |
- Oromo–English Dictionary
- Online Oromo – Qubee Dictionary
- Voice of America news broadcast in Oromo.
- Oromo Federalist Democratic Movement (OFDM) website contains many articles written in Oromo and audio.
- PanAfriL10n page on Oromo
- HornMorpho: software for morphological analysis and generation of Oromo (and Amharic and Tigrinya) words
- 500 Word Oromo Dictionary
- Oromo – Daily News