Viscoelasticity
| Continuum mechanics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
|
Laws
|
||||
Viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like honey, resist shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Elastic materials strain when stretched and quickly return to their original state once the stress is removed. Viscoelastic materials have elements of both of these properties and, as such, exhibit time-dependent strain. Whereas elasticity is usually the result of bond stretching along crystallographic planes in an ordered solid, viscosity is the result of the diffusion of atoms or molecules inside an amorphous material.[1]
Background
In the nineteenth century, physicists such as Maxwell, Boltzmann, and Kelvin researched and experimented with creep and recovery of glasses, metals, and rubbers.[2] Viscoelasticity was further examined in the late twentieth century when synthetic polymers were engineered and used in a variety of applications.[2] Viscoelasticity calculations depend heavily on the viscosity variable, η. The inverse of η is also known as fluidity, φ. The value of either can be derived as a function of temperature or as a given value (i.e. for a dashpot).[1]

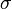 ) to a change in strain rate (d
) to a change in strain rate (d /dt)
/dt)Depending on the change of strain rate versus stress inside a material the viscosity can be categorized as having a linear, non-linear, or plastic response. When a material exhibits a linear response it is categorized as a Newtonian material.[1] In this case the stress is linearly proportional to the strain rate. If the material exhibits a non-linear response to the strain rate, it is categorized as Non-Newtonian fluid. There is also an interesting case where the viscosity decreases as the shear/strain rate remains constant. A material which exhibits this type of behavior is known as thixotropic.[1] In addition, when the stress is independent of this strain rate, the material exhibits plastic deformation.[1] Many viscoelastic materials exhibit rubber like behavior explained by the thermodynamic theory of polymer elasticity. In reality all materials deviate from Hooke's law in various ways, for example by exhibiting viscous-like as well as elastic characteristics. Viscoelastic materials are those for which the relationship between stress and strain depends on time. Anelastic solids represent a subset of viscoelastic materials: they have a unique equilibrium configuration and ultimately recover fully after removal of a transient load.
Some phenomena in viscoelastic materials are:
- if the stress is held constant, the strain increases with time (creep)
- if the strain is held constant, the stress decreases with time (relaxation)
- the effective stiffness depends on the rate of application of the load
- if cyclic loading is applied, hysteresis (a phase lag) occurs, leading to a dissipation of mechanical energy
- acoustic waves experience attenuation
- rebound of an object following an impact is less than 100%
- during rolling, frictional resistance occurs

All materials exhibit some viscoelastic response. In common metals such as steel or aluminum, as well as in quartz, at room temperature and at small strain, the behavior does not deviate much from linear elasticity. Synthetic polymers, wood, and human tissue as well as metals at high temperature display significant viscoelastic effects. In some applications, even a small viscoelastic response can be significant. To be complete, an analysis or design involving such materials must incorporate their viscoelastic behavior. Knowledge of the viscoelastic response of a material is based on measurement.
Some examples of viscoelastic materials include amorphous polymers, semicrystalline polymers, biopolymers, metals at very high temperatures, and bitumen materials. Cracking occurs when the strain is applied quickly and outside of the elastic limit. Ligaments and tendons are viscoelastic, so the extent of the potential damage to them depends both on the velocity of the change of their length as well as on the force applied.
A viscoelastic material has the following properties:
- hysteresis is seen in the stress–strain curve
- stress relaxation occurs: step constant strain causes decreasing stress
- creep occurs: step constant stress causes increasing strain
Elastic behavior versus viscoelastic behavior
Unlike purely elastic substances, a viscoelastic substance has an elastic component and a viscous component. The viscosity of a viscoelastic substance gives the substance a strain rate dependence on time.[1] Purely elastic materials do not dissipate energy (heat) when a load is applied, then removed.[1] However, a viscoelastic substance loses energy when a load is applied, then removed. Hysteresis is observed in the stress–strain curve, with the area of the loop being equal to the energy lost during the loading cycle.[1] Since viscosity is the resistance to thermally activated plastic deformation, a viscous material will lose energy through a loading cycle. Plastic deformation results in lost energy, which is uncharacteristic of a purely elastic material's reaction to a loading cycle.[1]
Specifically, viscoelasticity is a molecular rearrangement. When a stress is applied to a viscoelastic material such as a polymer, parts of the long polymer chain change positions. This movement or rearrangement is called Creep. Polymers remain a solid material even when these parts of their chains are rearranging in order to accompany the stress, and as this occurs, it creates a back stress in the material. When the back stress is the same magnitude as the applied stress, the material no longer creeps. When the original stress is taken away, the accumulated back stresses will cause the polymer to return to its original form. The material creeps, which gives the prefix visco-, and the material fully recovers, which gives the suffix -elasticity.[2]
Types of viscoelasticity
Linear viscoelasticity is when the function is separable in both creep response and load. All linear viscoelastic models can be represented by a Volterra equation connecting stress and strain:
or
where
- t is time
-
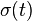 is stress
is stress -
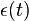 is strain
is strain -
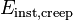 and
and 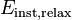 are instantaneous elastic moduli for creep and relaxation
are instantaneous elastic moduli for creep and relaxation - K(t) is the creep function
- F(t) is the relaxation function
Linear viscoelasticity is usually applicable only for small deformations.
Nonlinear viscoelasticity is when the function is not separable. It usually happens when the deformations are large or if the material changes its properties under deformations.
An anelastic material is a special case of a viscoelastic material: an anelastic material will fully recover to its original state on the removal of load.
Dynamic modulus
Viscoelasticity is studied using dynamic mechanical analysis, applying a small oscillatory stress and measuring the resulting strain.
- Purely elastic materials have stress and strain in phase, so that the response of one caused by the other is immediate.
- In purely viscous materials, strain lags stress by a 90 degree phase lag.
- Viscoelastic materials exhibit behavior somewhere in the middle of these two types of material, exhibiting some lag in strain.
Complex Dynamic modulus G can be used to represent the relations between the oscillating stress and strain:
where  ;
; 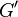 is the storage modulus and
is the storage modulus and 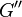 is the loss modulus:
is the loss modulus:
where 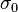 and
and 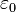 are the amplitudes of stress and strain and
are the amplitudes of stress and strain and 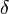 is the phase shift between them.
is the phase shift between them.
Constitutive models of linear viscoelasticity
Viscoelastic materials, such as amorphous polymers, semicrystalline polymers, biopolymers and even the living tissue and cells,[3] can be modeled in order to determine their stress and strain or force and displacement interactions as well as their temporal dependencies. These models, which include the Maxwell model, the Kelvin–Voigt model, and the Standard Linear Solid Model, are used to predict a material's response under different loading conditions. Viscoelastic behavior has elastic and viscous components modeled as linear combinations of springs and dashpots, respectively. Each model differs in the arrangement of these elements, and all of these viscoelastic models can be equivalently modeled as electrical circuits. In an equivalent electrical circuit, stress is represented by current, and strain rate by voltage. The elastic modulus of a spring is analogous to a circuit's capacitance (it stores energy) and the viscosity of a dashpot to a circuit's resistance (it dissipates energy).
The elastic components, as previously mentioned, can be modeled as springs of elastic constant E, given the formula:
where σ is the stress, E is the elastic modulus of the material, and ε is the strain that occurs under the given stress, similar to Hooke's Law.
The viscous components can be modeled as dashpots such that the stress–strain rate relationship can be given as,
where σ is the stress, η is the viscosity of the material, and dε/dt is the time derivative of strain.
The relationship between stress and strain can be simplified for specific stress rates. For high stress states/short time periods, the time derivative components of the stress–strain relationship dominate. A dashpot resists changes in length, and in a high stress state it can be approximated as a rigid rod. Since a rigid rod cannot be stretched past its original length, no strain is added to the system[4]
Conversely, for low stress states/longer time periods, the time derivative components are negligible and the dashpot can be effectively removed from the system - an "open" circuit. As a result, only the spring connected in parallel to the dashpot will contribute to the total strain in the system[4]
Maxwell model

The Maxwell model can be represented by a purely viscous damper and a purely elastic spring connected in series, as shown in the diagram. The model can be represented by the following equation:
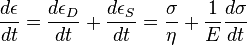 .
.
Under this model, if the material is put under a constant strain, the stresses gradually relax. When a material is put under a constant stress, the strain has two components. First, an elastic component occurs instantaneously, corresponding to the spring, and relaxes immediately upon release of the stress. The second is a viscous component that grows with time as long as the stress is applied. The Maxwell model predicts that stress decays exponentially with time, which is accurate for most polymers. One limitation of this model is that it does not predict creep accurately. The Maxwell model for creep or constant-stress conditions postulates that strain will increase linearly with time. However, polymers for the most part show the strain rate to be decreasing with time.[2]
Applications to soft solids: thermoplastic polymers in the vicinity of their melting temperature, fresh concrete (neglecting its aging), numerous metals at a temperature close to their melting point.
Kelvin–Voigt model

The Kelvin–Voigt model, also known as the Voigt model, consists of a Newtonian damper and Hookean elastic spring connected in parallel, as shown in the picture. It is used to explain the creep behaviour of polymers.
The constitutive relation is expressed as a linear first-order differential equation:
This model represents a solid undergoing reversible, viscoelastic strain. Upon application of a constant stress, the material deforms at a decreasing rate, asymptotically approaching the steady-state strain. When the stress is released, the material gradually relaxes to its undeformed state. At constant stress (creep), the Model is quite realistic as it predicts strain to tend to σ/E as time continues to infinity. Similar to the Maxwell model, the Kelvin–Voigt model also has limitations. The model is extremely good with modelling creep in materials, but with regards to relaxation the model is much less accurate.
Applications: organic polymers, rubber, wood when the load is not too high.
Standard linear solid model
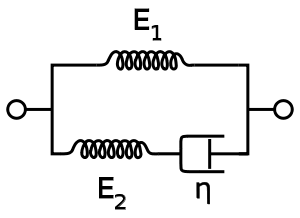
The Standard Linear Solid Model effectively combines the Maxwell Model and a Hookean spring in parallel. A viscous material is modeled as a spring and a dashpot in series with each other, both of which are in parallel with a lone spring. For this model, the governing constitutive relation is:
Under a constant stress, the modeled material will instantaneously deform to some strain, which is the elastic portion of the strain, and after that it will continue to deform and asymptotically approach a steady-state strain. This last portion is the viscous part of the strain. Although the Standard Linear Solid Model is more accurate than the Maxwell and Kelvin–Voigt models in predicting material responses, mathematically it returns inaccurate results for strain under specific loading conditions and is rather difficult to calculate.
Generalized Maxwell Model

The Generalized Maxwell model also known as the Maxwell–Wiechert model (after James Clerk Maxwell and E Wiechert [5][6]) is the most general form of the linear model for viscoelasticity. It takes into account that the relaxation does not occur at a single time, but at a distribution of times. Due to molecular segments of different lengths with shorter ones contributing less than longer ones, there is a varying time distribution. The Wiechert model shows this by having as many spring–dashpot Maxwell elements as are necessary to accurately represent the distribution. The figure on the right shows the generalised Wiechert model [7] Applications : metals and alloys at temperatures lower than one quarter of their absolute melting temperature (expressed in K).
Prony series
In a one-dimensional relaxation test, the material is subjected to a sudden strain that is kept constant over the duration of
the test, and the stress is measured over time. The initial stress is due to the elastic response of the material. Then, the
stress relaxes over time due to the viscous effects in the material. Typically, either a tensile, compressive, bulk
compression, or shear strain is applied. The resulting stress vs. time data can be fitted with a number of equations, called
models. Only the notation changes depending of the type of strain applied: tensile-compressive relaxation is denoted 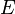 , shear
is denoted
, shear
is denoted 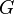 , bulk is denoted
, bulk is denoted 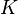 . The Prony series for the shear relaxation is
. The Prony series for the shear relaxation is
where 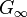 is the long term modulus once the material is totally relaxed,
is the long term modulus once the material is totally relaxed, 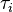 are the relaxation times (not to be confused with
are the relaxation times (not to be confused with 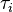 in the diagram); the higher
their values, the longer it takes for the stress to relax. The data is fitted with the equation by using a minimization
algorithm that adjust the parameters (
in the diagram); the higher
their values, the longer it takes for the stress to relax. The data is fitted with the equation by using a minimization
algorithm that adjust the parameters (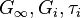 ) to minimize the error between the predicted and data values
.[8]
) to minimize the error between the predicted and data values
.[8]
An alternative form is obtained noting that the elastic modulus is related to the long term modulus by
Therefore,
This form is convenient when the elastic shear modulus 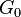 is obtained from data independent from the relaxation data, and/or
for computer implementation, when it is desired to specify the elastic properties separately from the viscous properties, as in
.[9]
is obtained from data independent from the relaxation data, and/or
for computer implementation, when it is desired to specify the elastic properties separately from the viscous properties, as in
.[9]
A creep experiment is usually easier to perform than a relaxation one, so most data is available as (creep) compliance vs. time.[10] Unfortunately, there is no known closed form for the (creep) compliance in terms of the coefficient of the Prony series. So, if one has creep data, it is not easy to get the coefficients of the (relaxation) Prony series, which are needed for example in.[9] An expedient way to obtain these coefficients is the following. First, fit the creep data with a model that has closed form solutions in both compliance and relaxation; for example the Maxwell-Kelvin model (eq. 7.18-7.19) in [11] or the Standard Solid Model (eq. 7.20-7.21) in [11] (section 7.1.3). Once the parameters of the creep model are known, produce relaxation pseudo-data with the conjugate relaxation model for the same times of the original data. Finally, fit the pseudo data with the Prony series.
Effect of temperature on viscoelastic behavior
The secondary bonds of a polymer constantly break and reform due to thermal motion. Application of a stress favors some conformations over others, so the molecules of the polymer will gradually "flow" into the favored conformations over time.[12] Because thermal motion is one factor contributing to the deformation of polymers, viscoelastic properties change with increasing or decreasing temperature. In most cases, the creep modulus, defined as the ratio of applied stress to the time-dependent strain, decreases with increasing temperature. Generally speaking, an increase in temperature correlates to a logarithmic decrease in the time required to impart equal strain under a constant stress. In other words, it takes less work to stretch a viscoelastic material an equal distance at a higher temperature than it does at a lower temperature.
Viscoelastic creep
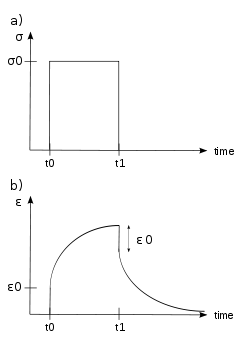
When subjected to a step constant stress, viscoelastic materials experience a time-dependent increase in strain. This phenomenon is known as viscoelastic creep.
At a time  , a viscoelastic material is loaded with a constant stress that is maintained for a sufficiently long time period. The material responds to the stress with a strain that increases until the material ultimately fails, if it is a viscoelastic liquid. If, on the other hand, it is a viscoelastic solid, it may or may not fail depending on the applied stress versus the material's ultimate resistance. When the stress is maintained for a shorter time period, the material undergoes an initial strain until a time
, a viscoelastic material is loaded with a constant stress that is maintained for a sufficiently long time period. The material responds to the stress with a strain that increases until the material ultimately fails, if it is a viscoelastic liquid. If, on the other hand, it is a viscoelastic solid, it may or may not fail depending on the applied stress versus the material's ultimate resistance. When the stress is maintained for a shorter time period, the material undergoes an initial strain until a time 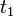 , after which the strain immediately decreases (discontinuity) then gradually decreases at times
, after which the strain immediately decreases (discontinuity) then gradually decreases at times 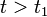 to a residual strain.
to a residual strain.
Viscoelastic creep data can be presented by plotting the creep modulus (constant applied stress divided by total strain at a particular time) as a function of time.[13] Below its critical stress, the viscoelastic creep modulus is independent of stress applied. A family of curves describing strain versus time response to various applied stress may be represented by a single viscoelastic creep modulus versus time curve if the applied stresses are below the material's critical stress value.
Viscoelastic creep is important when considering long-term structural design. Given loading and temperature conditions, designers can choose materials that best suit component lifetimes.
Measuring viscoelasticity
Though there are many instruments that test the mechanical and viscoelastic response of materials, broadband viscoelastic spectroscopy (BVS) and resonant ultrasound spectroscopy (RUS) are more commonly used to test viscoelastic behavior because they can be used above and below ambient temperatures and are more specific to testing viscoelasticity. These two instruments employ a damping mechanism at various frequencies and time ranges with no appeal to time–temperature superposition.[14] Using BVS and RUS to study the mechanical properties of materials is important to understanding how a material exhibiting viscoelasticity will perform.[14]
See also
- Viscosity
- Elasticity
- Blood Viscoelasticity
- Viscoplasticity
- Bingham plastic
- Polymer
- Creep
- Stress relaxation
- Hysteresis
- Biomaterial
- Biomechanics
- Rubber Elasticity
- Rheology
- Glass transition
- Constant Viscosity Elastic (Boger) Fluids
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 Meyers and Chawla (1999): "Mechanical Behavior of Materials", 98-103.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 McCrum, Buckley, and Bucknell (2003): "Principles of Polymer Engineering," 117-176.
- ↑ Biswas, Abhijit; Manivannan, M.; Srinivasan, Mandyam A. (2015). "Multiscale Layered Biomechanical Model of the Pacinian Corpuscle". IEEE Transactions on Haptics 8 (1): 31–42. doi:10.1109/TOH.2014.2369416. PMID 25398182.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Van Vliet, Krystyn J. (2006); "3.032 Mechanical Behavior of Materials"
- ↑ Wiechert, E (1889); "Ueber elastische Nachwirkung", Dissertation, Königsberg University, Germany
- ↑ Wiechert, E (1893); "Gesetze der elastischen Nachwirkung für constante Temperatur", Annalen der Physik, 286, 335–348, 546–570
- ↑ Roylance, David (2001); "Engineering Viscoelasticity", 14-15
- ↑ E. J. Barbero. Time-temperature-age Superposition Principle for Predicting Long-term Response of Linear Viscoelastic Materials, chapter 2 in Creep and fatigue in polymer matrix composites. Woodhead, 2011..
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Simulia. Abaqus Analysis User's Manual, 19.7.1 Time domain vicoelasticity, 6.10 edition, 2010
- ↑ Computer Aided Material Preselection by Uniform Standards
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 E. J. Barbero. Finite Element Analysis of Composite Materials. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 2007.
- ↑ S.A. Baeurle, A. Hotta, A.A. Gusev, Polymer 47, 6243-6253 (2006).
- ↑ Rosato, et al. (2001): "Plastics Design Handbook", 63-64.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Rod Lakes (1998). Viscoelastic solids. CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-9658-1.
- Silbey and Alberty (2001): Physical Chemistry, 857. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Allen and Thomas (1999): The Structure of Materials, 51.
- Crandal et al. (1999): An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids 348
- J. Lemaitre and J. L. Chaboche (1994) Mechanics of solid materials
- Yu. Dimitrienko (2011) Nonlinear continuum mechanics and Large Inelastic Deformations, Springer, 772p
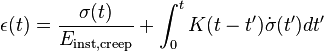
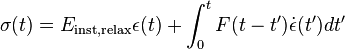
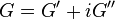
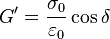
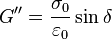
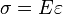
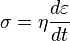
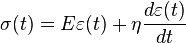
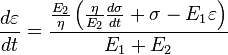
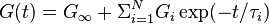
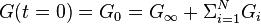
![G(t) = G_0 - \Sigma_{i=1}^{N} G_i [1-\exp(-t/\tau_i)]](../I/m/bb9953b83a719a3b4801b16f8bdf614a.png)