Acylhydrazine
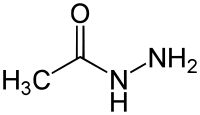
An example of an acylhydrazine. This compound has been called acetylhydrazide, acetohydrazide, or acetic acid hydrazide.[1]
An acylhydrazine is analogous to an amide, but the -OH portion of a carboxylic acid is replaced by hydrazine rather than ammonia (one less hydrogen at the point of attachment). Acylhydrazines are a type of hydrazides.
Acylhydrazines are intermediates in chemical syntheses. For example, a synthesis of sunitinib begins by mixing 5-fluoroisatin slowly into hydrazine hydrate.[2] After 4 hours at 110 °C, the indole ring structure has been broken into (2-amino-5-fluoro-phenyl)-acetic acid hydrazide with reduction of the ketone at the 3-position. Subsequent annelation in strong acid creates the 1,3-dihydro-2-oxo indole structure required for the drug.
References
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.