Acre
| Acre | |
|---|---|
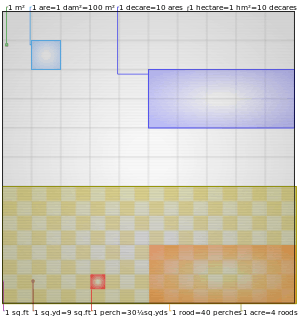 Comparison of some Imperial and metric units of area | |
| Unit information | |
| Unit system | US customary units |
| Unit of | Area |
| Symbol | acre |
| Unit conversions | |
| 1 acre in ... | ... is equal to ... |
| SI units | 4,046.9 m2 |
The acre is a unit of land area used in the imperial and US customary systems. It is defined as the area of 1 chain by 1 furlong (66 by 660 feet), which is exactly equal to 1⁄640 of a square mile, 43,560 square feet, approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare.
The acre is commonly used in Antigua and Barbuda,[1] Australia, American Samoa,[2] the Bahamas,[3] Belize,[4] the British Virgin Islands,[5] the Cayman Islands,[6] Canada,[7] Dominica,[8] the Falkland Islands,[9] Grenada,[10] Ghana, Guam,[11] the Northern Mariana Islands,[12] India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, Ireland,[13] Jamaica,[14] Montserrat,[15] Myanmar, Pakistan, Samoa,[16] St. Lucia,[17] St. Helena,[18] St. Kitts and Nevis,[19] St. Vincent and the Grenadines,[20] Turks and Caicos,[21] the United Kingdom, the United States and the US Virgin Islands.[22]
The international symbol of the acre is ac. The most commonly used acre today is the international acre. In the United States both the international acre and the US survey acre are in use, but differ by only two parts per million, see below. The most common use of the acre is to measure tracts of land. One international acre is defined as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres.
An acre was defined in the Middle Ages, being the amount of land that could be ploughed in one day by one man and one ox.
Description
One acre equals 0.0015625 square miles, 4,840 square yards, 43,560 square feet[23] or about 4,047 square metres (0.405 hectares) (see below). While all modern variants of the acre contain 4,840 square yards, there are alternative definitions of a yard, so the exact size of an acre depends on which yard it is based. Originally, an acre was understood as a selion of land sized at forty perches (660 ft, or 1 furlong) long and four perches (66 ft) wide;[24] this may have also been understood as an approximation of the amount of land a yoke of oxen could plough in one day. A square enclosing one acre is approximately 69.57 yards, or 208 feet 9 inches (63.63 metres) on a side. As a unit of measure, an acre has no prescribed shape; any area of 43,560 square feet is an acre.
Differences between international and US survey acres
In the international yard and pound agreement of 1959 the United States and five countries of the Commonwealth of Nations defined the international yard to be exactly 0.9144 metres.[25] Consequently, the international acre is exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres.
Both the international acre and the US survey acre contain 1⁄640 of a square mile or 4,840 square yards, but there are alternative definitions of a yard (see survey foot and survey yard), so the exact size of an acre depends on which yard it is based upon. The US survey acre is about 4,046.872609874252 square metres; its exact value (4046 13,525,426/15,499,969 m2) is based on an inch defined by 1 metre = 39.37 inches exactly, as established by the Mendenhall Order. Surveyors in the United States use both international and survey feet, and consequently, both varieties of acre.[26]
Since the difference between the US survey acre and international acre is only about a quarter of the size of an A4 sheet of paper (0.016 square metres, 160 square centimetres or 24.8 square inches), it is usually not important which one is being discussed. Areas are seldom measured with sufficient accuracy for the different definitions to be detectable.[27]
South Asia
In India, residential plots are measured in cents or decimal, which is one hundredth of an acre, or 435.60 square feet (40.469 m2). In Sri Lanka the division of an acre into 160 perches or 4 roods is common.[28]
Equivalence to other units of area
1 international acre is equal to the following metric units:
- 0.40468564224 hectare (A square with 100 m sides has an area of 1 hectare.)
- 4,046.8564224 square metres
1 United States survey acre is equal to:
- 0.404687261 hectare
- 4,046.87261 square metres (1 square kilometre is equal to 247.105 acres)
1 acre (both variants) is equal to the following customary units:
- 66 feet × 660 feet (43,560 square feet)
- 10 square chains (1 chain = 66 feet = 22 yards = 4 rods = 100 links)
- 1 acre is approximately 208.71 feet × 208.71 feet (a square)
- 4,840 square yards
- 43,560 square feet
- 160 perches. A perch is equal to a square rod (1 square rod is 0.00625 acre)
- 4 roods
- A furlong by a chain (furlong 220 yards, chain 22 yards)
- 40 rods by 4 rods, 160 rods2 (historically fencing was often sold in 40 rod lengths)
- 1⁄640 (0.0015625) square mile (1 square mile is equal to 640 acres)
Perhaps the easiest way for US residents to envisage an acre is as a rectangle measuring 88 yards by 55 yards ( 1⁄10 of 880 yards by 1⁄16 of 880 yards), about 9⁄10 the size of a standard American football field.

To be more exact, one acre is 90.75 percent of a 100 yards (91.44 metres) long by 53.33 yards (48.76 metres) wide American football field (without the end zones). The full field, including the end zones, covers approximately 1.32 acres (0.53 ha).
For residents of other countries, the acre might be envisaged as approximately half of a 105 metres (344.49 feet) long by 68 metres (223.10 feet) wide association football (soccer) pitch.
It may also be remembered as 44,000 square feet, less 1%.
Historical origin

- The rod is a historical unit of length equal to 5½ yards. It may have originated from the typical length of a mediaeval ox-goad. There are 4 rods in one chain.
- The furlong (meaning furrow length) was the distance a team of oxen could plough without resting. This was standardised to be exactly 40 rods or 10 chains.
- An acre was the amount of land tillable by one man behind one ox in one day. Traditional acres were long and narrow due to the difficulty in turning the plough and the value of river front access.
- An oxgang was the amount of land tillable by one ox in a ploughing season. This could vary from village to village, but was typically around 15 acres.
- A virgate was the amount of land tillable by two oxen in a ploughing season.
- A carucate was the amount of land tillable by a team of eight oxen in a ploughing season. This was equal to 8 oxgangs or 4 virgates.
The word acre is derived from Old English æcer originally meaning "open field", cognate to west coast Norwegian ækre and Swedish åker, German Acker, Dutch akker, Latin ager, Sanskrit ajr, and Greek αγρός (agros). In English it was historically spelled aker.
The acre was approximately the amount of land tillable by a yoke of oxen in one day.[29] This explains one definition as the area of a rectangle with sides of length one chain and one furlong. A long narrow strip of land is more efficient to plough than a square plot, since the plough does not have to be turned so often. The word "furlong" itself derives from the fact that it is one furrow long.
Before the enactment of the metric system, many countries in Europe used their own official acres. These were differently sized in different countries, for instance, the historical French acre was 4,221 square metres, whereas in Germany as many variants of "acre" existed as there were German states.
Statutory values for the acre were enacted in England, and, subsequently, the United Kingdom, by acts of:
- Edward I,
- Edward III,
- Henry VIII,
- George IV and
- Queen Victoria – the British Weights and Measures Act of 1878 defined it as containing 4,840 square yards.
Historically, the size of farms and landed estates in the United Kingdom was usually expressed in acres (or acres, roods, and perches), even if the number of acres was so large that it might conveniently have been expressed in square miles. For example, a certain landowner might have been said to own 32,000 acres of land, not 50 square miles of land.
The acre is related to the square mile, with 640 acres making up one square mile. One mile is 5280 feet (1760 yards). In western Canada and the western United States, divisions of land area were typically based on the square mile, and fractions thereof. If the square mile is divided into quarters, each quarter has a side length of 1⁄2 mile (880 yards) and is 1⁄4 square mile in area, or 160 acres. These subunits would typically then again be divided into quarters, with each side being 1⁄4 mile long, and being 1⁄16 of a square mile in area, or 40 acres. In the United States, farmland was typically divided as such, and the phrase "the back 40" would refer to the 40 acre parcel to the back of the farm. Most of the Canadian Prairie Provinces and the US midwest are on square mile grids for surveying purposes.
Legacy acres
- Customary acre – The customary acre was a measure of roughly similar size to the acre described above, but it was subject to considerable local variation similar to the variation found in carucates, virgates, bovates, nooks, and farundels. However, there were more ancient measures that were also farthingales. These may have been multiples of the customary acre, rather than the statute acre.
- Builder's acre – In US construction and real estate development, an area of 40,000 square feet. Used to simplify math and for marketing, it is nearly 10% smaller than a survey acre.
- Scottish acre, one of a number of obsolete Scottish units of measurement
- Irish acre = 7,840 square yards
- Cheshire acre = 10,240 square yards[30]
- stremma or Greek acre ≈ 10,000 square Greek feet, but now set at exactly 1,000 square metres (a similar unit was the zeugarion)[31]
- dunam or Turkish acre ≈ 1,600 square Turkish paces, but now set at exactly 1,000 square metres (a similar unit was the çift)[31]
- actus quadratus or Roman acre ≈ 14,400 square Roman feet (about 1,260 square metres)
- God's Acre – a synonym for a churchyard.[32]
See also
- Acre-foot
- Anthropic units
- Conversion of units
- French arpent – also used in Louisiana as length and area unit of measure
- Jugerum
- a Morgen ("morning") of land is usually set at 2⁄3 of a Tagwerk ("day work") of ploughing with an ox
- Public Land Survey System
- Quarter acre
- Section (United States land surveying)
- Spanish customary units
References
- ↑ "Gov’t Gifts ‘Bakka’ With Half-Acre Land | Antigua Observer Newspaper". web.archive.org. Archived from the original on 2013-10-04. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "National Park of American Samoa completes two successful forest projects | Samoa News". samoanews.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "The Nassau Guardian". thenassauguardian.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "2,225-acre Cobia farm proposed near Lark and Bugle Cayes | Amandala Newspaper". amandala.com.bz. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "Work continues on development". bvibeacon.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "Kai drama over 50-acre development :: cayCompass.com". compasscayman.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "Canada Farms and Ranches for sale, Canada Acreage for Sale, Canada Lots for Sale at LandWatch.com". landwatch.com. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
- ↑ "Dominica not meeting quota for international banana markets | Dominica News Online". dominicanewsonline.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "Farm Yarns with Elaine - Farm yarns with Elaine Turner - Part 13". penguin-news.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "Grenada Broadcast - George Grant - THE GRENADA SPICES INDUSTRY". grenadabroadcast.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "Local News | Pacific Daily News | guampdn.com". guampdn.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "Saipan Tribune.". saipantribune.com. Archived from the original on 17 October 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "Irish Statute Book, Metrology Act 1996, pp22". Retrieved June 2017. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ http://supremecourt.gov.jm/sites/default/files/judgments/Tropicrop%20Mushrooms%20Ltd%20v%20Saint%20Thomas%20Parish%20Council%2C%20etal.pdf
- ↑ "Beresford Allen of St. Peters Montserrat is a Wanted Man! | The Montserrat Reporter". themontserratreporter.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "Conflicting stories about Nu’u estate". samoaobserver.ws. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "The Voice - The national newspaper of St. Lucia since 1885". thevoiceslu.com. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "FEATURE: We built an island dream on our own St Helena | St Helena Online". sthelenaonline.org. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "SIDF Sinks SKN Passport Money into Christophe Harbour :: The St. Kitts-Nevis Observer". thestkittsnevisobserver.com. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "PM vows to spend rest of life seeking reparations – I-Witness News". iwnsvg.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "Government gets $8million from Emerald Cay sale". suntci.com. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "Proposed dolphin facility will enclose about 2 acres of Water Bay - News - Virgin Islands Daily News". m.virginislandsdailynews.com. Archived from the original on 22 October 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ National Institute of Standards and Technology (n.d.) General Tables of Units of Measurement Archived 26 November 2006 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Klein, Herbert Arthur (3 December 2012). The Science of Measurement: A Historical Survey. Courier Corporation. p. 76. ISBN 978-0-486-14497-9. Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- ↑ National Bureau of Standards. (1959). Refinement of Values for the Yard and the Pound.
- ↑ National Geodetic Survey, (January 1991), "Policy of the National Geodetic Survey Concerning Units of Measure for the State Plane Coordinate System of 1983.
- ↑ Minimum Standard Detail Requirements For ALTA/ACSM Land Title Surveys Archived 4 September 2013 at the Wayback Machine.. Federick, MD: American Congress on Surveying and Mapping. 2011. [The standard uses "precision" in a sense more typically used for "accuracy"; the stated maximum allowable "precision" (page 3) is 2 cm and 50 parts per million. An instrument consistently measuring 2 cm short would measure the area of a one international acre square, 63.614907 m on a side, as 4044.3 square metres, 2.6 square metres less than the true value, a far greater discrepancy than the difference between the international and survey acres.]
- ↑ "SRI LANKA". webcache.googleusercontent.com. Archived from the original on 14 January 2016. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ↑ "acre, n.".
- ↑ Holland, Robert. (1886). A glossary of words used in the County of Chester. London: Trübner for the English Dialect Society. p. 3.
- 1 2 Malcolm, Noel (1999). Kosovo: A Short History. Harper Perennial. ISBN 978-0-06-097775-7.
- ↑ "God's Acre - Definition of God's acre by Merriam-Webster".
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Acre (land measure). |
- The Units of Measurement Regulations 1995 (United Kingdom)
- Cockeyed.com presents "How much is inside an acre?"