Voiceless labio-velar approximant
| Voiceless labio-velar approximant |
|---|
| ʍ |
|---|
| w̥ |
|---|
| IPA number |
169 |
|---|
| Encoding |
|---|
| Entity (decimal) |
ʍ |
|---|
| Unicode (hex) |
U+028D |
|---|
| X-SAMPA |
W |
|---|
| Kirshenbaum |
w<vls> |
|---|
| Braille |
 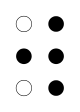 |
|---|
|
|
| Sound |
|---|
|
source · help |
The voiceless labiovelar (labialized velar) approximant (traditionally called a voiceless labiovelar fricative) is a type of consonantal sound, used in spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʍ⟩ (a rotated lowercase letter ⟨w⟩) or ⟨w̥⟩.
[ʍ] is generally called a "fricative" for historical reasons, but in English, the language that the letter ⟨ʍ⟩ is primarily used for, it is a voiceless approximant, equivalent to [w̥] or [hw̥]. On rare occasions the symbol is appropriated for a labialized voiceless velar fricative, [xʷ], in other languages.
Features
Features of the voiceless labial-velar approximant:
- Its phonation is voiceless, which means it is produced without vibrations of the vocal cords.
- It is an oral consonant, which means air is allowed to escape through the mouth only.
- It is a central consonant, which means it is produced by directing the airstream along the center of the tongue, rather than to the sides.
Occurrence
See also
References
Bibliography
- Greenberg, Mark L. (2006), A Short Reference Grammar of Standard Slovene, Kansas: University of Kansas
- Labov, William; Ash, Sharon; Boberg, Charles (2006), The Atlas of North American English, Berlin: Mouton-de Gruyter, ISBN 3-11-016746-8
- Lass, Roger (2002), "South African English", in Mesthrie, Rajend, Language in South Africa, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 9780521791052
- McMahon, April (2002), An Introduction to English Phonology, Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press Ltd, ISBN 0 7486 1252 1
- Rogers, Henry (2000), The Sounds of Language: An Introduction to Phonetics, Essex: Pearson Education Limited, ISBN 978-0-582-38182-7
- Skinner, Edith; Timothy Monich; Lilene Mansell (ed.) (1990). Speak with distinction (Second ed.). New York: Applause Theatre Book Publishers. ISBN 1-55783-047-9.
- Šuštaršič, Rastislav; Komar, Smiljana; Petek, Bojan (1999), "Slovene", Handbook of the International Phonetic Association: A guide to the use of the International Phonetic Alphabet, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 135–139, doi:10.1017/S0025100300004874, ISBN 0-521-65236-7
- Wells, J.C. (1982a), Accents of English, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Wells, J.C. (1982b). Accents of English 3: Beyond the British Isles. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-28541-0.
| |
|---|
| | IPA topics |
|---|
| | IPA | |
|---|
| | Phonetics | |
|---|
| | Special topics | |
|---|
| | Encodings | |
|---|
|
| | | |
|---|
|
| — These tables contain phonetic symbols, which may not display correctly in some browsers. [Help] |
| — Where symbols appear in pairs, left–right represent the voiceless–voiced consonants. |
| — Shaded areas denote pulmonic articulations judged to be impossible. |
| — Symbols marked with an asterisk (*) are not defined in the IPA. |
| | | Chart image |
- Pulmonics
- Non-pulmonics
- Affricates
- Co-articulated
|
|---|
|
| | |
|
.svg.png)
