Yerba mate
| Yerba mate, erva mate, mate, or maté Ilex paraguariensis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Ilex paraguariensis | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Asterids |
| Order: | Aquifoliales |
| Family: | Aquifoliaceae |
| Genus: | Ilex |
| Species: | I. paraguariensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Ilex paraguariensis A. St. Hil. | |
Yerba mate (from Spanish [ˈʝerβa ˈmate]; Portuguese: erva-mate [ˈɛʁvɐ ˈmatʃi]) is a species of the holly family (Aquifoliaceae), with the botanical name Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil.[1] named by the French botanist Auguste François César Prouvençal de Saint-Hilaire.[2]
It is well known as the source of the beverage called mate (Portuguese: chimarrão, tererê/tereré and other variations), traditionally consumed in central and southern South America, particularly Argentina, Bolivia, Southern and Center-Western Brazil, Uruguay, Paraguay and Southern Chile.[3] It is also very popular in Syria where it is imported from Argentina.[4] It was first used and cultivated by the Guaraní people and in some Tupí communities in southern Brazil, prior to the European colonization. It was scientifically classified by the Swiss botanist Moses Bertoni, who settled in Paraguay in 1895. Yerba mate can also be found in energy drinks.
Description
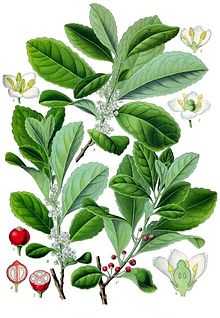
Yerba mate, Ilex paraguariensis, begins as a shrub and then matures to a tree and can grow up to 15 metres (49 ft) tall. The leaves are evergreen, 7–110 millimetres (0.3–4.3 in) long and 30–55 millimetres (1.2–2.2 in) wide, with a serrated margin. The leaves are often called yerba (Spanish) or erva (Portuguese), both of which mean "herb". They contain caffeine (known in some parts of the world as mateine) and also contains related xanthine alkaloids and are harvested commercially.
The flowers are small, greenish-white, with four petals. The fruit is a red drupe 4–6 millimetres (0.16–0.24 in) in diameter.
Cultivation
The Yerba mate plant is grown and processed in South America, specifically in northern Argentina (Corrientes, Misiones), Paraguay, Uruguay and southern Brazil (Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina, Paraná and Mato Grosso do Sul). Cultivators are known as yerbateros (Spanish) or ervateiros (Brazilian Portuguese).
Seeds used to germinate new plants are harvested from January until April only after they have turned dark purple. After harvest, they are submerged in water in order to eliminate floating non-viable seeds and detritus like twigs, leaves, etc. New plants are started between March and May. For plants established in pots, transplanting takes place April through September. Plants with bare roots are transplanted only during the months of June and July.[5]
Many of the natural enemies of yerba mate are difficult to control in a plantation setting. Insect pests include Gyropsylla spegazziniana, an insect that lays eggs in branches, Hedyphates betulinus, an insect that weakens the tree and makes it more susceptible to mold and mildew, "Perigonia lusca", an insect that eats the leaves, and several species of mites.[5]
When yerba mate is harvested, the branches are dried sometimes with a wood fire, imparting a smoky flavor. The plant Ilex paraguariensis can vary in strength of the flavor, caffeine levels and other nutrients depending on whether it is a male or female plant. Female plants tend to be milder in flavor, and lower in caffeine. They are also relatively scarce in the areas where yerba mate is planted and cultivated.[6]
According to FAO in 2012, Brazil is the biggest producer of mate in the world with 513,256 MT (58%), followed by Argentina with 290,000 MT (32%) and Paraguay with 85,490 MT (10%).[7]
Use as a beverage
The infusion, called mate in Spanish-speaking countries or chimarrão in Brazil, is prepared by filling a container, typically a gourd, about three-quarters full with dry leaves (and twigs) of the mate plant, and filling it up with water at a temperature of 70–80 °C (158–176 °F), hot but not boiling. Sugar may or may not be added; and the mate may be prepared with cold water (tereré).[8]
Drinking mate with friends from a hollow gourd (also called a guampa, porongo or mate in Spanish, cabaça or cuia in Portuguese, or zucca in Italian) through a metal straw (a bombilla in Spanish, bomba in Portuguese), refilling and passing to the next person after finishing the few mouthfuls of beverage, is a common social practice in Uruguay, Argentina and southern Brazil among people of all ages.
Yerba mate is most popular in Uruguay, where people are seen walking on the street carrying the mate and termo (thermal vacuum flask) in their arms and where you can find hot water stations to refill the termo while on the road. In Argentina 5 kg (11 lb) of yerba mate is consumed annually per capita; in Uruguay, the largest consumer, consumption is 10 kg (22 lb).[9] The amount of the herb used to prepare the infusion is very much greater than that used for tea and other beverages, accounting for the large weight used.[10]
The flavor of brewed mate resembles an infusion of vegetables, herbs, and grass, and is reminiscent of some varieties of green tea. Some consider the flavor to be very agreeable, but it is generally bitter if steeped in boiling water. Flavored mate is also sold, in which the mate leaves are blended with other herbs (such as peppermint) or citrus rind.[11]

In Paraguay, Brazil and Argentina, a toasted version of mate, known as mate cocido (Paraguay), chá mate (Brazil) or just mate, is sold in teabags and in a loose leaf form. It is often served sweetened in specialized shops or on the street, either hot or iced, pure or with fruit juice (especially lime – known in Brazil as limão) or milk. In Argentina and southern Brazil, this is commonly consumed for breakfast or in a café for afternoon tea, often with a selection of sweet pastries.
An iced, sweetened version of toasted mate is sold as an uncarbonated soft drink, with or without fruit flavoring. In Brazil, this cold version of chá mate is specially popular in the South and Southeast regions, and can easily be found in retail stores in the same cooler as soft-drinks.[12] Mate batido, which is toasted, has less of a bitter flavor and more of a spicy fragrance. Mate batido becomes creamy when shaken. Mate batido is more popular in the coastal cities of Brazil, as opposed to the far southern states, where it is consumed in the traditional way (green, consumed with a silver straw from a shared gourd), and called chimarrão (cimarrón in Spanish, particularly that of Argentina[13]).
In Paraguay, western Brazil (Mato Grosso do Sul, west of São Paulo) and the Argentine littoral, a mate infusion, called tereré in Spanish and Portuguese or tererê in Portuguese in southern regions of Brazil, is also consumed as a cold or iced beverage, usually sucked out of a horn cup called guampa with a bombilla. Tereré can be prepared with cold water (the most common way in Paraguay and Brazil), or fruit juice (the most common way in Argentina). The version with water is bitterer; fruit juice acts as a sweetener (in Brazil, that is usually avoided with the addition of table sugar). Medicinal or culinary herbs, known as yuyos (weeds), may be crushed with a pestle and mortar, and added to the water for taste or medicinal reasons. Tereré is most popular in Paraguay, Brazil, and the Litoral (northeast Argentina).[14]
In the same way as people meet for tea or coffee, friends often gather and drink mate (matear) in Argentina, southern Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. Sharing mate is almost a ritual, following customary rules. In warm weather the hot water is sometimes replaced by lemonade, but not in Uruguay.
The gourd (mate in Spanish) is given by the brewer to each person, often in a circle, in turn; the recipient does not give thanks, drinks the few mouthfuls and returns the mate to the brewer, who refills it and gives it to the next person in clockwise order.
During August, Paraguayans have a tradition of mixing mate with crushed leaves, stems, and flowers of the plant known as flor de agosto[15] (the flower of August, plants of the Senecio genus), which contain pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Modifying mate in this fashion is potentially toxic, as these alkaloids can cause a rare condition of the liver, veno-occlusive disease, which produces liver failure due to progressive occlusion of the small venous channels in the liver.[16]
In South Africa, mate is not well known, but has been introduced to Stellenbosch by a student who sells it nationally. In the tiny hamlet of Groot Marico in the northwest province, mate was introduced to the local tourism office by the returning descendants of the Boers, who in 1902 had emigrated to Patagonia in Argentina after losing the Anglo Boer War. It is also commonly consumed in Lebanon, Syria and some other parts of the Middle East mainly by Druze and Alawite population, following emigration to South America and return by many people, and worldwide by expatriates from the Southern Cone.[17]
Chemical composition and properties
Polyphenols
Yerba mate contains a variety of polyphenols such as the flavonoids quercetin and rutin.[18]
Xanthines
Yerba mate contains three xanthines: caffeine, theobromine and theophylline, the main one being caffeine. Caffeine content varies between 0.7% and 1.7% of dry weight[19] (compared with 0.4– 9.3% for tea leaves, 2.5–7.6% in guarana, and up to 3.2% for ground coffee);[20] theobromine content varies from 0.3% to 0.9%; theophylline is present in small quantities, or can be completely absent.[21] A substance previously called "mateine" is a synonym for caffeine (like theine and guaranine).
Mineral content
Yerba mate also contains elements such as potassium, magnesium, and manganese.[22]
Health effects
As of 2011 there have not been any double-blind, randomized prospective clinical trials of mate drinking with respect to chronic disease.[23] Yerba mate has been claimed to have various effects on human health and these effects have been attributed to the high quantity of polyphenols found in mate tea.[18]
Yerba mate may improve allergy symptoms[24] and reduce the risk of diabetes mellitus and high blood sugar in mice.[25]
Mate also contains compounds that act as an appetite suppressant and weight loss tool,[26] increase mental energy and focus,[27] improve mood,[28] and promote deeper sleep; however, sleep may only be affected in people who are sensitive to caffeine.[27]
Lipid metabolism
Some non-blinded studies have found mate consumption to be effective in lipid lowering.[23]
Cancer
The consumption of hot mate tea is associated with oral cancer[29] esophageal cancer,[30] cancer of the larynx,[30] and squamous cell cancers of the head and neck.[31][32] Studies show a correlation between tea temperature and likelihood of cancer, making it unclear how much of a role mate itself plays as a carcinogen.[30]
Weight loss
Yerba mate contains polyphenols such as flavonoids and phenolic acids, which work by inhibiting enzymes like pancreatic lipase[33] and lipoprotein lipase, which in turn play a role in fat metabolism. Yerba mate has been shown to increase satiety by slowing gastric emptying. Effects on weight loss may be due to reduced absorption of dietary fats and/or altered cholesterol metabolism.
Despite yerba mate’s potential for reducing body weight, there is minimal data on the effects of yerba mate on body weight in humans.[34] Therefore, yerba mate should not be recommended over diet and physical exercise,[35] further study on its effects being warranted.
Mechanism of action
E-NTPDase activity
Research also shows that mate preparations can alter the concentration of members of the ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase (E-NTPDase) family, resulting in an elevated level of extracellular ATP, ADP, and AMP. This was found with chronic ingestion (15 days) of an aqueous mate extract, and may lead to a novel mechanism for manipulation of vascular regenerative factors, i.e., treating heart disease.
Antioxidants
In an investigation of mate antioxidant activity, there was a correlation found between content of caffeoyl-derivatives and antioxidant capacity (AOC). Amongst a group of Ilex species, Ilex paraguariensis antioxidant activity was the highest.
Monoamine oxidase inhibition activity
A paper from the University of São Paulo cites yerba mate extract as an inhibitor of MAO activity; the maximal inhibition observed in vitro was 40–50%. A monoamine oxidase inhibitor is a type of antidepressant, so there is some data to suggest that yerba mate has a calming effect in this regard.[36]
History

Mate was first consumed by the indigenous Guaraní and also spread in the Tupí people that lived in southern Brazil and Paraguay, and became widespread with the European colonization. In the Spanish colony of Paraguay in the late 16th century, both Spanish settlers and indigenous Guaranís, who had, to some extent, before the Spanish arrival, consumed it. Mate consumption spread in the 17th century to the River Plate and from there to Argentina, Chile, Bolivia and Peru. This widespread consumption turned it into Paraguay's main commodity above other wares, such as tobacco, and indigenous peoples labour was used to harvest wild stands.
In the mid 17th century, Jesuits managed to domesticate the plant and establish plantations in their Indian reductions in Misiones, Argentina, sparking severe competition with the Paraguayan harvesters of wild stands. After their expulsion in the 1770s, their plantations fell into decay, as did their domestication secrets. The industry continued to be of prime importance for the Paraguayan economy after independence, but development in benefit of the Paraguayan state halted after the War of the Triple Alliance (1864–1870) that devastated the country both economically and demographically. Some regions with mate plantations in Paraguay became Argentine territory.
Brazil then became the largest producer of mate.[37] In Brazilian and Argentine projects in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the plant was domesticated once again, opening the way for plantation systems. When Brazilian entrepreneurs turned their attention to coffee in the 1930s, Argentina, which had long been the prime consumer,[38] took over as the largest producer, resurrecting the economy in Misiones Province, where the Jesuits had once had most of their plantations. For years, the status of largest producer shifted between Brazil and Argentina.[38]
Now, Brazil is the largest producer, with 53%, followed by Argentina, 37% and Paraguay, 10%.[7][39]
In the city of Campo Largo, state of Paraná, Brazil, there is a Mate Historic Park (Portuguese: Parque Histórico do Mate), funded by that state's government, to educate people on the sustainable harvesting methods needed to maintain the integrity and vitality of the oldest wild forests of mate in the world. As of June 2014, however, the park is closed to public visitation.[40]
Nomenclature
The name given to the plant in Guaraní, language of the indigenous people who first cultivated and enjoyed mate, is ka'a, which has the same meaning as "herb". Congonha, in Portuguese, is derived from the Tupi expression, meaning something like "what keeps us alive", but a term rarely used nowadays. Mate is from the Quechua mati,[41] a word that means container for a drink, infusion of an herb, as well as gourd.[42] The word mate is used in both Portuguese and Spanish languages.
The pronunciation of yerba mate in Spanish is [ˈʝe̞rβ̞ä ˈmäte̞][41] The accent on the word is on the first syllable, not the second as might be implied by the variant spelling maté.[41] The word hierba is Spanish for "herb"; yerba is a variant spelling of it which was quite common in Argentina.[43] (Nowadays in Argentina yerba refers exclusively to the yerba mate plant.[43]) Yerba mate, therefore, originally translated literally as the "gourd herb", i.e. the herb one drinks from a gourd.
The (Brazilian) Portuguese name for the plant is either erva-mate [ˈɛʁvɐ ˈmätʃi] (pronounced [ˈɛɾvɐ ˈmäte], [ˈɛɾvə ˈmätɪ] or [ˈɛɻvɐ ˈmätʃɪ] in the regions of traditional consumption, [ˈæə̯ʀvə ˈmäˑtɕ] in coastal, urban Rio de Janeiro), the most used term, or rarely congonha [kõˈɡõȷ̃ɐ], from Old Tupi kõ'gõi, which means "what sustains the being".[44] The drinks it is used to prepare are chimarrão (hot), tereré (cold) or chá mate (hot or cold). While the chá mate (tea) is made with the toasted leaves, the other drinks are made with green leaves, and are very popular in the south and center-west of the country. Most people colloquially address both the plant and the beverage simply by the word mate.[12]
Both the spellings "mate" and "maté" are used in English, but the latter spelling is never used in either Spanish or Portuguese; in Spanish, maté means "I killed" as opposed to "gourd" (the similarly pronounced Portuguese matei also meaning "I killed").[45] There are no variation of spellings in Spanish.[41] The addition of the acute accent over the final "e" was likely added as a hypercorrection, indicating that the word and its pronunciation are distinct from the common English word "mate".[46][47][48][49][50]
According to both Spanish and Portuguese spelling rules, an acute accent in that position shifts the tonic syllable to the last one, whereas in both languages the word is pronounced with the first syllable as the tonic one. Additionally, in Portuguese it changes the pronunciation of a few vowels. (É being more open and never final unstressed /ɛ/, like ó /ɔ/ and á /a/, and ê being more closed /e/, like ô /o/ and â /ɐ/ – the usual pronunciation of the mate vowel is [i ~ ɪ ~ e], never [ɛ]; the standard in all regions where the Portuguese language is official is for unstressed vowels, particularly final ones, to be reduced, in the case of e through [i] in Brazil, here strongly palatalizing, and most of Africa, and [ɯ], or occasionally non-palatalizing [i], in Portugal, Cape Verde and Macau, among a few others.)
Use as a health food
Mate is consumed as a health food. Packages of yerba mate are available in health food stores and are frequently stocked in the large supermarkets of Europe, Australia and the United States. By 2013, Asian interest in the drink had seen significant growth and led to significant export trade.[51]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ilex paraguariensis. |
- Black drink
- Club-Mate
- Matte Leão
- Ilex guayusa—known as guayusa, another caffeine-containing holly species of the Ilex genus, native to the Ecuadorian Amazon rainforest.
- Kuding—Ilex kudingcha
- Materva mate soft drink
- Nativa beverage
- Ilex vomitoria—a caffeine-containing holly species of the Ilex genus, from North America.
References
- ↑ "ITIS Report". itis.gov. Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- ↑ "Index of Botanists". harvard.edu. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ↑ World Conservation Monitoring Centre (1998). Ilex paraguariensis. 2006. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN 2006. www.iucnredlist.org. Retrieved on 9 May 2006.
- ↑ "Argentina’s 'yerba mate' crunch". globalpost.com. Retrieved 30 April 2015.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Burtnik, Oscar José, "Yerba Mate Production", 3rd Edition, 2006, retrieved on 24 May 2013
- ↑ "Nativa Yerba Mate". http://www.nativayerbamate.com/harvest.html. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "FAOSTAT". http://faostat.fao.org/site/339/default.aspx. Retrieved 5 April 2015.
- ↑ How to make mate (Spanish)
- ↑ "Mate: The Bitter Tea South Americans Love to Drink", retrieved on 30 May 2013
- ↑ Article on yerba mate, with an illustration showing how the gourd is almost filled with yerba (Spanish)
- ↑ "Flavored Yerba Mate". http://www.ma-tea.com. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Mate: o chá da hora". Retrieved 4 September 2012.
- ↑ "Significado de 'cimarrón'". Retrieved 5 July 2013.
- ↑ "Terere". http://www.ma-tea.com. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ↑ "Flor de agosto".
- ↑ McGee, J; Patrick, R S; Wood, C B; Blumgart, L H (1976). "A case of veno-occlusive disease of the liver in Britain associated with herbal tea consumption". Journal of Clinical Pathology 29 (9): 788–94. doi:10.1136/jcp.29.9.788. PMC 476180. PMID 977780.
- ↑ Folch, C. (2009). "Stimulating Consumption: Yerba Mate Myths, Markets, and Meanings from Conquest to Present". Comparative Studies in Society and History 52: 6. doi:10.1017/S0010417509990314.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Gambero A, Ribeiro ML (January 2015). "The positive effects of yerba maté (Ilex paraguariensis) in obesity". Nutrients 7 (2): 730–50. PMC 4344557. PMID 25621503.
- ↑ Dellacassa, Cesio et al. Departamento de Farmacognosia, Facultad de Química, Universidad de la República, Uruguay, Noviembre: 2007
- ↑ "Activities of a Specific Chemical Query". Ars-grin.gov. Retrieved 5 June 2011.
- ↑ Vázquez, A; Moyna, P (1986). "Studies on mate drinking". Journal of Ethnopharmacology 18 (3): 267–72. doi:10.1016/0378-8741(86)90005-x. PMID 3821141.
- ↑ Valduga, Eunice; de Freitas, Renato João Sossela; Reissmann, Carlos B.; Nakashima, Tomoe (1997). "Caracterização química da folha de Ilex paraguariensis St. Hil. (erva-mate) e de outras espécies utilizadas na adulteração do mate". Boletim do Centro de Pesquisa de Processamento de Alimentos (in Portuguese) 15 (1): 25–36.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Bracesco, N.; Sanchez, A.G.; Contreras, V.; Menini, T.; Gugliucci, A. (2011). "Recent advances on Ilex paraguariensis research: Minireview". Journal of Ethnopharmacology 136 (3): 378–84. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2010.06.032. PMID 20599603.
- ↑ Bremner, Paul; Heinrich, Michael (2010). "Natural products as targeted modulators of the nuclear factor-KB pathway". Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology (Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology) 54 (4): 453–472. doi:10.1211/0022357021778637. PMID 11999122.
- ↑ Bracesco N, Sanchez AG, Contreras V, Menini T, Gugliucci A (July 2011). "Recent advances on Ilex paraguariensis research: minireview". J Ethnopharmacol 136 (3): 378–84. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2010.06.032. PMID 20599603.
- ↑ Wichtl, Max, ed. (2004). Herbal Drugs and Phytopharmaceuticals. Medpharm. ISBN 0849319617.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Sanz, Tenorio; Isasa, Torija (1991). "Mineral elements in mate herb (Ilex paraguariensis St. H.)". Arch Latinoam Nutr. (Arch Latinoam Nutr.) 41 (3): 441–454. PMID 1824521.
- ↑ Klein, Siegrid; Rister, Robert (1998). The Complete German Commission E Monographs: Therapeutic Guide to Herbal Medicines. The American Botanical Council. ISBN 096555550X.
- ↑ Dasanayake, Ananda P.; Silverman, Amanda J.; Warnakulasuriya, Saman (2010). "Maté drinking and oral and oro-pharyngeal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Oral Oncology 46 (2): 82–6. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2009.07.006. PMID 20036605.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 Loria, Dora; Barrios, Enrique; Zanetti, Roberto (2009). "Cancer and yerba mate consumption: A review of possible associations". Revista Panamericana de Salud Pública 25 (6): 530–9. doi:10.1590/S1020-49892009000600010. PMID 19695149.
- ↑ Goldenberg, D; Lee, J; Koch, W; Kim, M; Trink, B; Sidransky, D; Moon, C (2004). "Habitual risk factors for head and neck cancer". Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 131 (6): 986–93. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2004.02.035. PMID 15577802.
- ↑ Goldenberg, David; Golz, Avishay; Joachims, Henry Zvi (2003). "The beverage maté: A risk factor for cancer of the head and neck". Head & Neck 25 (7): 595–601. doi:10.1002/hed.10288.
- ↑ de la Garza AL, Milagro FI, Boque N, Campión J, Martínez JA (May 2011). "Natural inhibitors of pancreatic lipase as new players in obesity treatment". Planta medica 77 (8): 773–85. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1270924. PMID 21412692.
- ↑ Pittler MH, Schmidt K, Ernst E (May 2005). "Adverse events of herbal food supplements for body weight reduction: systematic review". Obes Rev 6 (2): 93–111. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2005.00169.x. PMID 15836459.
- ↑ Pittler MH, Ernst E (April 2004). "Dietary supplements for body-weight reduction: a systematic review". Am J Clin Nutr 79 (4): 529–36. PMID 15051593.
- ↑ http://globalsciencebooks.info/JournalsSup/images/0706/MAPSB_1(1)37-46o.pdf (Page 43)
- ↑ "Erva-mate - o ouro verde do Paraná" Retrieved on 10 July 2013
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 "History of Mate". Establecimiento Las Marías. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
- ↑ List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
- ↑ "Parque Histórico do Mate" [Mate Historic Park] (in Portuguese). Paraná State Secretariat for Culture. Retrieved 3 June 2014.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 41.2 41.3 Real Academia Española. "Mate". Retrieved on 23 May 2013
- ↑ AULEX, "Online Quechua-Spanish Dictionary" Retrieved on 23 May 2013
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 Real Academia Española. "Yerba". Retrieved on 23 May 2013
- ↑ FERREIRA, A. B. H. Novo Dicionário da Língua Portuguesa. Segunda edição. Rio de Janeiro: Nova Fronteira, 1986. p.453
- ↑ "Word Magic Spanish Dictionary" Retrieved on 23 May 2013
- ↑ Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, 2002, shows the main entry for the word as ma·té or ma·te. The explanatory material for main entries on page 14a, headed 1.71, says "When a main entry is followed by the word or and another spelling or form, the two spellings or forms are equal variants. Their order is usually alphabetical, and the first is no more to be preferred than the second..."
- ↑ The New Oxford American Dictionary
- ↑ The Oxford English Dictionary
- ↑ "American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language". Dictionary.reference.com. Retrieved 5 June 2011.
- ↑ "Merriam-Webster's Online Dictionary". M-w.com. 13 August 2010. Retrieved 5 June 2011.
- ↑ "La yerba mate sigue ganando adeptos en países asiáticos". Territorio Digital (Argentina). 24 January 2013. Retrieved 24 January 2013.
Bibliography
- López, Adalberto. The Economics of Yerba Mate in Seventeenth-Century South America in Agricultural History. Agricultural History Society 1974.

