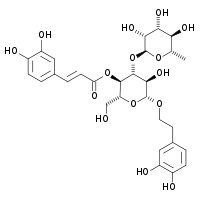
Verbascoside
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6R)-6-[2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]-5-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-3-yl] (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
Acteoside Kusaginin Orobanchin | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.112.547 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H36O15 | |
| Molar mass | 624.59 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Verbascoside is a caffeoyl phenylethanoid glycoside (CPG).[1] It is an ester formed with the phenylethanoid hydroxytyrosol, the phenylpropanoid caffeic acid and the sugar alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->3)-beta-D-glucopyranose.
Occurrences
Natural occurrences
Verbascoside can be found in species in all the families of the Lamiales order (syn. Scrophulariales).[2] Only two examples are known from outside the order,[3] in the clade Asterids.
- in the Lamiales
In the family Lamiaceae, it can be found in the medicinal plants in the genus Phlomis,[4] in the Scrophulariaceae, in Verbascum phlomoides,[5] Verbascum mallophorum,[6] or, in the Buddlejaceae family, in Buddleja globosa[7] or Buddleja cordata,[8] in the Bignoniaceae family, in Pithecoctenium sp and Tynanthus panurensis, in the Orobanchaceae family, in Cistanche sp and Orobanche rapum-genistae,[9] in the Plantaginaceae, in Plantago lanceolata,[10] in Verbenaceae, in Verbena officinalis (common vervain),[11] Aloysia citrodora (lemon verbena) and Lantana camara,[12] in the Oleaceae, in Olea europaea (olive),[13] in the Lentibulariaceae, in the carnivorous plant Pinguicula lusitanica,[3] and, in the Byblidaceae, in Byblis liniflora.[2]
Derivatives
Verbascoside derivatives can be found in the Verbascum undulatum[14] and notably apiosides in Verbascum sp.[15]
In in vitro cultures
It can also be produced in plant cell cultures of Leucosceptrum sp (Lamiaceae) and Syringa sp (Oleaceae).[16] It can also be produced in hairy roots cultures of Paulownia tomentosa (empress tree, Paulowniaceae).[17]
Biological activity
Verbascoside has an antimicrobial activity,[7] notably against Staphylococcus aureus.[8] It can also have anti-inflammatory properties.[6]
Although some in vitro genotoxicity of verbascoside has been reported on human lymphocytes with an involvement of PARP-1 and p53 proteins,[18] subsequent in vivo tests reported no genotoxicity for high dosage oral administration.[19] It is a protein kinase C inhibitor.[12]
References
- ↑ Taskova, R.M.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Jensen, S.R. (2005). "Chemotaxonomic markers in Digitalideae (Plantaginaceae)". Phytochemistry. 66 (12): 1440–1447. PMID 15907957. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2005.04.020.
- 1 2 Schlauer, Jan; Budzianowski, Jaromir; Krystyna; Ratajczak, Lidia (2004). "Acteoside and related phenylethanoid glycosides in Byblis liniflora Salisb. plants propagated in vitro and its systematic significance". Acta Societatis Botanicorum Poloniae. 73 (1): 9–15. doi:10.5586/asbp.2004.002.
- 1 2 Grevenstuk, Tomás; van der Hooft, Justin J.J.; Vervoort, Jacques; de Waard, Pieter; Romano, Anabela (2009). "Iridoid and caffeoyl phenylethanoid glycosides of the endangered carnivorous plant Pinguicula lusitanica L. (Lentibulariaceae)". Biochemical Systematics and Ecology. 37 (4): 285–289. doi:10.1016/j.bse.2009.05.003.
- ↑ Sarkhail, P; Nikan, M; Sarkheil, P; Gohari, AR; Ajani, Y; Hosseini, R; Hadjiakhoondi, A; Saeidnia, S (2014). "Quantification of verbascoside in medicinal species of Phlomis and their genetic relationships". DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 22 (1): 32. doi:10.1186/2008-2231-22-32.
- ↑ Gvazava, L. N.; Kikoladze, V. S. (2007). "Verbascoside from Verbascum phlomoides". Chemistry of Natural Compounds. 43 (6): 710–711. doi:10.1007/s10600-007-0240-9.
- 1 2 Speranza, L; Franceschelli, S; Pesce, M; Menghini, L; Patruno, A; Vinciguerra, I; De Lutiis, MA; Felaco, M; et al. (2009). "Anti-inflammatory properties of the plant Verbascum mallophorum". Journal of biological regulators and homeostatic agents. 23 (3): 189–95. PMID 19828096.
- 1 2 Pardo F, Perich F, Villarroel L, Torres R (August 1993). "Isolation of verbascoside, an antimicrobial constituent of Buddleja globosa leaves". J Ethnopharmacol. 39 (3): 221–2. PMID 8258981. doi:10.1016/0378-8741(93)90041-3.
- 1 2 Guillermo Avila, José; De Liverant, Juliana G.; Martı́Nez, Andrés; Martı́Nez, Gabriel; Muñoz, José Luis; Arciniegas, Amira; Romo De Vivar, Alfonso (1999). "Mode of action of Buddleja cordata verbascoside against Staphylococcus aureus". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 66 (1): 75–8. PMID 10432210. doi:10.1016/S0378-8741(98)00203-7.
- ↑ Andary, C.; Wylde, R.; Laffite, C.; Privat, G.; Winternitz, F. (1982). "Structures of verbascoside and orobanchoside, caffeic acid sugar esters from Orobanche rapum-genistae". Phytochemistry. 21 (5): 1123–1127. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)82429-2.
- ↑ Murai, Michiko; Tamayama, Yasuhiko; Nishibe, Sansei (1995). "Phenylethanoids in the Herb of Plantago lanceolata and Inhibitory Effect on Arachidonic Acid-Induced Mouse Ear Edema". Planta Med. 61 (5): 479–480. doi:10.1055/s-2006-958143.
- ↑ Deepak, Mundkinajeddu; Swami Handa, Sukhdev (2000). "Antiinflammatory activity and chemical composition of extracts of Verbena officinalis". Phytotherapy Research. 14 (6): 463–465. doi:10.1002/1099-1573(200009)14:6<463::AID-PTR611>3.0.CO;2-G.
- 1 2 Herbert, J. M.; Maffrand, J. P.; Taoubi, K.; Augereau, J. M.; Fouraste, I.; Gleye, J. (1991). "Verbascoside Isolated from Lantana camara, an Inhibitor of Protein Kinase C". Journal of Natural Products. 54 (6): 1595–600. PMID 1812212. doi:10.1021/np50078a016.
- ↑ Cardinali, A; Pati, S; Minervini, F; D'Antuono, I; Linsalata, V; Lattanzio, V (2012). "Verbascoside, isoverbascoside, and their derivatives recovered from olive mill wastewater as possible food antioxidants". J Agric Food Chem. 60 (7): 1822–1829. PMID 22268549. doi:10.1021/jf204001p.
- ↑ Magiatis, P.; Mitaku, S.; Tsitsa, E.; Skaltsounis, A. L.; Harvala, C. (1998). "Verbascoside Derivatives and Iridoid Glycosides fromVerbascum Undulatum". Natural Product Letters. 12 (2): 111–115. doi:10.1080/10575639808048278.
- ↑ Klimek, B (1996). "6'-0-apiosyl-verbascoside in the flowers of mullein (Verbascum species)". Acta poloniae pharmaceutica. 53 (2): 137–40. PMID 8960288.
- ↑ Inagaki, Nobuyuki; Nishimura, Hiroaki; Okada, Minoru; Mitsuhashi, Hiroshi (1991). "Verbascoside production by plant cell cultures". Plant Cell Reports. 9 (9). doi:10.1007/BF00232101.
- ↑ Rózga, M. (1998). "Establishment of transformed root cultures of Paulownia tomentosa for verbascoside production". Journal of Plant Physiology. 152 (1): 78–83. doi:10.1016/S0176-1617(98)80105-3.
- ↑ Santoro, Antonietta; Bianco, Giuseppe; Picerno, Patrizia; Aquino, Rita Patrizia; Autore, Giuseppina; Marzocco, Stefania; Gazzerro, Patrizia; Lioi, Maria Brigida; Bifulco, Maurizio (2008). "Verminoside- and verbascoside-induced genotoxicity on human lymphocytes: Involvement of PARP-1 and p53 proteins". Toxicology Letters. 178 (2): 71–6. PMID 18395372. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.02.006.
- ↑ Santos-Cruz, Luis Felipe; Ávila-Acevedo, José Guillermo; Ortega-Capitaine, Diego; Ojeda-Duplancher, Jesús Clemente; Perdigón-Moya, Juana Laura; Hernández-Portilla, Luis Barbo; López-Dionicio, Héctor; Durán-Díaz, Ángel; et al. (2012). "Verbascoside is not genotoxic in the ST and HB crosses of the Drosophila wing spot test, and its constituent, caffeic acid, decreases the spontaneous mutation rate in the ST cross". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 50 (3–4): 1082–90. PMID 22197714. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.12.006.