Virgin Islands
| Virgin Islands | |
 U.S. Virgin Islands |
 British Virgin Islands |
 Puerto Rico | |
 | |
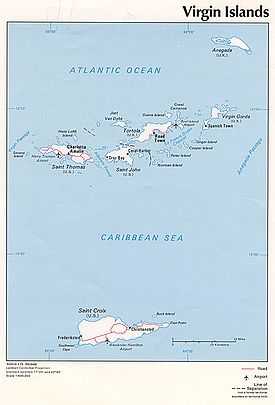
The Virgin Islands are the western island group of the Leeward Islands, which are the northern part of the Lesser Antilles, and form the border between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Politically, the eastern islands form the British Virgin Islands and the western ones form the Virgin Islands of the United States. The British Virgin Islands is an overseas territory of the United Kingdom comprising approximately 60 islands and cays including Tortola, Virgin Gorda, Jost Van Dyke, and Anegada.
The U.S. Virgin Islands is one of five inhabited insular areas of the United States, along with American Samoa, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, and Puerto Rico. The territory comprises a number of islands including St. Croix, St. John, St. Thomas and Water Island.
The Virgin Passage separates the American Virgin Islands from the so-called Spanish Virgin Islands of Vieques and Culebra, which are part of Puerto Rico. The United States dollar is the official currency on both the British and American Virgin Islands as well as the Spanish/Puerto Rican Virgin Islands.
Etymology

Christopher Columbus named the islands after Saint Ursula and the 11,000 Virgins (Spanish: Santa Úrsula y las Once Mil Vírgenes), shortened to the Virgins (las Vírgenes). The official name of the British territory is the Virgin Islands, and the official name of the U.S. territory is the Virgin Islands of the United States. In practice, the two island groups are almost universally referred to as the British Virgin Islands and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
History
The Virgin Islands were originally inhabited by the Arawak, Carib, and Cermic, all of whom are thought to have perished during the colonial period due to enslavement, foreign disease, and mass extermination brought by European colonists.
European colonists later settled here and established sugar plantations, at least one tobacco plantation, and purchased slaves acquired from Africa. The plantations are gone, but the descendants of the slaves remain the bulk of the population, sharing a common African-Caribbean heritage with the rest of the English-speaking Caribbean.
In 1916 and 1917, Denmark and the U.S., respectively, ratified a treaty in which Denmark sold the Danish West Indies to the United States of America for $25 million in gold.
In the 1990s a Puerto Rican tourism campaign renamed the Passage Islands as the Spanish Virgin Islands, though they are seldom identified as such on maps and atlases. They are part of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, located east of the main island of Puerto Rico. They are closer to St. Thomas than St. Thomas is to St. Croix.
Traffic control
Motor vehicles are driven on the left-hand side of the road in both the British and the U.S. Virgin Islands, although the steering wheels on most cars are located on the left side (as is the norm for drive-on-the-right localities). Only on the so-called Spanish Virgin Islands are vehicles driven on the right-hand side of the road.
Larger Islands
| Rank | Island | Area (km) | Area (sq mi) | Population (2010) | Administration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Saint Croix | 214 km² | 82 sq mi | 50,601 | |
| 2 | Vieques (not historically considered part of the Virgin Islands) | 135 km² | 52 sq mi | 9,301 | |
| 3 | Saint Thomas | 80.91 km² | 31.23 sq mi | 51,634 | |
| 4 | Tortola | 55.7 km² | 21.5 sq mi | 23,908 | |
| 5 | Saint John | 51 km² | 19.6 sq mi | 4,170 | |
| 6 | Anegada | 38 km² | 15 sq mi | 200 | |
| 7 | Culebra (not historically considered part of the Virgin Islands) | 30.1 km² | 11 sq mi | 1,818 | |
| 8 | Virgin Gorda | 21 km² | 8 sq mi | 3,000 | |
See also
- Culture of the Virgin Islands
- Music of the Virgin Islands
- Virgin Islands Creole
- British Virgin Islands
- Dutch Virgin Islands
- Danish West Indies
- Lesser Antilles
- Spanish Virgin Islands
- United States Virgin Islands
References
- Colin Thomas J.,William Albert Allard,Cary Wolinsky, "Paradise Comes of age:The U.S. Virgin Islands",National Geographic, February 1981, vol.159,no.2, pp.225-243 (16 pictures.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Virgin Islands. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Virgin Islands. |