Actinophryid
| Actinophryids | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| (unranked): | SAR |
| Superphylum: | Heterokonta |
| Phylum: | Ochrophyta |
| Class: | Actinochrysophyceae |
| Order: | Actinophryida Hartmann 1913 |
| Genera | |
|
Actinophrys | |
The actinophryids are small, familiar group of heliozoans. They are the most common heliozoa in fresh water, and are especially frequent in lakes and rivers, but a few are found in marine and soil habitats as well. Each actinophryid are unicellular and roughly spherical in shape, without any shell or test, and with many pseudopodia supported by axopods radiating outward from the cell body, which adhere to passing prey and allows it to roll or float about. The outer portion of the cell, or ectoplasm, is distinct and is filled with many tiny vacuoles. The organism regulates buoyancy and maintains homeostasis through the use of contractile vacuoles, which are visible as clear bulges when full.
There are two genera included here. Actinophrys have a single, central nucleus. Most are around 40-50 μm in diameter, with axopods up to 100 μm in length, though this varies. Actinosphaerium are several times larger, from 200-1000 μm in diameter, with many nuclei, and are found exclusively in fresh water. Two other genera, Echinosphaerium and Camptonema, have been described but appear to be synonyms.
Reproduction takes place by fission, with open mitosis. Under unfavourable conditions, the organism will form a cyst, which is multi-walled and covered in spikes. While encysted it may undergo a peculiar process of autogamy or self-fertilization, where it goes through meiosis and divides to form two gametes, which then fuse together again. This is the only form of sexual reproduction that occurs within the group, though it is really more genetic reorganization than reproduction.
The axopods are supported by microtubules arranged in a unique and characteristic double-coil pattern. In Actinophrys, these arise from the nuclear membrane, while in Actinosphaerium some do and others don't. Other heliozoa where the microtubules arise from the nucleus have been considered possible relatives, and it now appears that the actinophryids developed from axodines such as Pedinella. These are specialized heterokont algae, related to golden algae, diatoms, brown algae, and the like, which have microtubule-supported tentacles.
Actinophyrys feeds on small flagellates, cilates, and algae, etc.
Originally placed in Heliozoa (Sarcodina), the group was moved to Actinochrysophyceae (Axodines), or to Raphidomonadea.
Taxonomy
Classification based on Cavalier-Smith and Scoble 2013[1][2]
- In class Raphidomonadea Silva 1980 emend. Cavalier-Smith 2013 [Raphidophyceae Chadefaud 1950 emend. Silva 1980 s.l.]
- In subclass Raphopoda Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Order Actinophyrida Hartmann 1913 [Actinophrydia Kühn 1926; Actinophrydea Hartmann 1913]
- Family Actinosphaeriidae Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Genus Actinosphaerium Ritter von Stein 1857 [Camptonema Schaudinn 1894; Echinosphaerium Hovasse 1965]
- Family Helioraphidae Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Genus Heliorapha Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Family Actinophryidae Dujardin 1841
- Genus Actinophrys Ehrenberg 1830 [Trichoda Müller 1773 nomen oblitum; Peritricha Bory de St.Vincent 1824 nomen dubium non Stein 1859]
- Family Actinosphaeriidae Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Order Actinophyrida Hartmann 1913 [Actinophrydia Kühn 1926; Actinophrydea Hartmann 1913]
- In subclass Raphopoda Cavalier-Smith 2013
References
- ↑ Cavalier-Smith, T; Scoble, J. M. (2013). "Phylogeny of Heterokonta: Incisomonas marina, a uniciliate gliding opalozoan related to Solenicola (Nanomonadea), and evidence that Actinophryida evolved from raphidophytes". European Journal of Protistology. 49 (3): 328–353. doi:10.1016/j.ejop.2012.09.002.
- ↑ Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. (2016). "Raphidophyceae". AlgaeBase. Retrieved 2016-08-26.
Gallery

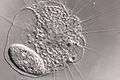
 Microtubules structure from an axopodium
Microtubules structure from an axopodium
| Wikispecies has information related to: Actinophryida |