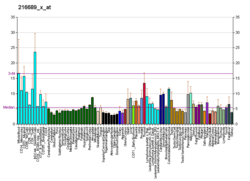
ARHGAP1
Rho GTPase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ARHGAP1 gene.[3][4]
Interactions
ARHGAP1 has been shown to interact with:
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Lancaster CA, Taylor-Harris PM, Self AJ, Brill S, van Erp HE, Hall A (February 1994). "Characterization of rhoGAP. A GTPase-activating protein for rho-related small GTPases". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (2): 1137–42. PMID 8288572.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: ARHGAP1 Rho GTPase activating protein 1".
- 1 2 Low BC, Lim YP, Lim J, Wong ES, Guy GR (November 1999). "Tyrosine phosphorylation of the Bcl-2-associated protein BNIP-2 by fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 prevents its binding to Cdc42GAP and Cdc42". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (46): 33123–30. PMID 10551883. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.46.33123.
- ↑ Low BC, Seow KT, Guy GR (December 2000). "The BNIP-2 and Cdc42GAP homology domain of BNIP-2 mediates its homophilic association and heterophilic interaction with Cdc42GAP". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (48): 37742–51. PMID 10954711. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004897200.
- ↑ Nagata Ki, Puls A, Futter C, Aspenstrom P, Schaefer E, Nakata T, Hirokawa N, Hall A (January 1998). "The MAP kinase kinase kinase MLK2 co-localizes with activated JNK along microtubules and associates with kinesin superfamily motor KIF3". EMBO J. 17 (1): 149–58. PMC 1170366
 . PMID 9427749. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.1.149.
. PMID 9427749. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.1.149. - 1 2 Li R, Zhang B, Zheng Y (December 1997). "Structural determinants required for the interaction between Rho GTPase and the GTPase-activating domain of p190". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (52): 32830–5. PMID 9407060. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.52.32830.
- 1 2 Zhang B, Chernoff J, Zheng Y (April 1998). "Interaction of Rac1 with GTPase-activating proteins and putative effectors. A comparison with Cdc42 and RhoA". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (15): 8776–82. PMID 9535855. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.15.8776.
- ↑ Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (October 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. PMID 16189514. doi:10.1038/nature04209.
- ↑ Zhang B, Zheng Y (April 1998). "Regulation of RhoA GTP hydrolysis by the GTPase-activating proteins p190, p50RhoGAP, Bcr, and 3BP-1". Biochemistry. 37 (15): 5249–57. PMID 9548756. doi:10.1021/bi9718447.
External links
- Human ARHGAP1 genome location and ARHGAP1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Diekmann D, Brill S, Garrett MD, Totty N, Hsuan J, Monfries C, Hall C, Lim L, Hall A (1991). "Bcr encodes a GTPase-activating protein for p21rac". Nature. 351 (6325): 400–2. PMID 1903516. doi:10.1038/351400a0.
- Garrett MD, Major GN, Totty N, Hall A (1991). "Purification and N-terminal sequence of the p21rho GTPase-activating protein, rho GAP". Biochem. J. 276 ( Pt 3) (3): 833–6. PMC 1151079
 . PMID 1905930.
. PMID 1905930. - Barfod ET, Zheng Y, Kuang WJ, Hart MJ, Evans T, Cerione RA, Ashkenazi A (1993). "Cloning and expression of a human CDC42 GTPase-activating protein reveals a functional SH3-binding domain". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (35): 26059–62. PMID 8253717.
- Aspenström P, Lindberg U, Hall A (1996). "Two GTPases, Cdc42 and Rac, bind directly to a protein implicated in the immunodeficiency disorder Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome". Curr. Biol. 6 (1): 70–5. PMID 8805223. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00423-2.
- Barrett T, Xiao B, Dodson EJ, Dodson G, Ludbrook SB, Nurmahomed K, Gamblin SJ, Musacchio A, Smerdon SJ, Eccleston JF (1997). "The structure of the GTPase-activating domain from p50rhoGAP". Nature. 385 (6615): 458–61. PMID 9009196. doi:10.1038/385458a0.
- Hu KQ, Settleman J (1997). "Tandem SH2 binding sites mediate the RasGAP-RhoGAP interaction: a conformational mechanism for SH3 domain regulation". EMBO J. 16 (3): 473–83. PMC 1169651
 . PMID 9034330. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.3.473.
. PMID 9034330. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.3.473. - Rittinger K, Walker PA, Eccleston JF, Nurmahomed K, Owen D, Laue E, Gamblin SJ, Smerdon SJ (1997). "Crystal structure of a small G protein in complex with the GTPase-activating protein rhoGAP". Nature. 388 (6643): 693–7. PMID 9262406. doi:10.1038/41805.
- Zhang B, Wang ZX, Zheng Y (1997). "Characterization of the interactions between the small GTPase Cdc42 and its GTPase-activating proteins and putative effectors. Comparison of kinetic properties of Cdc42 binding to the Cdc42-interactive domains". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (35): 21999–2007. PMID 9268338. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.35.21999.
- Li R, Zhang B, Zheng Y (1997). "Structural determinants required for the interaction between Rho GTPase and the GTPase-activating domain of p190". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (52): 32830–5. PMID 9407060. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.52.32830.
- Zhang B, Zheng Y (1998). "Regulation of RhoA GTP hydrolysis by the GTPase-activating proteins p190, p50RhoGAP, Bcr, and 3BP-1". Biochemistry. 37 (15): 5249–57. PMID 9548756. doi:10.1021/bi9718447.
- Low BC, Lim YP, Lim J, Wong ES, Guy GR (1999). "Tyrosine phosphorylation of the Bcl-2-associated protein BNIP-2 by fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 prevents its binding to Cdc42GAP and Cdc42". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (46): 33123–30. PMID 10551883. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.46.33123.
- Graham DL, Eccleston JF, Chung CW, Lowe PN (1999). "Magnesium fluoride-dependent binding of small G proteins to their GTPase-activating proteins". Biochemistry. 38 (45): 14981–7. PMID 10555980. doi:10.1021/bi991358e.
- Low BC, Seow KT, Guy GR (2000). "Evidence for a novel Cdc42GAP domain at the carboxyl terminus of BNIP-2". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (19): 14415–22. PMID 10799524. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.19.14415.
- Low BC, Seow KT, Guy GR (2000). "The BNIP-2 and Cdc42GAP homology domain of BNIP-2 mediates its homophilic association and heterophilic interaction with Cdc42GAP". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (48): 37742–51. PMID 10954711. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004897200.
- Zhou YT, Soh UJ, Shang X, Guy GR, Low BC (2002). "The BNIP-2 and Cdc42GAP homology/Sec14p-like domain of BNIP-Salpha is a novel apoptosis-inducing sequence". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (9): 7483–92. PMID 11741952. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109459200.
- Fidyk NJ, Cerione RA (2002). "Understanding the catalytic mechanism of GTPase-activating proteins: demonstration of the importance of switch domain stabilization in the stimulation of GTP hydrolysis". Biochemistry. 41 (52): 15644–53. PMID 12501193. doi:10.1021/bi026413p.
- Qin W, Hu J, Guo M, Xu J, Li J, Yao G, Zhou X, Jiang H, Zhang P, Shen L, Wan D, Gu J (2003). "BNIPL-2, a novel homologue of BNIP-2, interacts with Bcl-2 and Cdc42GAP in apoptosis". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 308 (2): 379–85. PMID 12901880. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)01387-1.
- Shang X, Zhou YT, Low BC (2003). "Concerted regulation of cell dynamics by BNIP-2 and Cdc42GAP homology/Sec14p-like, proline-rich, and GTPase-activating protein domains of a novel Rho GTPase-activating protein, BPGAP1". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (46): 45903–14. PMID 12944407. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304514200.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.