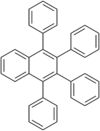
1,2,3,4-Tetraphenylnaphthalene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2,3,4-Tetra(phenyl)naphthalene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.151.838 | ||
| PubChem CID |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C34H24 | |||
| Molar mass | 432.55 g/mol | ||
| Melting point | 199 to 201 °C (390 to 394 °F; 472 to 474 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R36/37/38 | ||
| S-phrases (outdated) | S26 S36 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
1,2,3,4-Tetraphenylnaphthalene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon commonly prepared in the undergraduate teaching laboratory as an introduction to the Diels-Alder reaction, in this case between benzyne, which acts as the dienophile, (generated in situ) and tetraphenylcyclopentadienone, which acts as the diene.[2] It has two crystalline forms, and therefore has two different melting points.
References
- ↑ 1,2,3,4-Tetraphenylnaphthalene at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 5, p.1037 (1973); Vol. 46, p.107 (1966). Link
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.