Von Zeipel theorem
In astrophysics, the von Zeipel theorem states that the radiative flux 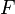 in a uniformly rotating star is proportional to the local effective gravity
in a uniformly rotating star is proportional to the local effective gravity  . Specifically,
. Specifically,
where the luminosity 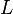 and mass
and mass  are evaluated on a surface of constant pressure
are evaluated on a surface of constant pressure 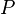 . The effective temperature
. The effective temperature  can then be found at a given colatitude
can then be found at a given colatitude 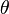 from the local effective gravity
from the local effective gravity
The theorem is named after Swedish astronomer Edvard Hugo von Zeipel.
References
- ↑ von Zeipel, Edvard Hugo (1924). "The radiative equilibrium of a rotating system of gaseous masses". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 84: 665–719. Bibcode:1924MNRAS..84..665V.
- ↑ Maeder, André (1999). "Stellar evolution with rotation IV: von Zeipel's theorem and anistropic losses of mass and angular momentum". Astronomy and Astrophysics 347: 185–193. Bibcode:1999A&A...347..185M.
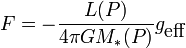
 .
.