Adenosine monophosphate
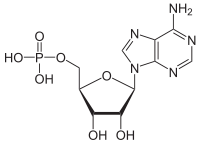 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names
Adenosine 5'-monophosphate, 5'-Adenylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.455 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Adenosine+monophosphate |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14N5O7P | |
| Molar mass | 347.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
| Density | 2.32 g/mL |
| Melting point | 178 to 185 °C (352 to 365 °F; 451 to 458 K) |
| Boiling point | 798.5 °C (1,469.3 °F; 1,071.7 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.9, 3.8, 6.1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine, which does not have the typical high energy bond of the so-called adenosine monophosphate ("AMP") that arises on the hydrolysis of ATP. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine. As a substituent it takes the form of the prefix adenylyl-.
Production and degradation
AMP can be produced during ATP synthesis by the enzyme adenylate kinase by combining two ADP molecules:
- 2 ADP → ATP + AMP
Or AMP may be produced by the hydrolysis of one high energy phosphate bond of ADP:
- ADP → AMP + Pi
AMP can also be formed by hydrolysis of ATP into AMP and pyrophosphate:
- ATP → AMP + PPi
When RNA is broken down by living systems, nucleoside monophosphates, including adenosine monophosphate, are formed.
AMP can be regenerated to ATP as follows:
- AMP + ATP → 2 ADP (adenylate kinase in the opposite direction)
- ADP + Pi → ATP (this step is most often performed in aerobes by the ATP synthase during oxidative phosphorylation)
AMP can be converted into IMP by the enzyme myoadenylate deaminase, freeing an ammonia group.
In a catabolic pathway, adenosine monophosphate can be converted to uric acid, which is excreted from the body.
cAMP
AMP can also exist as a cyclic structure known as cyclic AMP (or cAMP). Within certain cells the enzyme adenylate cyclase makes cAMP from ATP, and typically this reaction is regulated by hormones such as adrenaline or glucagon. cAMP plays an important role in intracellular signaling.
See also
References
External links
- GMD MS Spectrum
- Ming D, Ninomiya Y, Margolskee RF (1999). "Blocking taste receptor activation of gustducin inhibits gustatory responses to bitter compounds". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 96 (17): 9903–9908. PMC 22308
 . PMID 10449792. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.17.9903.
. PMID 10449792. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.17.9903.