Acanthochondria limandae
| Acanthochondria limandae | |
|---|---|
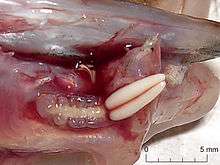 | |
| Female Acanthochondria limandae attached to Limanda limanda. The two white cylindrical objects are its egg sacs. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Crustacea |
| Class: | Maxillopoda |
| Subclass: | Copepoda |
| Order: | Poecilostomatoida |
| Family: | Chondracanthidae |
| Genus: | Acanthochondria |
| Species: | A. limandae |
| Binomial name | |
| Acanthochondria limandae (Krøyer, 1863) | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Chondracanthus limandae Krøyer, 1863 | |
Acanthochondria limandae is a species of copepods in the genus Acanthochondria. They are host-specific ectoparasites of two species of flatfish: the common dab (Limanda limanda) and the European flounder (Platichthys flesus). They attach themselves to the bases of the gill arches of their hosts. They can infest as much as 2 to 30% of fish in a given population.[2]
Acanthochondria limandae is classified under the family Chondracanthidae in the copepod order Poecilostomatoida. It was first described by the Danish zoologist Henrik Nikolai Krøyer in 1863 as Chondracanthus limandae.[1]
References
- 1 2 G. Boxshall (2011). T. C. Walter & G. Boxshall, eds. "Acanthochondria limandae (Krøyer, 1863)". World of Copepods database. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved February 12, 2012.
- ↑ Z. Kabata (1959). "Ecology of the genus Acanthochondria Oakley (Copepod, Parasitica)" (PDF). Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. The Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 38: 249–261. doi:10.1017/s0025315400006056.
External links
| External identifiers for Acanthochondria limandae | |
|---|---|
| Encyclopedia of Life | 1018974 |
| GBIF | 113185754 |
| ITIS | 206229 |
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.