Flag of Tonga
Tonga|
|
 |
| Use |
Civil and state flag, civil and state ensign |
|---|
| Proportion |
1:2 |
|---|
| Adopted |
4 November 1875 |
|---|
| Design |
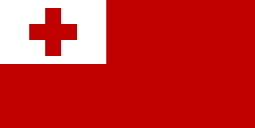
A red field with the white rectangle on the upper hoist-side corner bearing the red Greek Cross in the center. |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|

Variant flag of Tonga |
| Name |
Naval Ensign of Tonga |
|---|
| Use |
Naval ensign |
|---|
| Proportion |
1:2 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|

Variant flag of Tonga |
| Name |
Royal Standard of Tonga |
|---|
| Use |
Other |
|---|
| Proportion |
26:37 |
|---|
|
|
The flag of Tonga consists of a red field with a white canton charged with a red couped cross. Adopted in 1875 after being officially enshrined into the nation's constitution, it has been the flag of the Kingdom of Tonga since that year. The constitution stipulates that the national flag can never be changed.
History
The British first arrived in Tonga in the late-18th century, when Captain James Cook made three visits to the islands between 1773 and 1777.[1] Approximately fifty years later, English Wesleyan Methodist missionaries came to Tonga and began converting the islanders to Christianity.[2] In 1831, they succeeded in converting "paramount chief" Taufa'ahau Tupou,[1] who became King George Tupou I in 1845.[2] It was during this time (circa 1840s) that the first Tongan flag was adopted. It consisted of a white field with a cross (either red or blue in colour) at all four corners, and the letters "A" (in red) and "M" (in blue) at the centre that symbolise the king.[3]
Upon his accession to the throne, the king sought to design a new flag for the nation,[3] one that would represent Christianity.[4] He befriended Shirley Waldemar Baker – a member of the United Kingdom's Tongan mission who later became the Prime Minister of Tonga – and they worked together to formulate a new flag, coat of arms and national anthem for Tonga.[2] The new design resembled the British Red Ensign, in that three-quarters of it consisted of a simple red field, with a "distinctive canton" featured in the upper hoist section; this was first used in 1866.[3] A new constitution for the kingdom was formulated and proclaimed on 4 November 1875.[2] It "codified" the new flag design,[3] and marks when it was adopted as the national flag.[4] Under Article 47 of the Constitution, this flag can "never be altered" and "shall always be the flag" of Tonga.[5]
Design
Symbolism
The colours and symbols of the flag carry cultural, political, and regional meanings. The red couped cross alludes to Christianity,[3] the religion practised by approximately 97% of the country's population.[6] The white epitomises purity,[4][6] while the red evokes the sacrifice of the Blood of Christ, which he shed during his Crucifixion.[3][4][6]
Similarities
The previous design of the flag featured a plain white field charged with the red couped cross. However, it was later discovered that this flag was almost identical to the emblem of the International Red Cross, which had been adopted in 1863. As a result of this finding, the Tongan flag was set at the canton of a red field instead, leading to the present design of the flag.[4] The previous design, nonetheless, remains a national symbol of Tonga.[6] The current flag of Tonga also has some similarities with the flags of Switzerland and Georgia.
Gallery
|
 |
| Customs Service Ensign |
|
 |
| Quarantine Ensign |
|
 |
| Pilot flag |
|
Historical flags
|
.svg.png) |
| Tonga (1862–1866) |
|
.svg.png) |
| Royal Standard of Tonga (1862–1875) |
|
|
References
- 1 2 "Tonga profile". BBC News. BBC. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 Fletcher, Matt; Keller, Nancy (2001). Tonga. Lonely Planet. pp. 14–15. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Smith, Whitney (24 November 2013). "Flag of Tonga". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 9 August 2014. (subscription required)
- 1 2 3 4 5 Kindersley Ltd., Dorling (6 January 2009). Complete Flags of the World. Penguin. p. 235. Retrieved 9 August 2014.
- ↑ Peaslee, Amos J. (1985). "Tonga". Constitutions of Nations. Springer Netherlands: 1577. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-1147-0_13. Retrieved 11 August 2014. (registration required)
- 1 2 3 4 "Tonga". The World Factbook. CIA. Retrieved 9 August 2014.
External links
|
|---|
| Sovereign states | |
|---|
Associated states
of New Zealand | |
|---|
Dependencies
and other territories | |
|---|
|
|---|
| National flags | |
|---|
| National coats of arms | |
|---|







.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)