Acetoxycycloheximide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
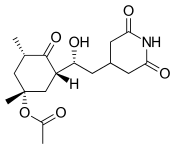
| IUPAC name
(1R,3S,5S)-3-[(1R)-2-(2,6-Dioxo-4-piperidinyl)-1-hydroxyethyl]-1,5-dimethyl-4-oxocyclohexyl acetate | |
| Other names
Acetyloxycycloheximide E-73 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H25NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 339.39 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Acetoxycycloheximide is an organic chemical compound. It can be considered as the acetylated analogue of cycloheximide. It is a potent Protein synthesis inhibitor in animal cells[1] and can inhibit the formation of memories.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ Mahy, Brian W J (2001). A dictionary of virology (3. ed.). San Diego, Calif. [u.a.]: Academic Press. p. 2. ISBN 0-12-465327-8.
- ↑ Flood, James F.; Bennett, Edward L.; Orme, Ann E.; Rosenzweig, Mark R. (February 1975). "Effects of protein synthesis inhibition on memory for active avoidance training". Physiology & Behavior. 14 (2): 177–184. doi:10.1016/0031-9384(75)90163-8.
- ↑ Flexner, L. B.; Flexner, J. B.; Roberts, R. B. (1 August 1966). "Stages of memory in mice treated with acetoxycycloheximide before or immediately after learning.". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 56 (2): 730–735. doi:10.1073/pnas.56.2.730.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.