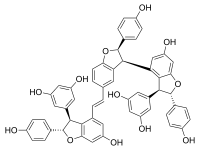
Vitisin C
Vitisin C
 |
| Identifiers |
| |
180580-73-8  N N |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL442911  Y Y |
| ChemSpider |
17301998  Y Y |
InChI=1S/C56H42O12/c57-35-10-4-29(5-11-35)54-50(33-19-38(60)23-39(61)20-33)49-32(18-42(64)26-47(49)67-54)3-1-28-2-16-46-44(17-28)52(56(66-46)31-8-14-37(59)15-9-31)45-25-43(65)27-48-53(45)51(34-21-40(62)24-41(63)22-34)55(68-48)30-6-12-36(58)13-7-30/h1-27,50-52,54-65H/b3-1+/t50-,51-,52+,54+,55+,56-/m0/s1  Y YKey: WZKKRZSJTLGPHH-WHSOPTDBSA-N  Y YInChI=1/C56H42O12/c57-35-10-4-29(5-11-35)54-50(33-19-38(60)23-39(61)20-33)49-32(18-42(64)26-47(49)67-54)3-1-28-2-16-46-44(17-28)52(56(66-46)31-8-14-37(59)15-9-31)45-25-43(65)27-48-53(45)51(34-21-40(62)24-41(63)22-34)55(68-48)30-6-12-36(58)13-7-30/h1-27,50-52,54-65H/b3-1+/t50-,51-,52+,54+,55+,56-/m0/s1
Key: WZKKRZSJTLGPHH-WHSOPTDBBK
|
| Jmol-3D images |
Image
Image |
| PubChem |
16145527 |
OC(C=C1)=CC=C1[C@@H](O2)[C@@H](C3=CC(O)=CC(O)=C3)C4=C2C=C(O)C=C4/C=C/C5=CC([C@H](C6=C([C@H](C7=CC(O)=CC(O)=C7)[C@@H](C8=CC=C(O)C=C8)O9)C9=CC(O)=C6)[C@H](C%10=CC=C(O)C=C%10)O%11)=C%11C=C5 Oc1ccc(cc1)[C@H]4Oc2cc(O)cc(c2[C@@H]4c3cc(O)cc(O)c3)\C=C\c%10ccc%11O[C@@H](c5ccc(O)cc5)[C@@H](c7cc(O)cc8O[C@H](c6ccc(O)cc6)[C@H](c78)c9cc(O)cc(O)c9)c%11c%10
|
| Properties |
| Molecular formula |
C56H42O12 |
| Molar mass |
906.93 g·mol−1 |
Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) |
 N verify (what is: N verify (what is:  Y/ Y/ N?) N?) |
| Infobox references |
|
|
Vitisin C is a hydroxystilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis (grapevines).[1][2]
References
- ↑ Ito, J (1996). "Absolute structures of new hydroxystilbenoids, vitisin C and viniferal, from Vitis vinifera 'Kyohou'". Tetrahedron 52 (30): 9991. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(96)00543-1.
- ↑ Seya, K; Furukawa, K; Taniguchi, S; Kodzuka, G; Oshima, Y; Niwa, M; Motomura, S (2003). "Endothelium-dependent vasodilatory effect of vitisin C, a novel plant oligostilbene from Vitis plants (Vitaceae), in rabbit aorta". Clinical science (London, England : 1979) 105 (1): 73–9. doi:10.1042/CS20020288. PMID 12605596.
External links
|
|---|
|
- Diptoindonesin C
- Diptoindonesin F
- Gnetin H
- Hemsleyanol D
- Isohopeaphenol
- Laetevirenol A, B, C, D and E
- Suffruticosol A and B
- Viniferal
- E-ω-viniferin
- Z-ω-viniferin
| | | Dimers |
- Diptoindonesin G
- Jezonodione
- B
- Scirpusin A
- Tibeticanol (piceatannol dimer)
|
|---|
| | Trimers |
- Amurensin B
- Gnetin E
- Gneyulin A
- Johorenol A
- Ampelopsin E
- Vaticanol G
|
|---|
| | Tetramers: |
- Dibalanocarpol
- Gnetin J (3"-hydroxygnetin E)
- Gnetin K (3"-methoxygnetin E)
- Gnetuhainin R (isorhapontigenin tetramer)
- Laetevirenol F and G
|
|---|
| Higher polymers
(five units or more) | |
|---|
| Oligomeric forms
of resveratrol | Dimers | |
|---|
| Trimers | |
|---|
| Tetramers | |
|---|
| Pentamers | |
|---|
| Hexamers | |
|---|
| Higher polymers |
- γ-viniferin
- Valeriaphenol A
|
|---|
|
|---|
| | Glycosides or conjugates |
- Diptoindonesin A (C-glucoside of ε-viniferin)
- Foeniculoside I (glucoside of miyabenol C), II, III and IV
- Laevifonol (an ε-viniferin-ascorbic acid hybrid compound)
- Laevifoside (O-glucoside of ampelopsin A)
|
|---|
|
