4-Pyrone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Pyran-4-one | |
| Other names
γ-Pyrone 4-Pyranone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.305 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 96.08 |
| Melting point | 32 to 34 °C (90 to 93 °F; 305 to 307 K) |
| Boiling point | 210 to 215 °C (410 to 419 °F; 483 to 488 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 101 °C (214 °F; 374 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
4-Pyrone (γ-pyrone or pyran-4-one) is an unsaturated cyclic chemical compound with the molecular formula C5H4O2. It is isomeric with 2-pyrone.
Preparation
4-Pyrone is prepared via the thermal decarboxylation of chelidonic acid.[2]
Reactions
4-Pyrone, and its derivatives, react with amines in protic solvents to form 4-Pyridones.[2][3][4]
Derivatives
4-Pyrone forms the central core of several natural chemical compounds including maltol and kojic acid and of the important class of the Flavones.

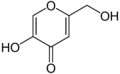
Maltol Kojic acid
See also
References
- ↑ 4H-Pyran-4-one at Sigma-Aldrich
- 1 2 Weygand, Conrad (1972). Hilgetag, G.; Martini, A., eds. Weygand/Hilgetag Preparative Organic Chemistry (4th ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 533–534, & 1009. ISBN 0471937495.
- ↑ Van Allan, J. A.; Reynolds, G. A.; Alessi, J. T.; Chie Chang, S.; C. Joines, R. (1971). "Reactions of 4‐pyrones with primary amines. A new class of ionic associates". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry. 8 (6): 919–922. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570080606.
- ↑ Cook, Denys (1963). "The Preparation, Properties, and Structure of 2,6-bis-(Alkyamino)-2,5-heptadien-4-ones". Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 41 (6): 1435–1440. doi:10.1139/v63-195.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.