Yeghegnadzor
| Yeghegnadzor Եղեգնաձոր | |
|---|---|
|
Yeghegnadzor landscape | |
 Yeghegnadzor Եղեգնաձոր | |
| Coordinates: 39°45′40″N 45°20′00″E / 39.76111°N 45.33333°ECoordinates: 39°45′40″N 45°20′00″E / 39.76111°N 45.33333°E | |
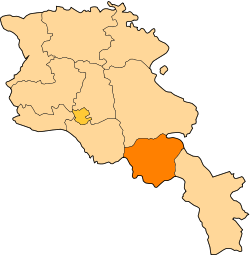
| Country | Armenia |
| Marz | Vayots Dzor |
| First mentioned | 5th century |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | David Harutyunuan |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6 km2 (2 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 1,194 m (3,917 ft) |
| Population (2009) | |
| • Total | 8,200 |
| • Density | 1,400/km2 (3,500/sq mi) |
| Time zone | GMT +4 (UTC+4) |
| Area code(s) | (+374) 281 |
| Website | official website |
| Sources: Population [1] | |
Yeghegnadzor (Armenian: Եղեգնաձոր); anciently Yeghegik, until 1935 Keshishkend, between 1935 and 1957 Mikoyan, is the capital of the Armenian province of Vayots Dzor. The name of the city means "the valley of canes" in the Armenian language. During the rule of Joseph Stalin, the city was renamed after the Soviet politician Anastas Mikoyan. The town is located 123 km south of the capital Yerevan, on a small river called "Serkoghunk" (Armenian: Սրկողունք), at a height of 1194 meters above sea level.[2]
General information
Yeghegnadzor is one of the ancient settlements of the Vayots Dzor canton within the historic province of Syunik; the 9th province of Greater Armenia (Armenia Major). It was first mentioned in history during the 5th century. The ruins of a medieval fortress could be found near the city.
The economy of the town is based on the construction sector and food-processing industry. The most notable industrial plant of the toen is the wine factory. There are many firms as well for electro-mechanical tools production. Lighter productions of canned foods, textile and jewellery are also found in the town.
However, the agricultural sector remains the main activity of the population in the suburbs of Yeghegnadzor.
History
Yeghegnadzor, the "kingdom of gorges," is the administrative center of Vayots Dzor, located in southeastern Armenia.
Vayots Dzor was also named Eghegnadzor or Yeghegeats Dzor. According to data from the first quarter of the 9th century, when Syunats Prince Philipe, son of Vasak, changed his residency from Sisian to Vayots Dzor and established it in Yeghegis, the name Yeghegnadzor or Yeghegeats Dzor spread across the whole province.
Yeghegnadzor is one of the ancient habitats of the Armenian Highlands. The excavated layer of a cemetery and the remains of a mausoleum from the first millennium BC serves as a proof. In the middle ages, according to historical resources, from the early 19th century Yeghegnadzor was named Pondzatagh, Skhtoralez, Yeghegik, Yeghegyats, and Keshishkend. In the Soviet era, Keshishkend was the regional center.
In 1935, Keshishkend was renamed Mikoyan, in the honor of prominent Soviet politician Anastas Mikoyan. On December 6, 1958, the region of Mikoyan was renamed Yeghegnadzor under the order of the Supreme Council of the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic. In 1996, the regions of Yeghegnadzor and Vayk reunited and became a province with the name of Vayots Dzor while the borough became a city.
The city is distributed across right and left banks of the Arpa River’s Srkoghk stream and it is flanked by Gladzor and Vernashen villages. The highway linking the Syunik Province with The Republic of Artsakh passes through Yeghegnadzor. The city is 119 km away from Yerevan.
Yeghegnadzor is situated at 1250m above sea level. The lower and medium highlands are mainly semi-deserts. The area has severe dry continental climate and large diurnal temperature fluctuations with the average annual rainfalls of 400 mm and mountain-valley winds. The average air temperature in January is 5-6◦C, with a coldest temperature of -22◦C and highest of +35◦C in July. The dry prairie landscape is overwhelming. There are some mammals (bezoar goat, wolf, fox, hare), reptiles (adder, viper) and birds (partridge, sparrow).
The nature is beautiful, the air is clear, the climate is mild with snowy winters and warm summers.
The area of the city is rich in such mineral resources as the building stone and glass stuff.
According to the census carried out in 2001, the city has a population of 8187 people. And according to the data of January 1, 2009, the population is 9394 people, the number of the families is 2582.
Yeghegnadzor was a major industrial center until the 1990s. The city's largest relay factory used to accommodate 1100 workers; there were 500 people working for the knitwear factory and 200 for the shoe factory. Placements were available at the cheese factory and carpet factory as well. The industrial companies that used to provide job opportunities for 35% of the population are now inactive.
Currently, the biggest company is the relay factory with 300 work positions, where mostly car relays are produced. There is also a road construction and maintenance company with 94 workers. Due to new conditions, small companies such as wineries, barrel making, stone processing, bakeries, and furniture making tend to develop. All these companies employ 120 workers. The territory of the administrative region is 2642 hectares; in addition, 25 hectares of the available land are for industrial purposes, 1777 hectares for agricultural land, and 70 hectares for administrative offices.
The populated territory comprises 450 hectares. Agricultural operations include cattle breeding, farming, gardening, and bee-keeping. Wine, honey, meat, milk, cheese, egg, grain, and fruit are produced all over Yeghegnadzor. The privatization of the lands was carried out by 1740 families, the area of each land was 3000 sq km. About 12% of the population is engaged in agriculture. The city produces wine, honey, meat, milk, cheese, egg, grain and fruit.
“Gitelik” university was founded in 2004. With its newly built four-story academic building, student and staff housing and the sport center, it is a big part of Yeghegnadzor’s educational setting. Armenian State University of Economics has been operating its branch since 2008. Other educational institutions in the city include Vayots Dzor college, the comprehensive lyceum, the high school, two main schools as well as three kindergartens, an art school, children’s creative school, sport school and sport center, cultural center, geological museum and a library with one of the biggest collections in the region.
The hospital includes surgical, gynecological, pediatric, therapeutics, infections, blood transfusion departments, emergency care, and a biochemical laboratory. The city has 4 parks. The garden named after Momik has a playground and renovated amphitheater used for events and concerts.
Vayots Dzor was also named Eghegnadzor or Yeghegeats Dzor. According to data from the first quarter of the 9th century, when Syunats Prince Philipe, son of Vasak, changed his residency from Sisian to Vayots Dzor and established it in Yeghegis, the name Yeghegnadzor or Yeghegeats Dzor spread across the whole province.
Geography
Topography and location
The city is spread out across the right and left banks of the Srkoghk tributary of the Arpa River and is flanked by the villages of Gladzor and Vernashen.
Yeghegnadzor is situated at 1250m above sea level. The lower and mid-level highlands are mainly semi-deserts.
Climate
The area has severe dry continental climate and large diurnal temperature fluctuations with average annual rainfalls of 400 mm and mountain-valley winds. The average air temperature in January is 5–6◦C, with a coldest temperature of −22◦C and highest of +35◦C in July.
Flora and Fauna
Flora
There are about 960 species of plants from 400 genera and 82 families. More than 280 species are rare and endemic species in Vayots Dzor. Sixty species are registered in the Red Book of Armenia. There are 18 endemics of Armenia out of which 6 are narrow endemics of Vayots Dzor. One of the biggest centers of wild cereals is the Gnishik-Grav region.
Fauna
The mountain grasslands and subalpine meadows of Yeghegnadzor are currently inhabited by 30 species of mammals. Two species (leopard and mouflon) have vanished. Out of 32 species, 9 are listed in the Red Book of Armenia. Noravank canyon is identified as an important area for birds. Of about 345 species of birds reported in Armenia, over 190 species can be found throughout Vayots Dzor. There are also 4 species of amphibians and 22 species of reptiles.
Demographics
Many ancestors of Yeghegnadzor's current population migrated from Khoy and Salmast. According to Yeghegnadzor town hall's given data in 2009 the population consists of 9394 people; the number of families is 2582.
| Year | 1831 | 1897 | 1926 | 1939 | 1959 | 1980 | 2001 | 2004 | 2009 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | 332 | 1307 | 1583 | 2567 | 3567 | 7053 | 8178 | 8200 | 9394 |
Education and economy
The town has four public education schools, three kindergartens, one intermediate college, one music and art school and one sport school. The geological museum of the town was opened in 2002. Since 2004 "the Gitelik" pedagogical university is established with its 12 faculties. The University provides undergraduate and graduate programs according to European standards. Since 2008 the branch of Armenian University of economics is established. Here are taught "Management, including tourism management", "Finance", "International Economic Relations" major, both for free and paid. The State College has 13 departments, schools, children gardens, children creative center, music center, art school, cultural house, sport school. There are 4 departments in library including 56119 books.
The population is engaged in agriculture, fruit growing and cattle. The town has also building stones and glass materials production plants.
Health and Tourism
There is a hospital in Yeghegnadzor, which includes surgical, obstetric, pediatric, therapeutic, infection, blood transfusion departments, maternity home and emergency.
There are 4 parks. Momik State park, which has playground, carousels, amphitheater with comfortable stage, where mass events are held, concerts are given.
Historic sites
- Basilica of the Holy Mother of God: formerly known as Surp Sarkis church, built in the 12th century and renovated in 1878. The basilica is located at the center of Yeghegnadzor and serves as the seat of the Vayots Dzor Diocese of the Armenian Apostolic Church.[3]
- Proshaberd fortress (Boloraberd fortress) of the 13th century, located few kilometers to the north-east of Yeghegnadzor, near the villages of Gladzor and Vernashen.
- The historic University of Gladzor of the 13th century, located in the village of Gladzor at the outskirts of Yeghegnadzor.
- Agarakadzor bridge 13th century.
- Noravank Monastery of the 13th century, located few kilometers away from Yeghegnadzor, to the southwest of the town.
- Spitakavor Monastery of the Holy Mother of God built in 1321, located just to the north of Yeghegnadzor near the village of Vernashen.

References
- ↑ Armstats:Population
- ↑ Yeghegnadzor:Armenia page Archived 22 January 2011 at WebCite
- ↑ Historical sites in Vayots Dzor
- Yeghegnadzor at GEOnet Names Server
- Report of the results of the 2001 Armenian Census, National Statistical Service of the Republic of Armenia
- World Gazeteer: Armenia – World-Gazetteer.com
- Kiesling, Brady (2005), Rediscovering Armenia: Guide, Yerevan, Armenia: Matit Graphic Design Studio
- Brady Kiesling, Rediscovering Armenia, p. 125; original archived at Archive.org, and current version online on Armeniapedia.org.
External links
- Cilicia.com entry on the region
-
 Yeghegnadzor travel guide from Wikivoyage
Yeghegnadzor travel guide from Wikivoyage
| |||||||||||||||||||||