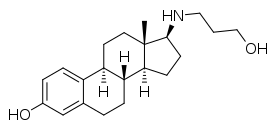
17β-Aminoestrogen
17β-Aminoestrogens are a group of synthetic, steroidal estrogens derived from estradiol which have an amine substitution in place of the hydroxyl group at the C17β position.[1][2] They are estrogenic similarly,[1] but, unlike estradiol, show sustained anticoagulant activity that appears to be mediated by non-genomic mechanisms.[2] As such, it is thought that they may have a reduced risk of venous thromboembolism.[2] The 17β-aminoestrogens include the base or parent estrogen aminoestradiol (AE2)[3] and the extended-chain derivatives butolame, hexolame, pentolame, prodiame, and prolame.[1][2] They are a homologous series of steroids.[4]
References
- 1 2 3 Lemini C, Rubio-Póo C, Silva G, García-Mondragón J, Zavala E, Mendoza-Patiño N, Castro D, Cruz-Almanza R, Mandoki JJ (1993). "Anticoagulant and estrogenic effects of two new 17 beta-aminoestrogens, butolame [17 beta-(4-hydroxy-1-butylamino)-1,3,5(10)-estratrien-3-ol] and pentolame [17 beta-(5-hydroxy-1-pentylamino)-1,3,5(10)-estratrien-3-ol]". Steroids. 58 (10): 457–61. PMID 8256254. doi:10.1016/0039-128x(93)90002-5.
- 1 2 3 4 González G, Alvarado-Vasquez N, Fernández-G JM, Cruz-Robles D, Del Valle L, Pinzón E, Torres I, Rodriguez E, Zapata E, Gómez-Vidales V, Montaño LF, de la Peña A (2010). "The antithrombotic effect of the aminoestrogen prolame (N-(3-hydroxy-1,3,5(10)-estratrien-17B-YL)-3-hydroxypropylamine) is linked to an increase in nitric oxide production by platelets and endothelial cells". Atherosclerosis. 208 (1): 62–8. PMID 19615684. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.06.017.
- ↑ Lemini C, Rubio-Póo C, Franco Y, Jaimez R, Avila ME, Medina M, Lemus AE (2013). "In vivo profile of the anticoagulant effect of 17ß-amino-1,3,5(10)estratrien-3-ol". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 700 (1-3): 210–6. PMID 23305838. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.12.030.
- ↑ Rubio-Póo C, Lemini C, Silva G, García-Mondragón J, Zavala E, Castro D, Mendoza-Patiño N, Mandoki JJ (1993). "Comparison of the time course of anticoagulant and estrogenic effects of prolame, butolame, pentolame and hexolame, a homologous series of 17 beta-amino estrogens". Proc. West. Pharmacol. Soc. 36: 143–7. PMID 8378368.
|
|---|
| ER | | Agonists |
- Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol
- 2-Hydroxyestrone
- 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol
- 3α-Androstanediol
- 3β-Androstanediol
- 4-Androstenediol
- 4-Androstenedione
- 4-Hydroxyestradiol
- 4-Hydroxyestrone
- 4-Methoxyestradiol
- 4-Methoxyestrone
- 5-Androstenediol
- 7-Oxo-DHEA
- 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone
- 8,9-Dehydroestradiol
- 8,9-Dehydroestrone
- 8β-VE2
- 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED)
- 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 16α-Hydroxyestrone
- 16α-Iodo-E2
- 16α-LE2
- 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17α-Dihydroequilenin
- 17α-Dihydroequilin
- 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17β-Dihydroequilenin
- 17β-Dihydroequilin
- Abiraterone
- Abiraterone acetate
- 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol)
- Alestramustine
- Almestrone
- Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters, methyltestosterone, metandienone (methandrostenolone), nandrolone and esters, many others; via estrogenic metabolites)
- Atrimustine
- Bolandiol
- Bolandiol dipropionate
- Butolame
- Clomestrone
- Cloxestradiol
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- Epiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol)
- Epimestrol
- Equilenin
- Equilin
- ERA-63 (ORG-37663)
- Estetrol
- Estradiol
- Estramustine
- Estramustine phosphate
- Estrapronicate
- Estrazinol
- Estriol
- Estrofurate
- Estromustine
- Estrone
- Etamestrol (eptamestrol)
- Ethinylestradiol
- Ethinylestriol
- Etynodiol diacetate
- Hexolame
- Hippulin
- Hydroxyestrone diacetate
- Mestranol
- Methylestradiol
- Moxestrol
- Mytatrienediol
- Nilestriol
- Noretynodrel
- Orestrate
- Pentolame
- Prodiame
- Prolame
- Promestriene
- Quinestradol
- Quinestrol
- Xenoestrogens: Anise-related (e.g., anethole, anol, dianethole, dianol, photoanethole)
- Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin, phloretin, phlorizin (phloridzin), wedelolactone)
- Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol, psoralidin)
- Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF, 8-prenylnaringenin, apigenin, baicalein, baicalin, biochanin A, calycosin, catechin, daidzein, daidzin, ECG, EGCG, epicatechin, equol, formononetin, glabrene, glabridin, genistein, genistin, glycitein, kaempferol, liquiritigenin, mirificin, myricetin, naringenin, penduletin, pinocembrin, prunetin, puerarin, quercetin, tectoridin, tectorigenin)
- Lavender oil
- Lignans (e.g., enterodiol, enterolactone, nyasol (cis-hinokiresinol))
- Metalloestrogens (e.g., cadmium)
- Pesticides (e.g., alternariol, dieldrin, endosulfan, fenarimol, methiocarb, methoxychlor, triclocarban, triclosan)
- Phytosteroids (e.g., digitoxin (digitalis), diosgenin, guggulsterone)
- Phytosterols (e.g., β-sitosterol, campesterol, stigmasterol)
- Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalanone, α-zearalenol, β-zearalenol, zearalenone, zeranol (α-zearalanol), taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol))
- Steroid-like (e.g., deoxymiroestrol, miroestrol)
- Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol)
- Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g., alkylphenols, bisphenols (e.g., BPA, BPF, BPS), DDT, parabens, PBBs, PHBA, phthalates, PCBs)
- Others (e.g., agnuside, rotundifuran)
|
|---|
| Mixed (SERMs) | |
|---|
| Antagonists | |
|---|
|
|---|
| GPER | |
|---|
|