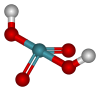
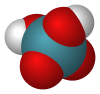
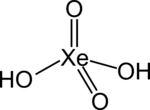
Xenic acid
 | |||
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ChemSpider | 10466143 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H2XeO4 | |||
| Molar mass | 197.31 g/mol | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds |
Perxenic acid Xenon trioxide | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Xenic acid or orthoxenic acid is an ortho acid (the only ortho acid of xenon) and a noble gas compound formed by the dissolution of xenon trioxide in water. Its chemical formula is H2XeO4. It is a very powerful oxidizing agent, and its decomposition is dangerous as it liberates a large amount of gaseous products - xenon, oxygen, and ozone.
Its existence was hypothesized by Linus Pauling in 1933.[1] Xenic acid has been used as an oxidizing agent in organic chemistry.
Salts of xenic acid are called xenates, containing the HXeO−
4 anion. They tend to disproportionate into xenon gas and perxenates:[2]
- 2 HXeO−
4 + 2 OH−
→ XeO4−
6 + Xe + O
2 + 2 H
2O
The energy given off is sufficient to form ozone from diatomic oxygen:
- 3 O
2 (g) → 2 O
3 (g)
Salts containing the completely deprotonated anion XeO2−
4 are presently unknown.[2]
External links
- Xenic Acid Reactions with vic-Diols[3]
References
- ↑ Linus Pauling (June 1933). "The Formulas of Antimonic Acid and the Antimonates". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 55, (5): 1895–1900. doi:10.1021/ja01332a016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Egon Wiberg; Nils Wiberg; Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001). Inorganic chemistry. Academic Press. p. 399. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ↑ Bruno Jaselskis, Stanislaus Vas (May 1964). "Xenic Acid Reactions with vic-Diols". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86, (10): 2078–2079. doi:10.1021/ja01064a041.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||