Abarelix
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Plenaxis |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 96–99% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
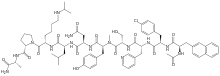
| Formula | C72H95ClN14O14 |
| Molar mass | 1416.06 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Abarelix (trade name Plenaxis) is an injectable gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist (GnRH antagonist). It is primarily used in oncology to reduce the amount of testosterone made in patients with advanced symptomatic prostate cancer for which no other treatment options are available.[2][3]
It was originally marketed by Praecis Pharmaceuticals as Plenaxis,[2] and is now marketed by Speciality European Pharma in Germany[4] after receiving a marketing authorisation in 2005. The drug was introduced in the United States in 2003, but was discontinued in this country in May 2005 due to poor sales and a higher-than-expected incidence of severe allergic reactions.[5]
References
- ↑ "Abarelix". PubChem. 2017-07-29.
- 1 2 Drugs.com: Abarelix
- ↑ Boccon-Gibod, L.; Van Der Meulen, E.; Persson, B. -E. (2011). "An update on the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists in prostate cancer". Therapeutic Advances in Urology. 3 (3): 127–140. PMC 3159401
 . PMID 21904569. doi:10.1177/1756287211414457.
. PMID 21904569. doi:10.1177/1756287211414457. - ↑ Pharmazeutische Zeitung online: Abarelix (in German)
- ↑ Boris Minev (13 January 2011). Cancer Management in Man: Chemotherapy, Biological Therapy, Hyperthermia and Supporting Measures. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 182–. ISBN 978-90-481-9704-0.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.