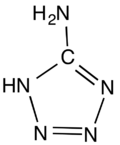
5-Aminotetrazole
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1H-Tetrazol-5-ylamine | |
| Other names
5-ATZ | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH3N5 | |
| Molar mass | 85.07 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.502 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 201–205 °C (394–401 °F; 474–478 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
5-Aminotetrazole is an organic compound with the formula HN4CNH2. It is a white solid that can be obtained both in anhydrous and hydrated forms. The compound has a particularly high nitrogen content of 80%. Partly for this reason, the compound is prone to decomposition to nitrogen gas (N2). It has been widely investigated for gas-generating systems, such as airbags and blowing agents.[1]
The molecule is planar.[2] The hydrogen bonding pattern in the hydrate supports the assignment of NH being adjacent to carbon in the ring.[3]
References
- ↑ Lesnikovich, A. I.; Ivashkevich, O. A.; Levchik, S. V.; Balabanovich, A. I.; Gaponik, P. N.; Kulak, A. A. "Thermal decomposition of aminotetrazoles" Thermochimica Acta 2002, vol. 388, pp. 233-251. doi:10.1016/S0040-6031(02)00027-8
- ↑ Hiroshi Fujihisa, Kazumasa Honda, Shigeaki Obata, Hiroshi Yamawaki, Satoshi Takeya, Yoshito Gotoha, Takehiro Matsunaga "Crystal structure of anhydrous 5-aminotetrazole and its high-pressure behavior" CrystEngComm, 2011, volume 13, pp. 99-102. doi:10.1039/C0CE00278J
- ↑ D. D. Bray and J. G. White "Refinement of the structure of 5-aminotetrazole monohydrate" Acta Crystallogr. (1979). B35, pp. 3089-3091.doi:10.1107/S0567740879011493
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.