1952 Summer Olympics
 | |||
| Host city | Helsinki, Finland | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nations participating | 69 | ||
| Athletes participating |
4,955 (4,436 men, 519 women) | ||
| Events | 149 in 17 sports | ||
| Opening ceremony | July 19 | ||
| Closing ceremony | August 3 | ||
| Officially opened by | President Juho Kusti Paasikivi | ||
| Athlete's Oath | Heikki Savolainen | ||
| Olympic Torch |
Paavo Nurmi and Hannes Kolehmainen | ||
| Stadium | Olympic Stadium | ||
| Summer: | |||
| |||
| Winter: | |||
| |||
The 1952 Summer Olympics (Finnish: Kesäolympialaiset 1952; Swedish: Olympiska sommarspelen 1952), officially known as the Games of the XV Olympiad, were an international multi-sport event held in Helsinki, Finland, in 1952. Helsinki had been earlier selected to host the 1940 Summer Olympics, which were cancelled due to World War II. It is the northernmost city at which a summer Olympic Games have been held. These were the first games to be held in a non-Indo-European language speaking country. It was also the Olympic Games at which the most number of world records were broken until surpassed by the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing.[1] The Soviet Union, the People's Republic of China, Indonesia, Israel, Thailand, and Saarland made their Olympic debuts in Helsinki 1952.
Host city selection
Helsinki was chosen as the host city over bids from Amsterdam and five American cities at the 40th IOC Session on June 21, 1947, in Stockholm, Sweden. Minneapolis and Los Angeles finished tied for second in the final voting.
The voting results in chart below:[2]
| 1952 Summer Olympics bidding results[3] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | Country | Round 1 | Round 2 | |||
| Helsinki | |
14 | 15 | |||
| Minneapolis | |
4 | 5 | |||
| Los Angeles | |
4 | 5 | |||
| Amsterdam | |
3 | 3 | |||
| Detroit | |
2 | — | |||
| Chicago | |
1 | — | |||
| Philadelphia | |
0 | — | |||
Highlights

- These were the final Olympic Games organised under the IOC presidency of Sigfrid Edström.
- For the first time, a team from the Soviet Union participated in the Olympics. The first gold medal for the USSR was won by Nina Romashkova in the women's discus throwing event. The Soviet women's gymnastics team won the first of its eight consecutive gold medals.
- Israel made its Olympic debut. The Jewish state had been unable to participate in the 1948 Games because of its War of Independence. A previous Palestine Mandate team had boycotted the 1936 Games in protest of the Nazi regime.
- Indonesia made its Olympic debut with three athletes.
- The newly established People's Republic of China (PRC) participated in the Olympics for the first time, although only one swimmer (Wu Chuanyu) of its 40-member delegation arrived in time to take part in the official competition.[4] The PRC would not return to the Summer Olympics until Los Angeles 1984.
- The Republic of China (Taiwan) withdrew from the Games on July 20, in protest of the IOC decision to allow athletes from the People's Republic of China to compete.[5]
- The Olympic Flame was lit by two Finnish heroes, runners Paavo Nurmi and Hannes Kolehmainen. Nurmi first lit the cauldron inside the stadium, and later the flame was relayed to the stadium tower where Kolehmainen lit it. Only the flame in the tower was burning throughout the Olympics.
- Hungary, a country of 9 million inhabitants, won 42 medals at these games, coming in third place behind the much more populous United States and Soviet Union.
- Hungary's Golden Team won the football tournament, beating Yugoslavia 2–0 in the final.
- Germany and Japan were invited after being barred in 1948. Following the post-war occupation and partition, three German states had been established. Teams from the Federal Republic of Germany and the Saarland (which joined the FRG after 1955) participated; the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) was absent. Though they won 24 medals, the fifth-highest total at the Games, German competitors failed to win a gold medal for the only time.
- Rules in equestrianism now allowed non-military officers to compete, including women. Lis Hartel of Denmark became the first woman in the sport to win a medal.
- Emil Zátopek of Czechoslovakia won three gold medals in the 5000 m, 10,000 m and the Marathon (which he had never run before).
- The India national field hockey team won its fifth consecutive gold.
- Bob Mathias of the United States became the first Olympian to successfully defend his decathlon title with a total score of 7,887 points.
- Josy Barthel of Luxembourg pulled a major surprise by winning the 1500 m.
Sports
The 1952 Summer Olympic programme featured 149 events in the following 17 sports:
|
|
Demonstration sports
Venues
With an annual average temperature of 5.9 °C, Helsinki is the coldest city to host the Summer Olympics.
- Hämeenlinna – Modern pentathlon
- Harmaja – Sailing
- Helsinki Football Grounds – Football
- Huopalahti – Shooting (shotgun)
- Käpylä – Cycling (road)
- Kotka – Football
- Laakso – Equestrian (eventing – riding)
- Lahti – Football
- Liuskasaari – Sailing
- Malmi Rifle Range – Shooting (pistol/ rifle)
- Maunula – Cycling (road)
- Meilahti – Rowing
- Messuhalli – Basketball (final), boxing, gymnastics, weightlifting, wrestling
- Olympic Stadium – Athletics, Equestrian (jumping), Football (final)
- Pakila – Cycling (road)
- Ruskeasuo Equestrian Hall – Equestrian (dressage, eventing)
- Swimming Stadium – Diving, Swimming, Water polo
- Taivallahti – Canoeing
- Tali Race Track – Equestrian (eventing steeplechase)
- Tampere – Football
- Tennis Palace – Basketball
- Turku – Football
- Velodrome – Cycling (track), Field hockey
- Westend Tennis Hall – Fencing
Participating NOCs
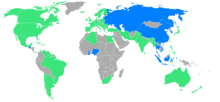

A total of 69 nations participated in these Games, up from 59 in the 1948 Games. Thirteen nations made their first Olympic appearance in 1952: The Bahamas, the People's Republic of China, Gold Coast (now Ghana), Guatemala, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Israel, Netherlands Antilles, Nigeria, Soviet Union (USSR), Thailand, and Vietnam.
Japan and Germany were both reinstated and permitted to send athletes after being banned for 1948 for their instigation of World War II. Due to the division of Germany, German athletes from Saar entered a separate team for the only time. Only West Germany would provide athletes for the actual Germany team, since East Germany refused to participate in a joint German team.
-
 Argentina (123)
Argentina (123) -
 Australia (87)
Australia (87) -
 Austria (112)
Austria (112) -
.svg.png) Bahamas (7)
Bahamas (7) -
.svg.png) Belgium (135)
Belgium (135) -
 Bermuda (6)
Bermuda (6) -
.svg.png) Brazil (97)
Brazil (97) -
.svg.png) Guyana (1)
Guyana (1) -
.svg.png) Bulgaria (63)
Bulgaria (63) -
.svg.png) Burma (5)
Burma (5) -
 Canada (107)
Canada (107) -
.svg.png) Ceylon (5)
Ceylon (5) -
 Chile (59)
Chile (59) -
 People's Republic of China (1)
People's Republic of China (1) -
 Cuba (29)
Cuba (29) -
 Czechoslovakia (99)
Czechoslovakia (99) -
 Denmark (129)
Denmark (129) -
.svg.png) Egypt (106)
Egypt (106) -
 Finland (258) (Host nation)
Finland (258) (Host nation) -
 France (245)
France (245) -
 Germany (205)
Germany (205) -
 Gold Coast (7)
Gold Coast (7) -
 Great Britain (257)
Great Britain (257) -
.svg.png) Greece (53)
Greece (53) -
 Guatemala (21)
Guatemala (21) -
.png) Hong Kong (4)
Hong Kong (4) -
.svg.png) Hungary (189)
Hungary (189) -
 Iceland (9)
Iceland (9) -
 India (69)
India (69) -
 Indonesia (3)
Indonesia (3) -
.svg.png) Iran (22)
Iran (22) -
 Ireland (19)
Ireland (19) -
 Israel (26)
Israel (26) -
 Italy (231)
Italy (231) -
.svg.png) Jamaica (8)
Jamaica (8) -
.svg.png) Japan (69)
Japan (69) -
 Lebanon (9)
Lebanon (9) -
 Liechtenstein (2)
Liechtenstein (2) -
 Luxembourg (44)
Luxembourg (44) -
.svg.png) Mexico (64)
Mexico (64) -
 Monaco (8)
Monaco (8) -
 Netherlands (104)
Netherlands (104) -
.svg.png) Netherlands Antilles (11)
Netherlands Antilles (11) -
 New Zealand (15)
New Zealand (15) -
 Nigeria (9)
Nigeria (9) -
 Norway (102)
Norway (102) -
 Pakistan (38)
Pakistan (38) -
 Panama (1)
Panama (1) -
.svg.png) Philippines (25)
Philippines (25) -
.svg.png) Poland (125)
Poland (125) -
 Portugal (71)
Portugal (71) -
 Puerto Rico (21)
Puerto Rico (21) -
.svg.png) Romania (114)
Romania (114) -
.svg.png) Saar (36)
Saar (36) -
.svg.png) Singapore (5)
Singapore (5) -
.svg.png) South Africa (64)
South Africa (64) -
.svg.png) South Korea (19)
South Korea (19) -
.svg.png) Soviet Union (295)
Soviet Union (295) -
.svg.png) Spain (30)
Spain (30) -
 Sweden (206)
Sweden (206) -
 Switzerland (157)
Switzerland (157) -
 Thailand (8)
Thailand (8) -
 Trinidad and Tobago (2)
Trinidad and Tobago (2) -
 Turkey (51)
Turkey (51) -
.svg.png) United States (286)
United States (286) -
 Uruguay (32)
Uruguay (32) -
.svg.png) Venezuela (38)
Venezuela (38) -
 Vietnam (8)
Vietnam (8) -
 Yugoslavia (96)
Yugoslavia (96)
Medal count
These are the top ten nations that won medals at the 1952 Games.[7]
| Rank | Nation | Gold | Silver | Bronze | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | | 40 | 19 | 17 | 76 |
| 2 | | 22 | 30 | 19 | 71 |
| 3 | | 16 | 10 | 16 | 42 |
| 4 | | 12 | 13 | 10 | 35 |
| 5 | | 8 | 9 | 4 | 21 |
| 6 | | 7 | 3 | 3 | 13 |
| 7 | | 6 | 6 | 6 | 18 |
| 8 | | 6 | 3 | 13 | 22 |
| 9 | | 6 | 2 | 3 | 11 |
| 10 | | 3 | 2 | 0 | 5 |
50th anniversary coin
The 50th anniversary of the Helsinki Olympic Games was the main motif for one of the first Finnish euro silver commemorative coins, the €10 silver coin minted in 2002. The reverse depicts part of the Helsinki Olympic Stadium, as well as a section of the 1952 500 markka coin. The obverse has lettering SUOMI FINLAND 10 EURO, a flame, and Finland is the only country highlighted on earth.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Bascomb, Neal (2005). The Perfect Mile: Three Athletes, One Goal, and Less Than Four Minutes to Achieve It. Mariner Books. ISBN 9780618562091.
- ↑ "International Olympic Committee Vote History". 9 September 2013. Retrieved 24 February 2015.
- ↑ "Past Olympic Host City Election Results". Games Bids. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ↑ Mulvenney, Nick (7 August 2008). "Chen Chengda, China's almost Olympian". Reuters. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ↑ "On This Day: 1952: 20 July: Zatopek wins gold at Helsinki". BBC News. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ↑ http://www.marketplace.org/2014/02/06/economy/numbers/9-weirdest-cities-have-hosted-olympics-and-why
- ↑ Byron, Lee; Cox, Amanda; Ericson, Matthew (4 August 2008). "A Map of Olympic Medals". The New York Times. Retrieved 24 February 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1952 Summer Olympics. |
- "Helsinki 1952". Olympic.org. International Olympic Committee.
- "Results and Medalists". Olympic.org. International Olympic Committee.
- Helsinki 1952 Official Olympic Report la84foundation.org
- Helsinki 1952 Official Olympic Report olympic-museum.de
| Preceded by London |
Summer Olympic Games Helsinki XV Olympiad (1952) |
Succeeded by Melbourne/Stockholm |