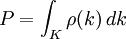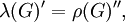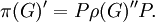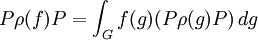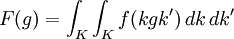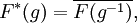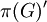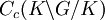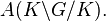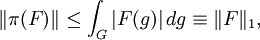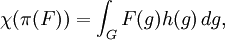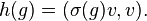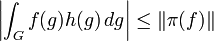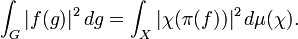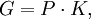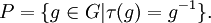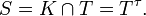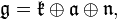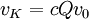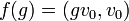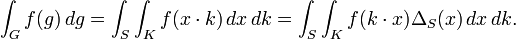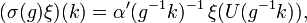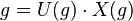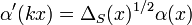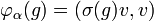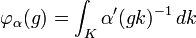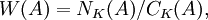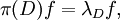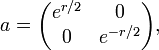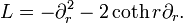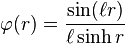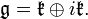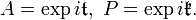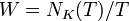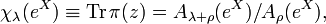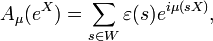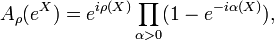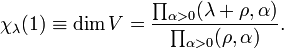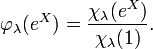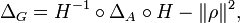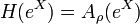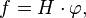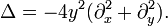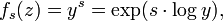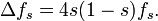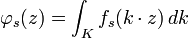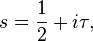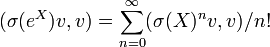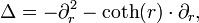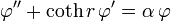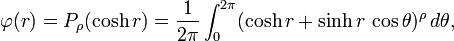Zonal spherical function
In mathematics, a zonal spherical function or often just spherical function is a function on a locally compact group G with compact subgroup K (often a maximal compact subgroup) that arises as the matrix coefficient of a K-invariant vector in an irreducible representation of G. The key examples are the matrix coefficients of the spherical principal series, the irreducible representations appearing in the decomposition of the unitary representation of G on L2(G/K). In this case the commutant of G is generated by the algebra of biinvariant functions on G with respect to K acting by right convolution. It is commutative if in addition G/K is a symmetric space, for example when G is a connected semisimple Lie group with finite centre and K is a maximal compact subgroup. The matrix coefficients of the spherical principal series describe precisely the spectrum of the corresponding C* algebra generated by the biinvariant functions of compact support, often called a Hecke algebra. The spectrum of the commutative Banach *-algebra of biinvariant L1 functions is larger; when G is a semisimple Lie group with maximal compact subgroup K, additional characters come from matrix coefficients of the complementary series, obtained by analytic continuation of the spherical principal series.
Zonal spherical functions have been explicitly determined for real semisimple groups by Harish-Chandra. For special linear groups, they were independently discovered by Israel Gelfand and Mark Naimark. For complex groups, the theory simplifies significantly, because G is the complexification of K, and the formulas are related to analytic continuations of the Weyl character formula on K. The abstract functional analytic theory of zonal spherical functions was first developed by Roger Godement. Apart from their group theoretic interpretation, the zonal spherical functions for a semisimple Lie group G also provide a set of simultaneous eigenfunctions for the natural action of the centre of the universal enveloping algebra of G on L2(G/K), as differential operators on the symmetric space G/K. For semisimple p-adic Lie groups, the theory of zonal spherical functions and Hecke algebras was first developed by Satake and Ian G. Macdonald. The analogues of the Plancherel theorem and Fourier inversion formula in this setting generalise the eigenfunction expansions of Mehler, Weyl and Fock for singular ordinary differential equations: they were obtained in full generality in the 1960s in terms of Harish-Chandra's c-function.
The name "zonal spherical function" comes from the case when G is SO(3,R) acting on a 2-sphere and K is the subgroup fixing a point: in this case the zonal spherical functions can be regarded as certain functions on the sphere invariant under rotation about a fixed axis.
Definitions
Let G be a locally compact unimodular topological group and K a compact subgroup and let H1 = L2(G/K). Thus H1 admits a unitary representation π of G by left translation. This is a subrepresentation of the regular representation, since if H= L2(G) with left and right regular representations λ and ρ of G and P is the orthogonal projection
from H to H1 then H1 can naturally be identified with PH with the action of G given by the restriction of λ.
On the other hand by von Neumann's commutation theorem[1]
where S' denotes the commutant of a set of operators S, so that
Thus the commutant of π is generated as a von Neumann algebra by operators
where f is a continuous function of compact support on G.[2]
However Pρ(f) P is just the restriction of ρ(F) to H1, where
is the K-biinvariant continuous function of compact support obtained by averaging f by K on both sides.
Thus the commutant of π is generated by the restriction of the operators ρ(F) with F in Cc(K\G/K), the K-biinvariant continuous functions of compact support on G.
These functions form a * algebra under convolution with involution
often called the Hecke algebra for the pair (G, K).
Let A(K\G/K) denote the C* algebra generated by the operators ρ(F) on H1.
The pair (G, K) is said to be a Gelfand pair [3] if one, and hence all, of the following algebras are commutative:
Since A(K\G/K) is a commutative C* algebra, by the Gelfand–Naimark theorem it has the form C0(X), where X is the locally compact space of norm continuous * homomorphisms of A(K\G/K) into C.
A concrete realization of the * homomorphisms in X as K-biinvariant uniformly bounded functions on G is obtained as follows.[3][4][5][6][7]
Because of the estimate
the representation π of Cc(K\G/K) in A(K\G/K) extends by continuity to L1(K\G/K), the * algebra of K-biinvariant integrable functions. The image forms a dense * subalgebra of A(K\G/K). The restriction of a * homomorphism χ continuous for the operator norm is also continuous for the norm ||·||1. Since the Banach space dual of L1 is L∞, it follows that
for some unique uniformly bounded K-biinvariant function h on G. These functions h are exactly the zonal spherical functions for the pair (G, K).
Properties
A zonal spherical function h has the following properties:[3]
- h is uniformly continuous on G
-
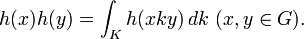
- h(1) =1 (normalisation)
- h is a positive definite function on G
- f * h is proportional to h for all f in Cc(K\G/K).
These are easy consequences of the fact that the bounded linear functional χ defined by h is a homomorphism. Properties 2, 3 and 4 or properties 3, 4 and 5 characterize zonal spherical functions. A more general class of zonal spherical functions can be obtained by dropping positive definiteness from the conditions, but for these functions there is no longer any connection with unitary representations. For semisimple Lie groups, there is a further characterization as eigenfunctions of invariant differential operators on G/K (see below).
In fact, as a special case of the Gelfand–Naimark–Segal construction, there is one-one correspondence between irreducible representations σ of G having a unit vector v fixed by K and zonal spherical functions h given by
Such irreducible representations are often described as having class one. They are precisely the irreducible representations required to decompose the induced representation π on H1. Each representation σ extends uniquely by continuity to A(K\G/K), so that each zonal spherical function satisfies
for f in A(K\G/K). Moreover, since the commutant π(G)' is commutative, there is a unique probability measure μ on the space of * homomorphisms X such that
μ is called the Plancherel measure. Since π(G)' is the centre of the von Neumann algebra generated by G, it also gives the measure associated with the direct integral decomposition of H1 in terms of the irreducible representations σχ.
Gelfand pairs
If G is a connected Lie group, then, thanks to the work of Cartan, Malcev, Iwasawa and Chevalley, G has a maximal compact subgroup, unique up to conjugation.[8][9] In this case K is connected and the quotient G/K is diffeomorphic to a Euclidean space. When G is in addition semisimple, this can be seen directly using the Cartan decomposition associated to the symmetric space G/K, a generalisation of the polar decomposition of invertible matrices. Indeed if τ is the associated period two automorphism of G with fixed point subgroup K, then
where
Under the exponential map, P is diffeomorphic to the -1 eigenspace of τ in the Lie algebra of G. Since τ preserves K, it induces an automorphism of the Hecke algebra Cc(K\G/K). On the other hand, if F lies in Cc(K\G/K), then
- F(τg) = F(g−1),
so that τ induces an anti-automorphism, because inversion does. Hence, when G is semisimple,
- the Hecke algebra is commutative
- (G,K) is a Gelfand pair.
More generally the same argument gives the following criterion of Gelfand for (G,K) to be a Gelfand pair:[10]
- G is a unimodular locally compact group;
- K is a compact subgroup arising as the fixed points of a period two automorphism τ of G;
- G =K·P (not necessarily a direct product), where P is defined as above.
The two most important examples covered by this are when:
- G is a compact connected semisimple Lie group with τ a period two automorphism;[11][12]
- G is a semidirect product
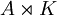 , with A a locally compact Abelian group without 2-torsion and τ(a· k)= k·a−1 for a in A and k in K.
, with A a locally compact Abelian group without 2-torsion and τ(a· k)= k·a−1 for a in A and k in K.
The three cases cover the three types of symmetric spaces G/K:[6]
- Non-compact type, when K is a maximal compact subgroup of a non-compact real semisimple Lie group G;
- Compact type, when K is the fixed point subgroup of a period two automorphism of a compact semisimple Lie group G;
- Euclidean type, when A is a finite-dimensional Euclidean space with an orthogonal action of K.
Cartan–Helgason theorem
Let G be a compact semisimple connected and simply connected Lie group and τ a period two automorphism of a G with fixed point subgroup K = Gτ. In this case K is a connected compact Lie group.[6] In addition let T be a maximal torus of G invariant under τ, such that T  P is a maximal torus in P, and set[13]
P is a maximal torus in P, and set[13]
S is the direct product of a torus and an elementary abelian 2-group.
In 1929 Élie Cartan found a rule to determine the decomposition of L2(G/K) into the direct sum of finite-dimensional irreducible representations of G, which was proved rigorously only in 1970 by Sigurdur Helgason. Because the commutant of G on L2(G/K) is commutative, each irreducible representation appears with multiplicity one. By Frobenius reciprocity for compact groups, the irreducible representations V that occur are precisely those admitting a non-zero vector fixed by K.
From the representation theory of compact semisimple groups, irreducible representations of G are classified by their highest weight. This is specified by a homomorphism of the maximal torus T into T.
The Cartan–Helgason theorem[14][15] states that
the irreducible representations of G admitting a non-zero vector fixed by K are precisely those with highest weights corresponding to homomorphisms trivial on S.
The corresponding irreducible representations are called spherical representations.
The theorem can be proved[6] using the Iwasawa decomposition:
where  ,
, 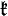 ,
, 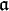 are the complexifications of the Lie algebras of G, K, A = T
are the complexifications of the Lie algebras of G, K, A = T 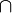 P and
P and
summed over all eigenspaces for T in 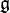 corresponding to positive roots α not fixed by τ.
corresponding to positive roots α not fixed by τ.
Let V be a spherical representation with highest weight vector v0 and K-fixed vector vK. Since v0 is an eigenvector of the solvable Lie algebra 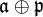 , the Poincaré–Birkhoff–Witt theorem
implies that the K-module generated by v0 is the whole of V. If Q is the orthogonal projection onto the fixed points of K in V obtained by averaging over G with respect to Haar measure, it follows that
, the Poincaré–Birkhoff–Witt theorem
implies that the K-module generated by v0 is the whole of V. If Q is the orthogonal projection onto the fixed points of K in V obtained by averaging over G with respect to Haar measure, it follows that
for some non-zero constant c. Because vK is fixed by S and v0 is an eigenvector for S, the subgroup S must actually fix v0, an equivalent form of the triviality condition on S.
Conversely if v0 is fixed by S, then it can be shown[16] that the matrix coefficient
is non-negative on K. Since f(1) > 0, it follows that (Qv0, v0) > 0 and hence that Qv0 is a non-zero vector fixed by K.
Harish-Chandra's formula
If G is a non-compact semisimple Lie group, its maximal compact subgroup K acts by conjugation on the component P in the Cartan decomposition. If A is a maximal Abelian subgroup of G contained in P, then A is diffeomorphic to its Lie algebra under the exponential map and, as a further generalisation of the polar decomposition of matrices, every element of P is conjugate under K to an element of A, so that[17]
- G =KAK.
There is also an associated Iwasawa decomposition
- G =KAN,
where N is a closed nilpotent subgroup, diffeomorphic to its Lie algebra under the exponential map and normalised by A. Thus S=AN is a closed solvable subgroup of G, the semidirect product of N by A, and G = KS.
If α in Hom(A,T) is a character of A, then α extends to a character of S, by defining it to be trivial on N. There is a corresponding unitary induced representation σ of G on L2(G/S) = L2(K),[18] a so-called (spherical) principal series representation.
This representation can be described explicitly as follows. Unlike G and K, the solvable Lie group S is not unimodular. Let dx denote left invariant Haar measure on S and ΔS the modular function of S. Then[6]
The principal series representation σ is realised on L2(K) as[19]
where
is the Iwasawa decomposition of g with U(g) in K and X(g) in S and
for k in K and x in S.
The representation σ is irreducible, so that if v denotes the constant function 1 on K, fixed by K,
defines a zonal spherical function of G.
Computing the inner product above leads to Harish-Chandra's formula for the zonal spherical function
as an integral over K.
Harish-Chandra proved that these zonal spherical functions exhaust the characters of the C* algebra generated by the Cc(K \ G / K) acting by right convolution on L2(G / K). He also showed that two different characters α and β give the same zonal spherical function if and only if α = β·s, where s is in the Weyl group of A
the quotient of the normaliser of A in K by its centraliser, a finite reflection group.
It can also be verified directly[3] that this formula defines a zonal spherical function, without using representation theory. The proof for general semisimple Lie groups that every zonal spherical formula arises in this way requires the detailed study of G-invariant differential operators on G/K and their simultaneous eigenfunctions (see below).[5][6] In the case of complex semisimple groups, Harish-Chandra and Felix Berezin realised independently that the formula simplified considerably and could be proved more directly.[6][20][21][22][23]
The remaining positive-definite zonal spherical functions are given by Harish-Chandra's formula with α in Hom(A,C*) instead of Hom(A,T). Only certain α are permitted and the corresponding irreducible representations arise as analytic continuations of the spherical principal series. This so-called "complementary series" was first studied by Bargmann (1947) for G = SL(2,R) and by Harish-Chandra (1947) and Gelfand & Naimark (1947) for G = SL(2,C). Subsequently in the 1960s, the construction of a complementary series by analytic continuation of the spherical principal series was systematically developed for general semisimple Lie groups by Ray Kunze, Elias Stein and Bertram Kostant.[24][25][26] Since these irreducible representations are not tempered, they are not usually required for harmonic analysis on G (or G / K).
Eigenfunctions
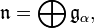
Harish-Chandra proved[5][6] that zonal spherical functions can be characterised as those normalised positive definite K-invariant functions on G/K that are eigenfunctions of D(G/K), the algebra of invariant differential operators on G. This algebra acts on G/K and commutes with the natural action of G by left translation. It can be identified with the subalgebra of the universal enveloping algebra of G fixed under the adjoint action of K. As for the commutant of G on L2(G/K) and the corresponding Hecke algebra, this algebra of operators is commutative; indeed it is a subalgebra of the algebra of mesurable operators affiliated with the commutant π(G)', an Abelian von Neumann algebra. As Harish-Chandra proved, it is isomorphic to the algebra of W(A)-invariant polynomials on the Lie algebra of A, which itself is a polynomial ring by the Chevalley–Shephard–Todd theorem on polynomial invariants of finite reflection groups. The simplest invariant differential operator on G/K is the Laplacian operator; up to a sign this operator is just the image under π of the Casimir operator in the centre of the universal enveloping algebra of G.
Thus a normalised positive definite K-biinvariant function f on G is a zonal spherical function if and only if for each D in D(G/K) there is a constant λD such that
i.e. f is a simultaneous eigenfunction of the operators π(D).
If ψ is a zonal spherical function, then, regarded as a function on G/K, it is an eigenfunction of the Laplacian there, an elliptic differential operator with real analytic coefficients. By analytic elliptic regularity, ψ is a real analytic function on G/K, and hence G.
Harish-Chandra used these facts about the structure of the invariant operators to prove that his formula gave all zonal spherical functions for real semisimple Lie groups.[27][28][29] Indeed the commutativity of the commutant implies that the simultaneous eigenspaces of the algebra of invariant differential operators all have dimension one; and the polynomial structure of this algebra forces the simultaneous eigenvalues to be precisely those already associated with Harish-Chandra's formula.
Example: SL(2,C)
The group G = SL(2,C) is the complexification of the compact Lie group K = SU(2) and the double cover of the Lorentz group. The infinite-dimensional representations of the Lorentz group were first studied by Dirac in 1945, who considered the discrete series representations, which he termed expansors. A systematic study was taken up shortly afterwards by Harish-Chandra, Gelfand–Naimark and Bargmann. The irreducible representations of class one, corresponding to the zonal spherical functions, can be determined easily using the radial component of the Laplacian operator.[6]
Indeed any unimodular complex 2×2 matrix g admits a unique polar decomposition g = pv with v unitary and p positive. In turn p = uau*, with u unitary and a a diagonal matrix with positive entries. Thus g = uaw with w = u* v, so that any K-biinvariant function on G corresponds to a function of the diagonal matrix
invariant under the Weyl group. Identifying G/K with hyperbolic 3-space, the zonal hyperbolic functions ψ correspond to radial functions that are eigenfunctions of the Laplacian. But in terms of the radial coordinate r, the Laplacian is given by[30]
Setting f(r) = sinh (r)·ψ(r), it follows that f is an odd function of r and an eigenfunction of 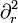 .
.
Hence
where 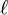 is real.
is real.
There is a similar elementary treatment for the generalized Lorentz groups SO(N,1) in Takahashi (1963) and Faraut & Korányi (1994) (recall that SO0(3,1) = SL(2,C) / ±I).
Complex case
If G is a complex semisimple Lie group, it is the complexification of its maximal compact subgroup K. If 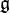 and
and 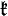 are their Lie algebras, then
are their Lie algebras, then
Let T be a maximal torus in K with Lie algebra 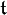 . Then
. Then
Let
be the Weyl group of T in K. Recall characters in Hom(T,T) are called weights and can be identified with elements of the weight lattice Λ in
Hom(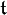 , R) =
, R) = 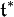 . There is a natural ordering on weights and every finite-dimensional irreducible representation (π, V) of K has a unique highest weight λ. The weights of the adjoint representation of K on
. There is a natural ordering on weights and every finite-dimensional irreducible representation (π, V) of K has a unique highest weight λ. The weights of the adjoint representation of K on 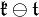 are called roots and ρ is used to denote half the sum of the positive roots α, Weyl's character formula asserts that for z = exp X in T
are called roots and ρ is used to denote half the sum of the positive roots α, Weyl's character formula asserts that for z = exp X in T
where, for μ in 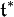 , Aμ denotes the antisymmetrisation
, Aμ denotes the antisymmetrisation
and ε denotes the sign character of the finite reflection group W.
Weyl's denominator formula expresses the denominator Aρ as a product:
where the product is over the positive roots.
Weyl's dimension formula asserts that
where the inner product on 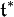 is that associated with the Killing form on
is that associated with the Killing form on 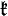 .
.
Now
- every irreducible representation of K extends holomorphically to the complexification G
- every irreducible character χλ(k) of K extends holomorphically to the complexification of K and
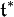 .
.
- for every λ in Hom(A,T) =
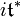 , there is a zonal spherical function φλ.
, there is a zonal spherical function φλ.
The Berezin–Harish–Chandra formula[6] asserts that for X in 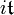
In other words:
- the zonal spherical functions on a complex semisimple Lie group are given by analytic continuation of the formula for the normalised characters.
One of the simplest proofs[31] of this formula involves the radial component on A of the Laplacian on G, a proof formally parallel to Helgason's reworking of Freudenthal's classical proof of the Weyl character formula, using the radial component on T of the Laplacian on K.[32]
In the latter case the class functions on K can be identified with W-invariant functions on T. The radial component of ΔK on T is just the expression for the restriction of ΔK to W-invariant functions on T, where it is given by the formula
where
for X in 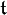 . If χ is a character with highest weight λ, it follows that φ = h·χ satisfies
. If χ is a character with highest weight λ, it follows that φ = h·χ satisfies
Thus for every weight μ with non-zero Fourier coefficient in φ,
The classical argument of Freudenthal shows that μ + ρ must have the form s(λ + ρ) for some s in W, so the character formula follows from the antisymmetry of φ.
Similarly K-biinvariant functions on G can be identified with W(A)-invariant functions on A. The radial component of ΔG on A is just the expression for the restriction of ΔG to W(A)-invariant functions on A. It is given by the formula
where
for X in 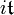 .
.
The Berezin–Harish–Chandra formula for a zonal spherical function φ can be established by introducing the antisymmetric function
which is an eigenfunction of the Laplacian ΔA. Since K is generated by copies of subgroups that are homomorphic images of SU(2) corresponding to simple roots, its complexification G is generated by the corresponding homomorphic images of SL(2,C). The formula for zonal spherical functions of SL(2,C) implies that f is a periodic function on 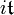 with respect to some sublattice. Antisymmetry under the Weyl group and the argument of Freudenthal again imply that ψ must have the stated form up to a multiplicative constant, which can be determined using the Weyl dimension formula.
with respect to some sublattice. Antisymmetry under the Weyl group and the argument of Freudenthal again imply that ψ must have the stated form up to a multiplicative constant, which can be determined using the Weyl dimension formula.
Example: SL(2,R)
The theory of zonal spherical functions for SL(2,R) originated in the work of Mehler in 1881 on hyperbolic geometry. He discovered the analogue of the Plancherel theorem, which was rediscovered by Fock in 1943. The corresponding eigenfunction expansion is termed the Mehler–Fock transform. It was already put on a firm footing in 1910 by Hermann Weyl's important work on the spectral theory of ordinary differential equations. The radial part of the Laplacian in this case leads to a hypergeometric differential equation, the theory of which was treated in detail by Weyl. Weyl's approach was subsequently generalised by Harish-Chandra to study zonal spherical functions and the corresponding Plancherel theorem for more general semimisimple Lie groups. Following the work of Dirac on the discrete series representations of SL(2,R), the general theory of unitary irreducible representations of SL(2,R) was developed independently by Bargmann, Harish-Chandra and Gelfand–Naimark. The irreducible representations of class one, or equivalently the theory of zonal spherical functions, form an important special case of this theory.
The group G = SL(2,R) is a double cover of the 3-dimensional Lorentz group SO(2,1), the symmetry group of the hyperbolic plane with its Poincaré metric. It acts by Möbius transformations. The upper half-plane can be identified with the unit disc by the Cayley transform. Under this identification G becomes identified with the group SU(1,1), also acting by Möbius transformations. Because the action is transitive, both spaces can be identified with G/K, where K = SO(2). The metric is invariant under G and the associated Laplacian is G-invariant, coinciding with the image of the Casimir operator. In the upper half-plane model the Laplacian is given by the formula[6][7]
If s is a complex number and z = x + i y with y > 0, the function
is an eigenfunction of Δ:
Since Δ commutes with G, any left translate of fs is also an eigenfunction with the same eigenvalue. In particular, averaging over K, the function
is a K-invariant eigenfunction of Δ on G/K. When
with τ real, these functions give all the zonal spherical functions on G. As with Harish-Chandra's more general formula for semisimple Lie groups, φs is a zonal spherical function because it is the matrix coefficient corresponding to a vector fixed by K in the principal series. Various arguments are available to prove that there are no others. One of the simplest classical Lie algebraic arguments[6][7][33][34][35] is to note that, since Δ is an elliptic operator with analytic coefficients, by analytic elliptic regularity any eigenfunction is necessarily real analytic. Hence, if the zonal spherical function corresponds is the matrix coefficient for a vector v and representation σ, the vector v is an analytic vector for G and
for X in 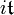 . The infinitesimal form of the irreducible unitary representations with a vector fixed by K were worked out classically by Bargmann.[33][34] They correspond precisely to the principal series of SL(2,R). It follows that the zonal spherical function corresponds to a principal series representation.
. The infinitesimal form of the irreducible unitary representations with a vector fixed by K were worked out classically by Bargmann.[33][34] They correspond precisely to the principal series of SL(2,R). It follows that the zonal spherical function corresponds to a principal series representation.
Another classical argument[36] proceeds by showing that on radial functions the Laplacian has the form
so that, as a function of r, the zonal spherical function φ(r) must satisfy the ordinary differential equation
for some constant α. The change of variables t = sinh r transforms this equation into the hypergeometric differential equation. The general solution in terms of Legendre functions of complex index is given by[3][37]
where α = ρ(ρ+1). Further restrictions on ρ are imposed by boundedness and positive-definiteness of the zonal spherical function on G.
There is yet another approach, due to Mogens Flensted-Jensen, which derives the properties of the zonal spherical functions on SL(2,R), including the Plancherel formula, from the corresponding results for SL(2,C), which are simple consequences of the Plancherel formula and Fourier inversion formula for R. This "method of descent" works more generally, allowing results for a real semisimple Lie group to be derived by descent from the corresponding results for its complexification.[38][39]
Further directions
- The theory of zonal functions that are not necessarily positive-definite. These are given by the same formulas as above, but without restrictions on the complex parameter s or ρ. They correspond to non-unitary representations.[6]
- Harish-Chandra's eigenfunction expansion and inversion formula for spherical functions.[40] This is an important special case of his Plancherel theorem for real semisimple Lie groups.
- The structure of the Hecke algebra. Harish-Chandra and Godement proved that, as convolution algebras, there are natural isomorphisms between Cc∞(K \ G / K ) and Cc∞(A)W, the subalgebra invariant under the Weyl group.[4] This is straightforward to establish for SL(2,R).[7]
- Spherical functions for Euclidean motion groups and compact Lie groups.[6]
- Spherical functions for p-adic Lie groups. These were studied in depth by Satake and Macdonald.[41][42] Their study, and that of the associated Hecke algebras, was one of the first steps in the extensive representation theory of semisimple p-adic Lie groups, a key element in the Langlands program.
See also
- Plancherel theorem for spherical functions
- Hecke algebra of a locally compact group
- Representations of Lie groups
- Non-commutative harmonic analysis
- Tempered representation
- Positive definite function on a group
- Symmetric space
- Gelfand pair
Notes
- ↑ Dixmier 1996, Algèbres hilbertiennes.
- ↑ If σ is a unitary representation of G, then
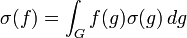 .
. - ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Dieudonné 1978
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Godement 1952
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Helgason 2001
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 Helgason 1984
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Lang 1985
- ↑ Cartier 1954-1955
- ↑ Hochschild 1965
- ↑ Dieudonné 1978, pp. 55–57
- ↑ Dieudonné 1977
- ↑ Helgason 1978, p. 249
- ↑ Helgason 1978, pp. 257–264
- ↑ Helgason 1984, pp. 534–538
- ↑ Goodman & Wallach 1998, pp. 549–550
- ↑ Goodman & Wallach 1998, p. 550
- ↑ Helgason 1978, Chapter IX.
- ↑ Harish-Chandra 1954a, p. 251
- ↑ Wallach 1973
- ↑ Berezin 1956a
- ↑ Berezin 1956b
- ↑ Harish-Chandra 1954b
- ↑ Harish-Chandra 1954c
- ↑ Kunze & Stein 1961
- ↑ Stein 1970
- ↑ Kostant 1969
- ↑ Harish-Chandra 1958
- ↑ Helgason 2001, pages 418–422, 427-434
- ↑ Helgason 1984, p. 418
- ↑ Davies 1990
- ↑ Helgason 1984, pp. 432–433
- ↑ Helgason 1984, pp. 501–502
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 Bargmann 1947
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Howe & Tan 1992
- ↑ Wallach 1988
- ↑ Helgason 2001, p. 405
- ↑ Bateman & Erdelyi 1953, p. 156
- ↑ Flensted-Jensen 1978
- ↑ Helgason 1984, pp. 489–491
- ↑ Helgason 1984, pp. 434–458
- ↑ Satake 1963
- ↑ Macdonald 1971
References
- Bargmann, V. (1947), "Irreducible Unitary Representations of the Lorentz Group", Annals of Mathematics (Annals of Mathematics) 48 (3): 568–640, doi:10.2307/1969129, JSTOR 1969129
- Barnett, Adam; Smart, Nigel P. (2003), "Mental Poker revisited, in Cryptography and Coding", Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Springer-Verlag) 2898: 370–383
- Bateman, Harry; Erdélyi, Arthur (1953), Higher transcendental functions, Vol.I, McGraw–Hill, ISBN 0-07-019546-3
- Berezin, F. A. (1956), "Операторы Лапласа на полупростых группах" [Laplace operators on semisimple groups], Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR 107: 9–12.
- Berezin, F. A. (1956b), "Representation of complex semisimple Lie groups in Banach space", Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR 110: 897–900
- Brychkov, Yu.A.; Prudnikov, A.P. (2001), "Spherical functions", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4
- Cartier, Pierre (1954–1955), Structure topologique des groupes de Lie généraux, Exposé No. 22, Séminaire "Sophus Lie" 1.
- Davies, E. B. (1990), Heat Kernels and Spectral Theory, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-40997-7
- Dieudonné, Jean (1977), Treatise on Analysis, Vol. V, Academic Press
- Dieudonné, Jean (1978), Treatise on Analysis, Vol. VI, Academic Press, ISBN 0-12-215506-8
- Dirac, P. A. M. (1945), "Unitary representations of the Lorentz group", Proceedings of the Royal Society A 183 (994): 284–295, doi:10.1098/rspa.1945.0003
- Dixmier, Jacques (1996), Les algèbres d'opérateurs dans l'espace hilbertien (algèbres de von Neumann), Les Grands Classiques Gauthier-Villars., Éditions Jacques Gabay, ISBN 2-87647-012-8
- Flensted-Jensen, Mogens (1978), "Spherical functions of a real semisimple Lie group. A method of reduction to the complex case", J. Funct. Anal. 30: 106–146, doi:10.1016/0022-1236(78)90058-7
- Gelfand, I.M.; Naimark, M.A. (1947), "Unitary representations of the Lorentz group", Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Mat. 37: 411–504
- Gelfand, I.M.; Naimark, M.A. (1948), "An analogue of Plancherel's theorem for the complex unimodular group", Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR 63: 609–612
- Gelfand, I.M.; Naimark, M.A. (1952), "Unitary representations of the unimodular group containing the identity representation of the unitary subgroup", Trudy Moscov. Mat. Obšč. 1: 423–475
- Godement, Roger (1952), "A theory of spherical functions. I", Transactions of the American Mathematical Society (American Mathematical Society) 73 (3): 496–556, doi:10.2307/1990805, JSTOR 1990805
- Goodman, Roe; Wallach, Nolan (1998), Representations and Invariants of the Classical Groups, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-66348-2
- Harish-Chandra (1947), "Infinite irreducible representations of the Lorentz group", Proceedings of the Royal Society A 189 (1018): 372–401, doi:10.1098/rspa.1947.0047
- Harish-Chandra (1954a), "Representations of Semisimple Lie Groups. II", Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 76: 26–65, doi:10.2307/1990743
- Harish-Chandra (1954b), "Representations of Semisimple Lie Groups. III", Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. (American Mathematical Society) 76 (2): 234–253, doi:10.2307/1990767, JSTOR 1990767 (Simplification of formula for complex semisimple Lie groups)
- Harish-Chandra (1954c), "The Plancherel formula for complex semisimple Lie groups", Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. (American Mathematical Society) 76 (3): 485–528, doi:10.2307/1990793, JSTOR 1990793 (Second proof of formula for complex semisimple Lie groups)
- Harish-Chandra (1958), "Spherical functions on a semisimple Lie group I, II", Amer. J. Math. (The Johns Hopkins University Press) 80 (2): 241–310, 553–613, doi:10.2307/2372786, JSTOR 2372786 (Determination of Plancherel measure)
- Helgason, Sigurdur (2001), Differential geometry and symmetric spaces (reprint of 1962 edition), American Mathematical Society, ISBN 0-8218-2735-9
- Helgason, Sigurdur (1978), Differential geometry, Lie groups and symmetric spaces, Academic Press, ISBN 0-12-338460-5
- Helgason, Sigurdur (1984), Groups and Geometric Analysis: Integral Geometry, Invariant Differential Operators, and Spherical Functions, Academic Press, ISBN 0-12-338301-3
- Hochschild, Gerhard P. (1965), The structure of Lie groups, Holden–Day
- Howe, Roger; Tan, Eng-chye (1992), Non-abelian Harmonic Analysis: Applications of SL(2,R), Universitext, Springer-Verlag, ISBN 0-387-97768-6
- Korányi, Adam (1994), Analysis on symmetric cones, Oxford Mathematical Monographs, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-853477-9, Chapter XIV.
- Kostant, Bertram (1969), "On the existence and irreducibility of certain series of representations", Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 75 (4): 627–642, doi:10.1090/S0002-9904-1969-12235-4
- Kunze, Raymond A.; Stein, Elias M. (1961), "Analytic continuation of the principal series", Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 67 (6): 593–596, doi:10.1090/S0002-9904-1961-10705-2
- Lang, Serge (1985), SL(2,R), Graduate Texts in Mathematics 105, Springer-Verlag, ISBN 0-387-96198-4
- Macdonald, Ian G. (1971), Spherical Functions on a Group of p-adic Type, Publ. Ramanujan Institute 2, University of Madras
- Stein, Elias M. (1970), "Analytic continuation of group representations", Advances in Math. 4 (2): 172–207, doi:10.1016/0001-8708(70)90022-8
- Satake, I. (1963), "Theory of spherical functions on reductive algebraic groups over p-adic fields", Publ. Math. I.H.E.S. 18: 5–70
- Wallach, Nolan (1973), Harmonic Analysis on Homogeneous Spaces, Marcel Decker, ISBN 0-8247-6010-7
- Wallach, Nolan (1988), Real Reductive Groups I, Academic Press, ISBN 0-12-732960-9
- Takahashi, R. (1963), "Sur les représentations unitaires des groupes de Lorentz généralisés", Bull. Soc. Math. France 91: 289–433
External links
- Casselman, William, Notes on spherical functions