Vitreous chamber
| Vitreous chamber | |
|---|---|
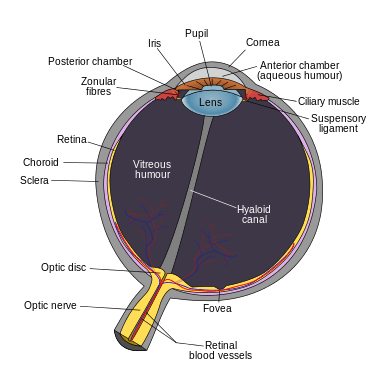 Schematic diagram of the human eye | |
| Details | |
| Latin | camera postrema |
| Identifiers | |
| TA | A15.2.06.006 |
| FMA | 58848 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The vitreous chamber is the space in the eye occupied by vitreous humor.
Structure
Within the vertebrate eye, there are considered to be three chambers: anterior, posterior, and vitreous. It is important to note that the eye can also be classified as having two cavities: anterior and posterior. Both the anterior and posterior chambers are located within the anterior cavity, while the vitreous chamber is located in the posterior cavity. The best way to distinguish between the two cavities is to use the lens as a dividing point. The vitreous chamber is the largest of the three chambers and is located behind the lens and in front of the optic nerve. This chamber is filled with a thick, clear gel-like substance called the vitreous humor (also vitreous body). The humor plays a crucial role in supporting the posterior side of the lens.[1]
Function
The vitreous fluid, along with supporting the lens, also functions in maintaining the shape of the entire vitreous chamber and posterior cavity. It is imperative that the eye remains the proper shape to ensure that the light passing through the lens and the fluid can focus properly on the retina. The composition of the fluid is 99% water and contains no cells, so the light can effectively pass through without it being deflected. The fluid is often thought to be a sort of liquid lens that further focuses the light that has already passed through the lens on the way to towards the retina.[2]
See also
- Vitreous humor
- Vitreous detachment
- Aqueous humor
References
- ↑ "Eye (Vertebrate)". Gale Virtual Reference Library. McGraw-Hill Professional. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ↑ Thomson, Marie. "Eye". Gale Virtual Reference Library. Gale. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

