World Federation of Scientific Workers
The World Federation of Scientific Workers (WFSW) is an international federation of scientific associations. It was a Cold War-era Communist front.[1][2] The group was composed of scientists who supported communism.[1] The federation opposed nuclear tests conducted by the United States.[3]
History
The WFSW was found at a conference in London July 20–21, 1946 held at the initiative of the British Association of Scientific Workers. The original conference was attended by 18 organizations, representing 14 countries.[4]
The WFSW was accused of towing the Soviet line during the Cold War. At the time of the Tito-Stalin split the Yugoslav affiliate was expelled from the Federation. During the Korean War it supported the Communist Chinese forces. The Federation protested against restrictions on the free exchange of scientific information or the movement of scientists by the withholding of visas or passports by Western countries, but never by Communist ones. Likewise, the WFSW spoke out against American, British and French nuclear testing, but not against Soviet nuclear testing. During the Cuban missile crisis the World Federation of Scientific Workers mobilized its members to send telegrams to John F. Kennedy and the United Nations condemning the quarantine of Cuba, however they never mentioned the presence of nuclear missiles on the island, nor was any protest sent to Nikita Khrushchev. After a series of Soviet nuclear tests in the early 1960s, the president of the Federation wished to protest, and threatened to resign from the organization, but was overruled. That same year the British and French affiliates also threatened to leave if statements kept on being issued without their approval. The WFSW toned down its rhetoric in order to keeps its two most important Western members.[5]
During the Vietnam War the Federation condemned American "aggression" and accused the US of breaking international agreements and using biological and chemical weapons. The 1966 Executive Council meeting in East Berlin adopted a "Scientists Statement on Vietnam" signed by 13 scientists - including 9 Nobel Prize winners - calling for financial aid to for laboratories, scientific equipment and scientific books for Hanoi University.[6]
The WFSW was also affected by the Sino-Soviet split. In 1963 a "Peking center of the World Federation of Scientific Workers" was founded. While it claimed to be an Asian regional branch of the Federation, it was in fact a rival to it. The Peking WFSW held an "International Scientific Symposium" in 1964 and a "Summer Symposium on Physics" in July 23-31 1966 which was held exclusively for physicists from Africa, Asia, Oceania and Latin America and drew participants from 33 countries. In September 1966 the Executive Council at Varna established a rival committee for scientific organizations in Africa, Asia and Latin America.[7]
Organization
The Associations highest body is the general assemble which meets every two to three years. Between meetings of the assembly the organization is run by the executive council and in between meeting of that body by the bureau.[7] The Executive Council consisted of 27 members of whom 17 were elected on an individual basis at the general assembly, and ten by regional organizations. The WFSW bureau consisted of the president, vice-presidents, treasurer, the Executive Councils' chairman and vice-chairmen, the chairmen of the editorial board (who also had to be a member of the Council) and the head of the regional centers. Further officials - the secretary general, assistant secretary general and five honorary assistant secretaries - are appointed and participate in the work of the bureau with a voice, but no vote. The Executive Council also elects a 16 member editorial board.[8]
The headquarters of the organization have historically been in London. In 1966 it was located at 40 Goodge Street London, W 1, while the secretary general operated out of an office at 10 rue Vaquelin, Paris 5.[9] The current headquarters are at 265 av. de Paris, 93000 Montreuil-sous-Bois, France - Métro Porte de Montreuil.[10]
The WFSW tried to set up regional centers and hold regional meetings. The first regional meeting was at New Delhi in 1955, followed by Prague in 1956, Paris in 1957 and Cambridge, England in 1961. By 1968 only two regional centers had been established - at New Dehlin and at Cairo.[11]
Presidents
Presidents of the WFSW have included:[10]
- 1946-1957: Frédéric Joliot-Curie, France (who was also president of the World Peace Council at the same time)[8]
- 1958-1968: Cecil Powell, United Kingdom
- 1969-1979: Eric Burhop, United Kingdom
- 1980-1992: Jean-Marie Legay, France
- 1992-1996: Con Russel, United Kingdom
- 1996: Masayasu Hazegawa, Japan
- 1997-2008: André Jaeglé, France
- 2009–present: Jean-Paul Lainé, France
General Assemblies
The WFSW has held the following assemblies:
- London, July 20–21, 1946[12]
- Dobříš, Czechoslovakia September 1948[7]
- Paris and Prague, April 1951[7]
- Budapest, September 1953[7]
- East Berlin, September 1955[7]
Beginning with the Helsinki assembly in 1957, each conference was held in conjunction with a scientific symposium on a particular subject.[7]
- Helsinki, 1957 "The training of students in science and technology"[7]
- Warsaw, 1959 "Science and the development of the economy and welfare of mankind"[7]
- Moscow, 1962 "Higher scientific and technological evolution"[7]
- Budapest, 1965 "Problems of the advancement of science in the developing countries and the role of scientific cooperation"[7]
Members
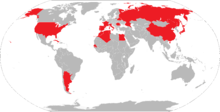
The Federation included affiliated organizations and individual corresponding members. In 1966, there were affiliated organization in 23 countries and corresponding members in 24 countries in which there were no affiliated groups.[7]
Current affiliated organizations include:[13]
 Algeria - Conseil National des Enseignants du Supérieur
Algeria - Conseil National des Enseignants du Supérieur Algeria - Fédération nationale des enseignants du supérieur, de la recherche et de l’éducation
Algeria - Fédération nationale des enseignants du supérieur, de la recherche et de l’éducation Algeria - Syndicat National des Chercheurs Permanents
Algeria - Syndicat National des Chercheurs Permanents Algeria - Syndicat national des enseignants universitaires
Algeria - Syndicat national des enseignants universitaires Argentina - Federación de Sindicatos de Docentes Universitarios de America del Sur
Argentina - Federación de Sindicatos de Docentes Universitarios de America del Sur Belarus - Trade Union of Scientific Workers of the Belarusian Academy of Science
Belarus - Trade Union of Scientific Workers of the Belarusian Academy of Science China - China Association for Science and Technology
China - China Association for Science and Technology Cuba - Sindicato Nacional de Trabajadores de la Ciencia
Cuba - Sindicato Nacional de Trabajadores de la Ciencia Egypt - General Trade Union of Education, Science and Research - Egyptian Trade Union Federation
Egypt - General Trade Union of Education, Science and Research - Egyptian Trade Union Federation France - Syndicat national des chercheurs scientifiques
France - Syndicat national des chercheurs scientifiques France - Syndicat national de l’enseignement supérieur
France - Syndicat national de l’enseignement supérieur Portugal - Associação de Bolseiros de Investigação Cientifica
Portugal - Associação de Bolseiros de Investigação Cientifica Portugal - Federação Nacional dos Professores
Portugal - Federação Nacional dos Professores Portugal - Organizaçao dos Trabalhadores Cientificos
Portugal - Organizaçao dos Trabalhadores Cientificos Russia - Trade Union of Scientific Workers of the Russian Academy of Science
Russia - Trade Union of Scientific Workers of the Russian Academy of Science Senegal - Syndicat autonome des enseignants du Sénégal
Senegal - Syndicat autonome des enseignants du Sénégal Senegal - Syndicat unique et démocratique des enseignants du Sénégal
Senegal - Syndicat unique et démocratique des enseignants du Sénégal Spain - Asociación del Personal Investigador del CSIC
Spain - Asociación del Personal Investigador del CSIC USA - United States Federation of Scientists and Scholars
USA - United States Federation of Scientists and Scholars
Other organizations the WFSW relationships with include [10]
 Japan - Japan Scientists Association
Japan - Japan Scientists Association Morocco - Syndicat national de l' enseignement supérieur
Morocco - Syndicat national de l' enseignement supérieur Italy - Fédération des Travaill eurs de la Connaissance
Italy - Fédération des Travaill eurs de la Connaissance Romania - Academia Oamenilor de Stiintax
Romania - Academia Oamenilor de Stiintax Tunisia - Fédération Générale de l’Ensei gnement Supérieur et de la Recherche Scientifique
Tunisia - Fédération Générale de l’Ensei gnement Supérieur et de la Recherche Scientifique Tunisia - Syndicat nat. des maîtres de conférence et profs. de l'enseignement supérieur
Tunisia - Syndicat nat. des maîtres de conférence et profs. de l'enseignement supérieur
Publications
Periodicals
The WFSW published a magazine, Scientific World, in English, French, German, Spanish, Russian and Czech.[14] Scientific World began as a twice yearly publication in 1957, became a quarterly in 1959 and ceased publication in 1993.[15] The WFSW also published an irregular Bulletin in English, French, German and Russian covering organizational news and was only available to members.[9][16]
"Science and Mankind"
Beginning in 1957 the WFSW published a series of pamphlets called "Science and Mankind":
- Josué de Castro Hunger and food London, World Federation of Scientific Workers 1958 "Science and Mankind" #1
- Ludwik Rajchman Science and health London World Federation of Scientific Workers 1961 "Science and Mankind" #2
- John Bernal Science for a developing world; An account of a symposium organized by the World Federation of Scientific workers on 'Science and the development of the economy and welfare of mankind,' Warsaw, September 1959. London World Federation of Scientific Workers 1962
- Training for tomorrow. Extracts from the International Symposium on Higher Scientific and Technological Education, Moscow 1962 London World Federation of Scientific Workers 1964
Other Publications
- The social responsibility of scientists: report of meeting held in Peking, on april 3, 1956 to celebrate the 10. anniversary of the founding of the World Federation of Scientific Workers Peking : All-China Federation of Scientific Societies, 1956
- Unmeasured hazards; an analysis of the effects of tests of atomic and thermonuclear weapons. London: World Federation of Scientific Workers, 1956 (published in English, French, Russian, Chinese, German, and Japanese)
- International Symposium on the Relations Between Science and Technology, 22-26 September Bratislava, Czechoslovakia, [World Federation of Scientific Workers] 1969
- Kurt Baudischl ABC weapons, disarmament and the responsibility of scientists: report on an International Conference of the World Federation of Scientific Workers, Berlin (GDR), 21st-23rd November, 1971. Berlin] Published by the Executive Council of Gerverkschaft Wissenschaft for the World Federation of Scientific Workers 1971
- Chemical weapons must be banned! an analysis of the level of development reached in the field of chemical warfare agents, the implications of their use and the possibilities of achieving an unconditional ban on all such agents London World Federation of Scientific Workers 1974
- Ending the arms race, the role of the scientist: with a glossary of terms commonly used in relation to the arms control and disarmament discussions and important statements, resolutions and other documents concerning the disarmament problem London: World Federation of Scientific Workers, 1977
- Proceedings of the Symposium on Science, Technology and Development, Algiers, 9-12 Sept. 1978 London: World Federation of Scientific Workers, 1979
- International Symposium on Science, Technology, and Development, March 1987: selected papers New Delhi: N.P. Gupta, Organising Secretary, 1989
"Science in the Service of Peace"
In addition to its print publications, the WFSW also produced a program "Science in the service of peace" in conjunction with the International Radio and Television Organisation which was broadcast from Eastern Europe.[7]
See also
- Christian Peace Conference
- International Association of Democratic Lawyers
- International Federation of Resistance Fighters – Association of Anti-Fascists
- International Organization of Journalists
- International Union of Students
- Women's International Democratic Federation
- World Federation of Democratic Youth
- World Federation of Trade Unions
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Louis Francis Budenz (1 June 1977). The techniques of communism. Ayer Publishing. pp. 242–. ISBN 978-0-405-09942-7. Retrieved 25 March 2012.
- ↑ communist propaganda techniques. Taylor & Francis. pp. 112–. Retrieved 25 March 2012.
- ↑ Lawrence S. Wittner (1997). Resisting the bomb: a history of the world nuclear disarmament movement, 1954-1970. Stanford University Press. pp. 86–. ISBN 978-0-8047-2918-5. Retrieved 25 March 2012.
- ↑ Hoover Institution Yearbook on international communist affairs 1966 Stanford, Calif., Hoover Institution Press. p.507
- ↑ Hoover Institution Yearbook on international communist affairs 1968 Stanford, Calif., Hoover Institution Press. p.507
- ↑ Hoover Institution Yearbook on international communist affairs 1968 Stanford, Calif., Hoover Institution Press. pp.737-8
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 7.9 7.10 7.11 7.12 Yearbook on international communist affairs 1966 pp.510-1, 518
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Yearbook on international communist affairs 1966 p.509
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Yearbook on international communist affairs 1966 p.510
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 World Federation of Scientific Workers PDF brochure
- ↑ Hoover Institution Yearbook on international communist affairs 1968 Stanford, Calif., Hoover Institution Press. p.737
- ↑ Yearbook on international communist affairs 1966 p.507
- ↑ Affiliated organizations. There are two, not entirely congruous, lists of affiliates on their website. The list on the PDF brochure includes all of these affiliated organizations listed on the html page cited here, except Sindicato Nacional de Trabajadores de la Ciencia of Cuba, which it listed under "Other organizations we have relationships with". The list of affiliates on the PDF brochure also includes "Vehivavy, Siansia, Fampandrosoana" of Madegascar.
- ↑ Hoover Institution Yearbook on international communist affairs 1968 Stanford, Calif., Hoover Institution Press. p.736
- ↑ http://catalog.crl.edu/search~S35?/o1918724/o1918724/1%2C3%2C3%2CB/frameset&FF=o1918724&1%2C1%2C
- ↑ Hoover Institution Yearbook on international communist affairs 1968 Stanford, Calif., Hoover Institution Press. p.736