Vertebra
| Vertebra | |
|---|---|
 A typical vertebra, superior view | |
 A section of the human vertebral column, showing multiple vertebrae in a left posterolateral view. | |
| Details | |
| Latin | Vertebratus |
| Identifiers | |
| TA | A02.2.01.001 |
| FMA | 9914 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.
Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.
Structure
The size of vertebrae varies according to placement, spinal loading, posture and pathology. Along the length of the vertebral column the vertebrae change to accommodate different needs related to stress and mobility.[1]
Every vertebra has a body, which consists of a large anterior middle portion called the centrum and a posterior vertebral arch, also called a neural arch.[2] The body is composed of cancellous bone, which is the spongy type of osseous tissue, whose micro-anatomy has been specifically studied within the pedicle bones.[3] This cancellous bone is in turn, covered by a thin coating of cortical bone (or compact bone), the hard and dense type of osseous tissue. The vertebral arch and processes have thicker coverings of cortical bone. The upper and lower surfaces of the body of the vertebra are flattened and rough in order to give attachment to the intervertebral discs. These surfaces are the vertebral endplates which are in direct contact with the intervertebral discs and form the joint. The endplates are formed from a thickened layer of the cancellous bone of the vertebral body, the top layer being more dense. The endplates function to contain the adjacent discs, to evenly spread the applied loads, and to provide anchorage for the collagen fibers of the disc. They also act as a semi-permeable interface for the exchange of water and solutes.[4]

The vertebral arch is formed by pedicles and laminae. Two pedicles extend from the sides of the vertebral body to join the body to the arch. The pedicles are short thick processes that extend, one from each side, posteriorly, from the junctions of the posteriolateral surfaces of the centrum, on its upper surface. From each pedicle a broad plate, a lamina, projects backwards and medialwards to join and complete the vertebral arch and form the posterior border of the vertebral foramen, which completes the triangle of the vertebral foramen.[5] The upper surfaces of the laminae are rough to give attachment to the ligamenta flava. These ligaments connect the laminae of adjacent vertebra along the length of the spine from the level of the second cervical vertebra. Above and below the pedicles are shallow depressions called vertebral notches (superior and inferior). When the vertebrae articulate the notches align with those on adjacent vertebrae and these form the openings of the vertebral foramina. The foramina allow the entry and exit of the spinal nerves from each vertebra, together with associated blood vessels. The articulating vertebrae provide a strong pillar of support for the body.
There are seven processes projecting from the vertebra; a spinous process, two transverse processes, and four articular processes. A major part of a vertebra is a backward extending spinous process which projects centrally. In humans this process points downwards but in those animals without an erect stance they are directed upwards. The spinous process serves to attach muscles and ligaments.
There are two transverse processes, on each side of the vertebral body which project from either side at the point where the lamina joins the pedicle, between the superior and inferior articular processes. They also serve for the attachment of muscles and ligaments. There is a facet on each of the transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae which articulates with the tubercle of the rib.[6] A facet on each side of the thoracic vertebral body articulates with the head of head of the rib. There are superior and inferior articular facets on each side of the vertebra, which serve to restrict the range of movement possible. These facets are joined by a thin portion of the neural arch called the pars interarticularis.
The transverse process of a lumbar vertebra is also sometimes called the costal[7][8] or costiform process[9] because it corresponds to a rudimentary rib (costa) which, as opposed to the thorax, is not developed in the lumbar region.[10][9]
Variation
The thirty-three vertebrae in the human vertebral column are named after the regions they occupy. There are seven cervical vertebrae, twelve thoracic vertebrae, five lumbar vertebrae, five fused sacral vertebrae forming the sacrum and three to five coccygeal vertebrae, forming the coccyx. The regional vertebrae increase in size as they progress downwards but become smaller in the coccyx.
Cervical vertebrae

There are seven cervical bones (but eight cervical spinal nerves) and these bones are, in general, small and delicate. Their spinous processes are short (with the exception of C2 and C7, which have palpable spinous processes). Numbered top-to-bottom from C1-C7, atlas (C1) and axis (C2), are the vertebrae that allow the neck and head so much movement. The atlanto-occipital joint allows the skull to move up and down, while the atlanto-axial joint allows the upper neck to twist left and right. The axis also sits upon the first intervertebral disc of the spinal column.
Cervical vertebrae possess transverse foramina to allow for the vertebral arteries to pass through on their way to the foramen magnum to end in the circle of Willis. These are the smallest, lightest vertebrae and the vertebral foramina are triangular in shape. The spinous processes are short and often bifurcated (the spinous process of C7, however, is not bifurcated, and is substantially longer than that of the other cervical spinous processes).
The term cervicothoracic is often used to refer to the cervical and thoracic vertebrae together, and sometimes also their surrounding areas.
The first and upper two cervical vertebrae of the neck differ from the others and have specific names of atlas (C1), and axis (C2). They form two joints which gives the head its greater range of movement and ability to twist round. These are the atlanto-occipital joint between the atlas and the occipital bone, and the atlanto-axial joint between the atlas and the axis.
The atlas differs from the other vertebrae in that it has no body and no spinous process. It has instead a ring-like form, having an anterior and a posterior arch and two lateral masses. At the outside centre points of both arches there is a tubercle; an anterior tubercle and a posterior tubercle for the attachment of muscles. The front surface of the anterior arch is convex and its anterior tubercle gives attachment to the longus colli muscle. The posterior tubercle is a rudimentary spinous process and gives attachment to the rectus capitis posterior minor muscle. The spinous process is small so as not to interfere with the movement between the atlas and the skull. On the under surface is a facet for articulation with the dens of the axis.
Specific to the cervical vertebra is the transverse foramen, (also known as foramen transversarium). This is an opening on each of the transverse processes which gives passage to the vertebral artery and vein and a sympathetic nerve plexus. On the cervical vertebrae other than the atlas, the anterior and posterior tubercles are on either side of the transverse foramen on each transverse process. The anterior tubercle on the sixth cervical vertebra is called the carotid tubercle because it separates the carotid artery from the vertebral artery.
There is a hook-shaped uncinate process on the side edges of the top surface of the bodies of the third to the seventh cervical vertebrae, and also of the first thoracic vertebra. This uncinate process prevents a vertebra from sliding backwards off the vertebra below it and limits lateral flexion (side-bending). Luschka's joints involve the vertebral uncinate processes.
Thoracic vertebrae

The twelve thoracic bones and their transverse processes have surfaces that articulate with the ribs. Some rotation can occur between the thoracic vertebrae, but their connection with the rib cage prevents much flexion or other excursion. They may also be known as 'dorsal vertebrae', in the human context.
The vertebral bodies are roughly heart-shaped and are about as wide anterio-posterioly as they are in the transverse dimension. Vertebral foramina are roughly circular in shape.
The term thoracolumbar is sometimes used to refer to the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae together, and sometimes also their surrounding areas.
The thoracic vertebrae attach to ribs and so have articular facets specific to them. As they progress down the spine they increase in size to match up with the adjoining lumbar section.
Lumbar vertebrae


These five lumbar vertebrae are the largest of the vertebrae and are very robust in construction, as they need to support more weight than the other vertebrae. They allow significant flexion, extension and moderate lateral flexion (side-bending). The discs between these vertebrae create a natural lumbar lordosis (a spinal curvature that is concave posteriorly).This is due to the difference in thickness between the front and back parts of the intervertebral discs.
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the ribcage and the pelvis and are the largest of the vertebrae. The pedicles are strong as are the laminae and the spinous process is thick and broad. The vertebral foramen is large and triangular. The transverse processes are long and narrow and three tubercles can be seen on them. These are a lateral cosiform process, a mammillary process and an accessory process.[11] The superior, or upper tubercle is the mammillary process which connects with the superior articular process. The multifidus muscle attaches to the mammillary process and this muscle extends through the length of the vertebral column, giving support. The inferior, or lower tubercle is the accessory process and this is found at the back part of the base of the transverse process. The term lumbosacral is often used to refer to the lumbar and sacral vertebrae together, and sometimes includes their surrounding areas.
Sacrum
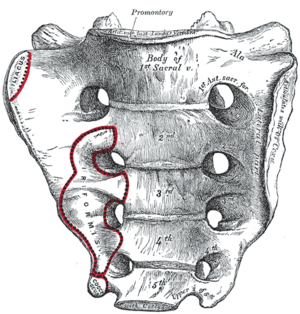
There are five sacral vertebrae (S1-S5) which are fused in maturity, into one large bone the sacrum with no intervertebral discs.[12]The sacrum with the ilium forms a sacroiliac joint on each side of the pelvis, which articulates with the hips.
Coccyx
The last three to five coccygeal vertebrae (but usually four) (Co1-Co5) make up the tailbone or coccyx. There are no intervertebral discs.
Development
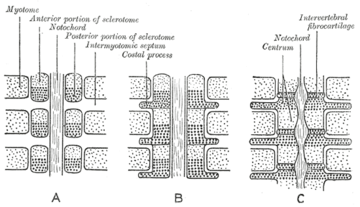
Somites form in the early embryo and some of these develop into sclerotomes. The sclerotome forms the vertebrae as well as the rib cartilage and part of the occipital bone. From their initial location within the somite, the sclerotome cells migrate medially towards the notochord. These cells meet the sclerotome cells from the other side of the paraxial mesoderm. The lower half of one sclerotome fuses with the upper half of the adjacent one to form each vertebral body.[13] From this vertebral body, sclerotome cells move dorsally and surround the developing spinal cord, forming the vertebral arch. Other cells move distally to the costal processes of thoracic vertebrae to form the ribs.[13]
Function
Functions of vertebrae include:
- Support. The vertebrae function in the skeletomuscular system by forming the vertebral column to support the body.
- Protection. Vertebrae contain a vertebral foramen for the passage of the spinal canal and its enclosed spinal cord and covering meninges. They also afford sturdy protection for the spinal cord. The upper and lower surfaces of the centrum are flattened and rough in order to give attachment to the intervertebral discs.
- Movement. The vertebrae also provide the openings, the intervertebral foramina which allow the entry and exit of the spinal nerves. Similarly to the surfaces of the centrum, the upper and lower surfaces of the fronts of the laminae are flattened and rough to give attachment to the ligamenta flava. Working together in the vertebral column their sections provide controlled movement and flexibility.
-

The spinal cord nested in the vertebral column.
-

Vertebral joint
-
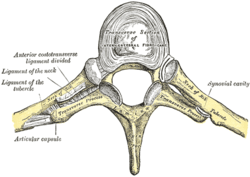
Costovertebral joint
-
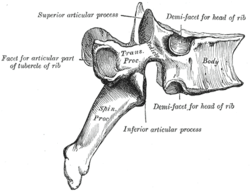
A zygapophysial joint between the superior and inferior articular processes (labeled at top and bottom).
Other animals

In other animals the vertebrae take the same regional names except for the coccygeal – in animals with tails the separate vertebrae are usually called the caudal vertebrae. Because of the different types of locomotion and support needed between the aquatic and other vertebrates, the vertebrae between them show the most variation, though basic features are shared. The spinous processes which are backward extending are directed upwards in animals without an erect stance. These processes can be very large in the larger animals as they attach to the muscles and ligaments of the body. In the elephant the vertebrae are connected by tight joints, which limit the backbone's flexibility.
Vertebrae with saddle-shaped articular surfaces on their bodies, are called "heterocoelous", which allows vertebrae to flex both vertically and horizontally, while preventing twisting motions. Such vertebrae are found in the necks of birds and some turtles.[14]
In many species, though not in mammals, the cervical vertebrae bear ribs. In many groups, such as lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. In the whale the cervical vertebrae are typically fused, an adaptation trading flexibility for stability during swimming.[15][16]All mammals except manatees and sloths have seven cervical vertebrae, whatever the length of the neck.[17]This includes seemingly unlikely animals such as the giraffe, the camel, and the blue whale, for example.
In all mammal species the thoracic vertebrae are connected to ribs and their bodies differ from the other regional vertebrae due to the presence of facets. Each vertebra has a facet on each side of the vertebral body which articulates with the head of a rib. There is also a facet on each of the transverse processes which articulates with the tubercle of a rib.
The number of thoracic vertebrae varies considerably across the species.[18] Most marsupials have thirteen, but koalas only have eleven.[19] The norm is twelve to fifteen in mammals, (twelve in the human), though there are from eighteen to twenty in the horse, tapir, rhinoceros and elephant. In certain sloths there is an extreme number of twenty-five and at the other end only nine in the cetacean.[20]
There are fewer lumbar vertebrae in the Pan genus species of chimpanzees and gorillas, which have three in contrast to the five in the Homo. This reduction in number gives an inability of the lumbar spine to lordose but gives an anatomy that favours vertical climbing, and hanging ability more suited to feeding locations in high-canopied regions.[21] The bonobo differs by having four lumbar vertebrae.
Caudal vertebrae are the bones that make up the tails of vertebrates.[14] They range in number from a few to fifty, depending on the length of the animal's tail. In humans and other tailless primates, they are called the coccygeal vertebrae, number from three to five and are fused into the coccyx.[22]
Clinical significance
There are a number of congenital vertebral anomalies, mostly involving variations in the shape or number of vertebrae, and many of which are unproblematic. Others though can cause compression of the spinal cord. Wedge-shaped vertebrae, called hemivertebrae can cause an angle to form in the spine which can result in the spinal curvature diseases of kyphosis, scoliosis and lordosis. Severe cases can cause spinal cord compression. Block vertebrae where some vertebrae have become fused can cause problems. Spina bifida can result from the incomplete formation of the vertebral arch.
Spinal disc herniation, more commonly called a slipped disc, is the result of a tear in the outer ring (anulus fibrosus) of the intervertebral disc, which lets some of the soft gel-like material, the nucleus pulposus, bulge out in a hernia.
A laminectomy is a surgical operation to remove the laminae in order to access the spinal canal.[23] The removal of just part of a lamina is called a laminotomy.
A pinched nerve caused by pressure from a disc, vertebra or scar tissue might be remedied by a foraminotomy to broaden the intervertebral foramina and relieve pressure. It can also be caused by a foramina stenosis, a narrowing of the nerve opening, as a result of arthritis.
Another condition is spondylolisthesis when one vertebra slips forward onto another. The reverse of this condition is retrolisthesis where one vertebra slips backwards onto another.
The vertebral pedicle is often used as a radiographic marker and entry point in vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty, and spinal fusion procedures.
The arcuate foramen is a common anatomical variation more frequently seen in females. It is a bony bridge found on the first cervical vertebra, the atlas where it covers the groove for the vertebral artery.[24]
Degenerative disc disease is a condition usually associated with ageing in which one or more discs degenerate. This can often be a painfree condition but can also be very painful.
Additional images
-
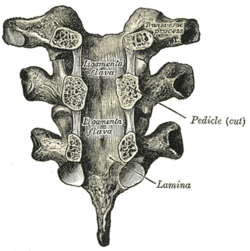
Vertebral arches of three thoracic vertebrae
-
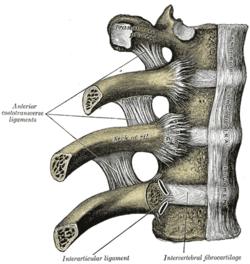
Costovertebral joints seen from the front
-
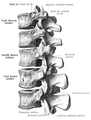
Lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebrae seen from the side
-

Cervical vertebrae seen from the back
-

Lumbar vertebra seen from above
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ McGraw-Hill Science and Technology
- ↑ Dorland's (2012). Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (32nd ed.). Elsevier Saunders. p. 329. ISBN 978-1-4160-6257-8.
- ↑ C.M. Gdyczynski and A. Manbachi, et al. "On estimating the directionality distribution in pedicle trabecular bone from micro-CT images." 'Journal of Physiological Measurements', 35(12):2415–2428, 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0967-3334/35/12/2415
- ↑ Muller-Gerbl, M et al. (Mar 2008). "The distribution of mineral density in the cervical vertebral endplates". Eur Spine J 17 (17(3)): 432–438. doi:10.1007/s00586-008-0601-5. PMID 18193299.
- ↑ http://www.medterms.com
- ↑ Standring, Susan (2008) Gray's Anatomy p.746 Thoracic vertebrae
- ↑ Platzer (2004), pp 42-43
- ↑ Latin costa refers to either a "rib" or "side" of the body. (Diab (1999), p 76)
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Tweedie, A. The library of medicine p.31
- ↑ Heinz Feneis, Wolfgang Dauber (2000) Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy: Based on the International Nomenclature p.2
- ↑ Postacchini, Franco (1999) Lumbar Disc Herniation p.19
- ↑ Drake et al, Gray's Anatomy for Students, Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier (2010), 2nd edition, chapter 2
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Walker, Warren F., Jr. (1987) Functional Anatomy of the Vertebrate San Francisco: Saunders College Publishing.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Kardong, Kenneth V. (2002). Vertebrates: comparative anatomy, function, evolution. McGraw-Hill. pp. 288–289. ISBN 0-07-290956-0.
- ↑ "Beluga Whale". Yellowmagpie.com. 2012-06-27. Retrieved 2012-08-12.
- ↑ "About Whales". Whalesalive.org.au. 2009-06-26. Retrieved 2013-08-12.
- ↑ books.google.com
- ↑ Hyman, Libbie (1922). Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 123.
- ↑ "Physical Characteristics of the Koala". Australian Koala Foundation. Retrieved 1 February 2012.
- ↑ Hyman (1922), p.124
- ↑ Lovejoy, C.O and McCullum, M.A. (2010). "Spinopelvic pathways to bipedality:why no hominids ever relied on a bent-hip-bent-knee gait". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society.Biological Sciences 365 (1556): 3289–99. doi:10.1098/rstb.2010.0112. PMC 2981964. PMID 20855303. Retrieved June 2014.
- ↑ Hyman, Libbie (1922). Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 125.
- ↑ Dorland's (2012). Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (32nd ed.). Elsevier Saunders. p. 1003. ISBN 978-1-4160-6257-8.
- ↑ Cakmak, O et al. (Sep 2005). "Arcuate foramen its clinical significance". Saudi Med J 26 (26(9)): 1409–13. PMID 16155658.
External links
- Atlas image: back_bone13 at the University of Michigan Health System - Axis & Atlas Articulated, Posterior View
- Anatomy image: skel/atlas2 at Human Anatomy Lecture (Biology 129), Pennsylvania State University
- Anatomy photo:26:os-0110 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy figure: 02:01-10 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy figure: 18:02-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Atlas image: back_bone28 at the University of Michigan Health System
- Anatomy figure: 02:02-08 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||