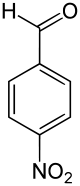
4-Nitrobenzaldehyde
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Nitrobenzaldehyde | |||
| Other names
p-Nitrobenzaldehyde | |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H5NO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 151.12 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | slightly yellowish crystalline powder | ||
| Density | 1.546 g/cm3[1] | ||
| Melting point | 103 to 106 °C (217 to 223 °F; 376 to 379 K)[2] | ||
| Boiling point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K)[1] | ||
| -66.57·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.259 | ||
| PubChem CID |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |  [2] [2] | ||
| H317, H319 | |||
| P280, P305+351+338 | |||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
4-Nitrobenzaldehyde is an organic aromatic compound containing a nitro group para-substituted to an aldehyde.
Nitrobenzyldiacetate is obtained by the reaction of 4-nitrotoluene and chromium(VI) oxide in acetic anhydride. 4-Nitrobenzaldehyde is obtained by hydrolysis by sulfuric acid in ethanol.[3]
References
- 1 2 4-Nitrobenzaldehyde(555-16-8) (Date Accessed 17 April 2013)
- 1 2 Sigma-Aldrich Co., 4-Nitrobenzaldehyde. Retrieved on 4 May 2011.
- ↑ 4-Nitrobenzaldehyd, Versuchsvorschrift aus: Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 2, p. 441 (1943); Vol. 18, p. 61 (1938).
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.