1-Testosterone
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEBI | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.058 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 288.42 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
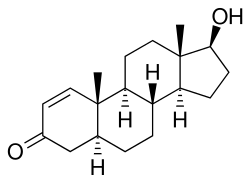
1-Testosterone (abbreviated and nicknamed as 1-Testo, 1-T), also known as δ1-dihydrotestosterone (δ1-DHT), as well as dihydroboldenone, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) which was never marketed. It differs from testosterone by having a 1(2)-double bond instead of a 4(5)-double bond in its A ring.[1] It was legally sold online in the United States until 2005, when it was reclassified as a Schedule III drug.
Side effects
Pharmacology
A 2006 study determined that 1-testosterone has a high androgenic and anabolic potency even without being metabolized, so it can be characterized as a typical anabolic steroid. 1-Testosterone binds in a manner that is highly selective to the androgen receptor (AR) and has a high potency to stimulate AR-dependent transactivation. In vivo, an equimolar dose of 1-testosterone has the same potency to stimulate the growth of the prostate, the seminal vesicles and the androgen-sensitive levator ani muscle as the reference anabolic steroid testosterone propionate, but, unlike testosterone propionate, 1-testosterone also increases liver weight.[2]
Chemistry
1-Testosterone, also known as 4,5α-dihydro-δ1-testosterone (Δ1-DHT) or as 5α-androst-1-en-17β-ol-3-one, is a synthetic androstane steroid and a derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Derivatives
Two prohormones of 1-testosterone are 1-androstenediol and 1-androstenedione, the latter of which may be synthesized from stanolone acetate.[3]
Mesabolone is a ketal made from 1-testosterone.
1-Testosterone also is known to be used to synthesize mestanolone and metenolone.
Methyl-1-testosterone is the 17α-methyl derivative of 1-testosterone.
Detection in body fluids
Doping with 1-testosterone can be detected in urine samples using gas chromatography.[4]
References
- ↑ William Llewellyn (2009). Anabolics (9 ed.). Molecular Nutrition. p. 22,135. ISBN 978-0-9679304-7-3.
- ↑ Friedel A, Geyer H, Kamber M, Laudenbach-Leschowsky U, Schänzer W, Thevis M, Vollmer G, Zierau O, Diel P (August 2006). "17beta-hydroxy-5alpha-androst-1-en-3-one (1-testosterone) is a potent androgen with anabolic properties". Toxicol. Lett. 165 (2): 149–55. PMID 16621347. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2006.03.001.
- ↑ Zhang H, Qiu Z (December 2006). "An efficient synthesis of 5α-androst-1-ene-3,17-dione". Steroids. 71 (13-14): 1088–90. PMID 17123559. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2006.09.008.
- ↑ S. Jain, A. Beotra and T. Kaur (2005). "A Case Study: Detection of 1-Testosterone in Urine by GC-MSD" (PDF). Recent Advances in Doping Analysis. 13: 407–410.