3rd century
| Millennium: | 1st millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Timelines: | |
| Decades: | |
| Categories: | Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |


| Millennium: | 1st millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Timelines: | |
| Decades: | |
| Categories: | Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |
The 3rd century was the period from 201 to 300 A.D.
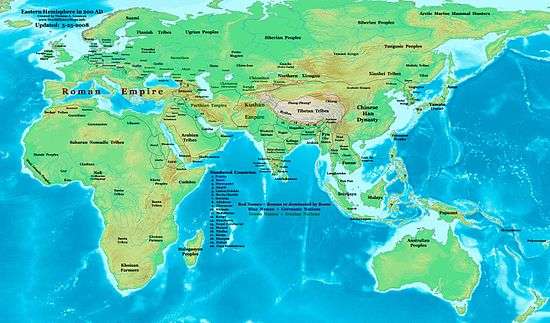
In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, marking the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire.
In India, the Kushan Empire was replaced by the Gupta Empire. China was in the Three Kingdoms period. The Xiongnu formed the Tiefu state under Liu Qubei. Korea was ruled by the Three Kingdoms of Korea. Japan entered the Kofun period.
At about this time in Sub-Saharan Africa, the Bantu expansion reached Southern Africa.
In Pre-Columbian America, the Adena culture of the Ohio River valley declined in favor of the Hopewell culture. The Maya civilization entered its Classic Era.
Roman Empire
After the death of Commodus in the previous century the Roman Empire was plunged into a civil war. When the dust settled, Septimius Severus emerged as emperor, establishing the Severan dynasty. Unlike previous emperors, he openly used the army to back his authority, and paid them well to do so. The regime he created is known as the Military Monarchy as a result. The system fell apart in the 230s, giving way to a fifty-year period known as the Military Anarchy or the Crisis of the Third Century, where no fewer than twenty emperors held the reins of power, most for only a few months. The majority of these men were assassinated, or killed in battle, and the empire almost collapsed under the weight of the political upheaval, as well as the growing Persian threat in the east. Under its new Sassanid rulers, Persia had grown into a rival superpower, and the Romans would have to make drastic reforms in order to better prepare their state for a confrontation. These reforms were finally realized late in the century under the reign of Diocletian, one of them being to divide the empire into an eastern and western half, and have a separate ruler for each.
Events

- Early 3rd century – Burial in catacombs becomes common place.
- 208: the Chinese naval Battle of Red Cliffs occurs.
- 211 – 217: Caracalla, Roman Emperor.
- 212: Constitutio Antoniniana grants citizenship to all free Roman men.
- 212 – 217: Baths of Caracalla.
- 220: The Han Dynasty comes to an end with establishment of the Three Kingdoms in ancient China.
- 220 – 280: The Three Kingdoms period.
- 222 – 235: Alexander Severus, Roman Emperor.
- 224: Ardashir I of the Sassanid dynasty conquers the Parthian empire at the Battle of Hormozdgān.
- 230 – 232: Sassanid dynasty of Persia launches a war to reconquer lost lands in the Roman east.
- 234: Zhuge Liang dies of illness at the standoff of Wuzhang Plains.
- 235 – 284: Crisis of the Third Century shakes Roman Empire.
- 244: Battle of Xingshi in China.
- 250 – 538: Kofun era, the first part of the Kofun period in Japan.
- 258: Valerian's massacre of Christians.
- 260: Roman Emperor Valerian I is taken captive by Shapur I of Persia.
- 263: Cao Wei conquers the Shu Han Kingdom.
- 265: The Jin Dynasty is founded after the overthrow of the Cao Wei Dynasty by Sima Yan.
- 280: The Jin Dynasty reunites China under one empire after the conquest of Eastern Wu.
- 284 – 305: Diocletian, Roman Emperor.
- 291 – 306: The War of the Eight Princes, a civil war by the Sima Clan in China.
- Sarnath becomes a center of Buddhist arts in India.
- Diffusion of maize as a food crop from Mexico into North America begins.
- The Kingdom of Funan reaches its zenith.
- The Goths move from Gothiscandza to Ukraine, giving birth to the Chernyakhov culture.
- Menorahs and Ark of the Covenant, wall painting in a Jewish catacomb, Villa Torlonia (Rome), are made.
- The Coptic period begins.
- Siddhartha in the Palace, detail of a relief from Nagarjunakonda, Andhra Pradesh, India, is made (approximate date). Later Andhra period. The artwork is now kept at National Museum, New Delhi.
- Jonah Swallowed and Jonah Cast Up, two statuettes of a group from the eastern Mediterranean, probably Asia Minor, are made. Now kept at The Cleveland Museum of Art.
- The Magerius Mosaic is made.
- Late 3rd century-early 4th century – Good Shepherd, Orants and Story of Jonah, painted ceiling of the Catacombs of Marcellinus and Peter in Rome, is made.
Significant people

- Ardashir I, founder of the Sasanid Empire
- Artabanus V, last ruler of the Parthian Empire
- Aurelian (Lucius Domitius Aurelianus), Roman emperor
- Clement of Alexandria, Christian head of Catechetical School of Alexandria
- Cao Cao, Chinese statesman
- Cao Pi, founding emperor of the Kingdom of Wei
- Cao Rui, emperor of Cao Wei
- Caracalla (Lucius Septimius Bassianus), Roman emperor
- Claudius Gothicus (Marcus Aurelius Valerius Claudius), Roman emperor
- Constantius Chlorus, Roman emperor
- Cornelius, bishop of Rome
- Cyprian, bishop of Carthage
- Diocletian, Roman emperor
- Elagabalus (Varius Avitus Bassianus), Roman emperor
- Gallienus (Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus), Roman emperor
- Guan Yu, Chinese general
- Julia Domna, Roman empress
- Julia Maesa, Roman noblewoman
- Liu Bei, founding emperor of the Kingdom of Shu
- Mani, founder of Manichaeism
- Marcus Aurelius Probus, Roman emperor
- Maximinus Thrax, Roman emperor
- Nagarjuna, Buddhist monk
- Odaenathus (Lucius Septimius Udaynath), king of the Palmyrene Empire
- Philip the Arab (Marcus Julius Philippus), Roman emperor
- Postumus, (Marcus Cassianius Latinius Postumus) emperor of the Gallic Empire
- Septimius Severus, Roman emperor
- Severus Alexander (Marcus Julius Gessius Bassianus Alexianus), Roman emperor
- Sima Shi, Chinese general, politician and regent
- Sima Yan, founding emperor of the Jin dynasty
- Sima Yi, Chinese general and statesman
- Sima Zhao, Chinese general and regent
- Shapur I, king of the Sasanid Empire
- Sri Gupta, founding king of the Gupta dynasty
- Sun Quan, founding emperor of the Kingdom of Wu
- Tetricus I (Gaius Pius Esuvius Tetricus), emperor of the Gallic Empire
- Trieu Thi Trinh, Vietnamese resistance leader
- Valerian (Publius Licinius Valerianus), Roman emperor
- Zenobia, queen of the Palmyrene Empire
- Zhang Fei, Chinese general
- Zhao Yun, Chinese general
- Zhuge Liang, known as the greatest strategist during the period of the Three Kingdoms.
Literature
- Cao Zhi, Chinese poet and writer
- Claudius Aelianus, Roman writer
- Diogenes Laërtius, Greek biographer
- Fu Xuan, Chinese poet and writer
- Heliodorus of Emesa, Greek writer
- Hippolytus, Roman Christian writer and theologian, first Antipope
- Liu Ling, Chinese poet
- Marius Maximus, Roman biographer
- Origen, Roman Christian writer and theologian
- Ruan Ji, Chinese poet
- Tertullian, Roman Christian writer and theologian
- Zuo Si, Chinese poet and writer
Science and Philosophy
- Aemilius Papinianus, Roman jurist
- Alexander of Aphrodisias, Greek philosopher
- Ammonius Saccas, Greek philosopher
- Cassius Dio, Roman historian
- Cassius Longinus, Greek philosopher
- Censorinus, Roman grammarian
- Chen Shou, Chinese historian
- Dexippus, Greek historian
- Diophantus of Alexandria, Greek mathematician
- Gaius Julius Solinus, Roman grammarian
- Herodian, Greek historian
- Huangfu Mi, Chinese scholar and physician
- Iamblichus, Hellenistic Syrian philosopher
- Ji Kang, Chinese philosopher
- Julius Paulus Prudentissimus, Roman jurist
- Liu Hui, Chinese mathematician
- Ma Jun, Chinese engineer and inventor
- Pappus of Alexandria, Greek mathematician
- Pei Xiu, Chinese cartographer and geographer
- Plotinus, Roman philosopher
- Porphyry, Hellenistic philosopher
- Ruan Xian, Chinese philosopher
- Sextus Julius Africanus, Roman historian
- Shan Tao, Chinese philosopher
- Wang Bi, Chinese philosopher
- Wang Rong, Chinese scholar
- Xiang Xiu, Chinese scholar
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
- The south-pointing chariot invented by Ma Jun, a wheeled mechanical device that acts as a directional compass
- An early type of hot air balloon used for military signalling, known as the Kongming lantern was said to be invented by Zhuge Liang.
- The repeating crossbow or semi-automatic crossbow is an improved version of a model that first appeared during the Warring States Period (though there is debate whether the original Warring States Period bow was semi-automatic, or rather shot multiple bolts at once). Nevertheless, Zhuge's version could shoot farther and faster.
- Some sources report that Zhuge Liang invented a primitive land mine type device.
- A mysterious but efficient automatic transportation device (initially used for grain) referred to as the "wooden ox and flowing horse" (木牛流馬) also invented by Zhuge, which is sometimes identified with the wheelbarrow.


_-_Foto_G._Dall'Orto_28-5-2006_(cropped_enhanced).jpg)
