Wilks's lambda distribution
In statistics, Wilks's lambda distribution (named for Samuel S. Wilks), is a probability distribution used in multivariate hypothesis testing, especially with regard to the likelihood-ratio test and multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA). It is a multivariate generalization of the univariate F-distribution, generalizing the F-distribution in the same way that the Hotelling's T-squared distribution generalizes Student's t-distribution.
Wilks's lambda distribution is related to two independent Wishart distributed variables, and is defined as follows,[1]
given
independent and with 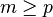
where p is the number of dimensions. In the context of likelihood-ratio tests m is typically the error degrees of freedom, and n is the hypothesis degrees of freedom, so that 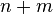 is the total degrees of freedom.[1]
is the total degrees of freedom.[1]
The distribution can be related to a product of independent beta-distributed random variables
For large m, Bartlett's approximation[2] allows Wilks's lambda to be approximated with a chi-squared distribution

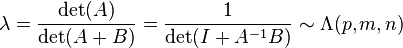
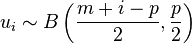
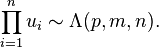
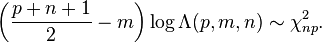
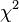 Approximations".
Approximations".