58534 Logos
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Mauna Kea Obs. |
| Discovery date | 4 February 1997 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | (58534) Logos |
| Pronunciation | /ˈloʊɡɒs/ LOH-goss or /ˈlɒɡɒs/ LOG-oss |
Named after | Logos |
| 1997 CQ29 | |
| Cubewano[1] | |
| Adjectives | Logian |
| Orbital characteristics[2] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 3 | |
| Observation arc | 5582 days (15.28 yr) |
| Aphelion | 51.153 AU (7.6524 Tm) |
| Perihelion | 39.945 AU (5.9757 Tm) |
| 45.549 AU (6.8140 Tm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.12304 |
| 307.42 yr (112284 d) | |
Average orbital speed | 4.41 km/s |
| 56.495° | |
| 0° 0m 11.542s / day | |
| Inclination | 2.8946° |
| 132.491° | |
| 339.21° | |
| Known satellites |
Zoe[3] (~66 km in diameter) |
| Earth MOID | 38.9613 AU (5.82853 Tm) |
| Jupiter MOID | 34.709 AU (5.1924 Tm) |
| Jupiter Tisserand parameter | 5.979 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 77 ± 18 km[4] |
| Mass | 2.7×1017 kg |
Mean density | 1.0 g/cm³ |
Equatorial surface gravity | 0.0112 m/s² |
Equatorial escape velocity | 0.0299 km/s |
| 0.39 ± 0.17[4] | |
| 6.6 | |
|
| |
58534 Logos (/ˈloʊɡɒs/ LOH-goss or /ˈlɒɡɒs/ LOG-oss; or as in Greek: λόγος) is a small Kuiper-belt object, more specifically a cubewano, notable for having a comparatively large satellite named Zoe. For a small KBO, about 80 km in diameter, it has a very high albedo.[4] The system mass is 4.58 ± 0.07×1017 kg.[5]
In the Gnostic tradition, Logos and Zoe are a paired emanation of the deity, and part of its creation myth.[6]
Zoe

Logos is a binary with the components of comparable size orbiting the barycentre on a moderately elliptical orbit.
Logos' companion was discovered on 17 November 2001 from Hubble Space Telescope observations by K. S. Noll, D. C. Stephens, W. M. Grundy, J. Spencer, R. L. Millis, M. W. Buie, D. Cruikshank, S. C. Tegler, and W. Romanishin and announced on 11 February 2002.
After the discovery, it received the provisional designation S/2001 (58534) 1. Once confirmed it was officially named (58534) Logos I Zoe (/ˈzoʊ.iː/; from Greek: Ζωή). It orbits Logos with a semi-major axis of 8217 ± 42 km in 309.9 ± 0.2 d with an eccentricity of 0.546 ± 0.008.[5] Its estimated diameter is 66 km,[3] and mass (0.15 ± 0.02)×1018 kg.
Orbit
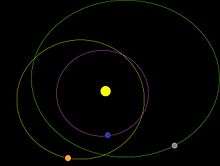
References
- ↑ Marc W. Buie (2003-05-31). "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 58534". SwRI (Space Science Department). Retrieved 2008-09-28.
- ↑ "58534 Logos (1997 CQ29)". JPL Small-Body Database. NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 12 April 2016.
- 1 2 Wm. Robert Johnston (2007-03-04). "(58534) Logos and Zoe". Johnston's Archive. Retrieved 2009-10-06.
- 1 2 3 Grundy, W. M; Noll, K. S.; Stephens, D. C. (2005). "Diverse albedos of small trans-neptunian objects". Icarus. 176 (1): 184–191. Bibcode:2005Icar..176..184G. arXiv:astro-ph/0502229
 . doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2005.01.007.
. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2005.01.007. - 1 2 Grundy, W. M.; Noll, K. S.; Nimmo, F.; Roe, H. G.; Buie, M. W.; Porter, S. B.; Benecchi, S. D.; Stephens, D. C.; Levison, H. F.; Stansberry, J. A. (2011). "Five new and three improved mutual orbits of transneptunian binaries" (pdf). Icarus. 213 (2): 678. Bibcode:2011Icar..213..678G. arXiv:1103.2751
 . doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2011.03.012.
. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2011.03.012. - ↑ JPL