Yamaguchi esterification
The Yamaguchi esterification is the chemical reaction of an aliphatic carboxylic acid and 2,4,6-trichlorobenzoyl chloride (TCBC, Yamaguchi reagent) to form a mixed anhydride which, upon reaction with an alcohol in the presence of stoichiometric amount of DMAP, produces the desired ester. It was first reported by Masaru Yamaguchi et al. in 1979.[1][2]
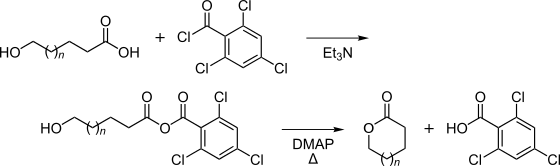
It is especially useful in the synthesis of macro-lactones and highly functionalised esters.
Reaction mechanism
The aliphatic carboxylate adds to the carbonyl carbon of Yamaguchi reagent, forming a mixed anhydride, which is then attacked by DMAP regioselectively at the less hindered carbon, producing acyl-substituted DMAP. It reacts with the alcohol to form the product ester.

The in situ formation of the symmetric aliphatic anhydride is proposed to explain the regioselectivity observed in the reactions of aliphatic acids, based on the fact that aliphatic carboxylates are more nucleophilic, and aliphatic anhydrides are more electrophilic towards DMAP and alcohol than their counterparts.
See also
References
- ↑ Inanaga, J.; Hirata, K.; Saeki, H.; Katsuki, T.; Yamaguchi, M. "A Rapid Esterification by Means of Mixed Anhydride and Its Application to Large-ring Lactonization". Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1979, 52, 1989–1993. doi:10.1246/bcsj.52.1989
- ↑ Kawanami, Y.; Dainobu, Y.; Inanaga, J.; Katsuki, T.; Yamaguchi, M. "Synthesis of Thiol Esters by Carboxylic Trichlorobenzoic Anhydrides". Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1981, 54, 943–944. doi:10.1246/bcsj.54.943
External links
- Yamaguchi esterification—organic-chemistry.org
- Investigation of the Yamaguchi Esterification Mechanism. Synthesis of a Lux-S Enzyme Inhibitor Using an Improved Esterification Method. I. Dhimitruka, J. SantaLucia, Org. Lett., 2006, 8, 47–50. Article