Vehicle registration plates of Romania

The standard format for vehicle registration plates in Romania is a blue vertical stripe (the "Euroband") on the left side of the plate displaying the 12 stars of the European Union and the country code of Romania (RO), followed – in black characters on a white background – by a one- or two-letter county code and a combination of two or three[1] digits and three capital letters. On plates issued before 1 January 2007 the flag of Romania was used instead of the 12 European stars. The digits and letters are usually assigned at random, unless a customization fee is paid. The plates are issued for each car and for each owner, and they must be returned when the car is either sold or scrapped, although the new buyer is entitled to request continued use of the old number plate. Letter combinations that may form obscene text in Romanian are not issued. The letter "Q" is not used as it may be confused with "O". Also the three-letter code cannot start with "I" or "O", as they can be mistaken with "1" or "0" (until 1999, "I" and "O" were not used at all).
The front plate usually carries a round label displaying the month and year until when the technical inspection of the vehicle is valid. They have different background colors depending on the year displayed.
From 1 January 2010, the authorities in Bucharest began issuing plates with three digits instead of the former two, as it was estimated that the number of available two-digit combinations would run out before the end of that year.[2]
Current license plates
There are six other types of license plates in use in Romania:
- The red plate, consisting of the European strip, followed by the county code and three to six digits, of which the first is always zero and the second is always non-zero. All the writing outside of the European-strip on this plate is in red font. These plates are valid for a maximum of 30 days and they can be issued again for a cumulative period of up to 90 days.[3] They are usually issued by car dealers as temporary registration for their new cars. (Unlike some countries, license plates don't usually stick with either the car or the driver and each new owner must do the car registration again. When the car changes its owner within the same county the plates usually stick to the car, unless the former owner wants to keep the plates or if the new owner wants new plates. When it is transferred to another county the plates are changed, receiving the new county code and a new series, but the former owner may also keep the previous plates.).
 Red plate
Red plate
- There is a variation of this format, used for test vehicles, and having 3 digits following the county code, and the "PROBE" text after the digits. The smallest number used is 100 or 101.
- The black plate, same as the red plate, except for the black number, and a right-sided red strip, containing the end date of the plate's validity (YY/MM format). This kind of plate is used for cars that fall under a leasing agreement, with the plate's validity ending when the contract expires. However, there are cars under leasing contracts, that have regular registration plates, that depending on the way the registration taxes are being paid. Foreign citizens, having temporary residence, have their cars registered with such plates.
 Temporary plate
Temporary plate - The diplomatic plate contains the European strip, followed in blue by the text CO, CD (Corp Diplomatic), or TC (Taxi creditar, usually issues to lower-ranking service staff) and 6 numbers. The first three numbers stand for the country or international organization, the last three usually for the rank of the owner. The lowest number for both sets of 3 is 101. Thus, a car with license plate number 123 101 would refer to Switzerland's (Switzerland is 123) ambassador (ambassadors' or heads of missions' official car usually is 101). The license plate is issued exclusively to diplomats, and cars having such plates enjoy diplomatic immunity. Initially, the countries or organizations received codes in their alphabetical order. Later, some countries like United States or Russia, received more than one code, although it could be up to 899 registered cars per country/organization code.Diplomatic plate
- MAI plateThe special plates can be issued by agencies, ministries and local administration for use on their vehicles. Currently, the Army, the Ministry of Administration and Interior and Mayor's Offices are allowed to issue such numbers. Their format, size and style is decided by each ministry via internal regulations - for example - the Army uses plates containing no European strip (as their regulations predate the 1992 regulation imposing the European strip), with the letter "A" (Army) followed by 3 to 7 digits (3 to 4 for small vehicles, and more than 4 for heavy vehicles). Army plates issued more recently (from 2002 onwards) have the European strip. The Ministry of Administration and Interior standard is identical to the one used by the Army, with the exception that it reads "MAI" instead of "A" and can be often seen on Gendarmerie or Police vehicles.Army plate
- The yellow background plates are issued by the local authorities such as municipalities, village or commune mayoralties for the registration of certain light vehicles, or other types of vehicles that do not need state level authorization, such as public utility vehicles, some light garbage trucks, lawn mowers, small sanitation vehicles, trolleybuses, trams, quad bikes, scooters, golf carts and non-road going vehicles, such as combine harvesters, non-road-going tractors, horse-drawn carts, etc. The format of the plate is not fully standardized. Most of the local authorities used the yellow plate, but there are exceptions like Cluj-Napoca, which used white plate similar to old German plates, but always bearing the letters CJ-N (from the city name's abbreviation), followed by 3 digits. Other cities or villages use their coat of arms or initials, or even their entire name, some times followed by the county name or abbreviation. All that is followed by a fixed-length number (4 to 6 digits, but same size for the same issuing authority). The first number to be issued is usually 1, zero-padded to the left if needed. These vehicles cannot leave the jurisdiction of the authority that issued the plate, but it is common to such vehicles (mostly scooters) to travel within the county limits, or even travel to other counties. Some of these vehicles bear temporary plates while being towed to their destination, if that means crossing the limits of the county where they have been initially registered. This usually happens to trolleybuses on their way from the factory to the transport company. Dual-powered buses are registered with standard number plates. Trams may not bear the plate itself, but are required to somehow bear the registration number, either painted or printed on a sticker, usually next to their fleet number. Rented vehicles keep the registration plates issued by the local authority of the region where the owner resides, aven though they are used in another jurisdiction.
 Yellow licence plate for Cisnădie
Yellow licence plate for Cisnădie - White on black background plates are extremely rare, and not clearly specified by the law. They belong to the administration of religious organizations, such as the Romanian Orthodox Church. There are not more than a dozen or two vehicles using such registration plates. They can be mostly seen around important monasteries. The format is identical to the standard one, excepting the reversal of the colours.
County codes
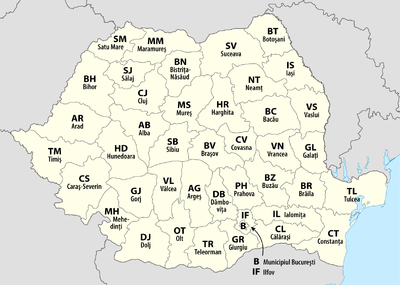
This is the list of counties and their county code (in parentheses the county capital city)
- AB - Alba (Alba Iulia)
- AG - Argeş (Piteşti)
- AR - Arad (Arad)
- B - Bucharest
- BC - Bacău (Bacău)
- BH - Bihor (Oradea)
- BN - Bistriţa-Năsăud (Bistriţa)
- BR - Brăila (Brăila)
- BT - Botoşani (Botoşani)
- BV - Braşov (Braşov)
- BZ - Buzău (Buzău)
- CJ - Cluj (Cluj-Napoca)
- CL - Călăraşi (Călăraşi)
- CS - Caraş-Severin (Reşiţa)
- CT - Constanţa (Constanţa)
- CV - Covasna (Sfântu Gheorghe)
- DB - Dâmboviţa (Târgovişte)
- DJ - Dolj (Craiova)
- GJ - Gorj (Târgu Jiu)
- GL - Galaţi (Galaţi)
- GR - Giurgiu (Giurgiu)
- HD - Hunedoara (Deva)
- HR - Harghita (Miercurea Ciuc)
- IF - Ilfov (Buftea)
- IL - Ialomiţa (Slobozia)
- IS - Iaşi (Iaşi)
- MH - Mehedinţi (Drobeta-Turnu Severin)
- MM - Maramureş (Baia Mare)
- MS - Mureş (Târgu Mureş)
- NT - Neamţ (Piatra Neamţ)
- OT - Olt (Slatina)
- PH - Prahova (Ploieşti)
- SB - Sibiu (Sibiu)
- SJ - Sălaj (Zalău)
- SM - Satu Mare (Satu Mare)
- SV - Suceava (Suceava)
- TL - Tulcea (Tulcea)
- TM - Timiş (Timişoara)
- TR - Teleorman (Alexandria)
- VL - Vâlcea (Râmnicu Vâlcea)
- VN - Vrancea (Focşani)
- VS - Vaslui (Vaslui)
History
1900s - 1908
Plates were first issued at the beginning of the twentieth century. The plates took the simple form of white numbers on a black background, and were home made. The numbers belonged to the owner and not the car, and the list of owners and their numbers was published monthly in the Revista Automobila magazine, edited by the Romanian Royal Automobile club. As there were so few cars (139 in 1908), it was not necessary to note the region on the number plate. Registration was done centrally by the Mayor of Bucharest. Interestingly, the first number registered was 0, to Prince Bibescu, president of the Automobile Club (ACR). Institutes as well as individuals could own the numbers.
1908 - 1966
In 1908, a letter to the Mayor of Bucharest addressed the need for a more standardized system with a regional indicator also appearing on the license plate. This was approved in September or October and the new licence plates appeared within the month. In Bucharest and most other counties, the standard plate was a number, followed by a hyphen and the regional abbreviation. Bucharest, for example, was B (Bc before 1914), while Craiova was Cv. In some districts, however, the county code did not come after the number until the 1920s. Period photos of, for example, Lugoj, show the abbreviation Lgs, appearing both before and after the number, depending on whether the owner had changed the license plates to conform to the new regulations. Official royal cars generally had a crown displayed on the plate instead of any other combination.
This system was in place until 1966. However, the frequent territorial and administrative changes of the period meant that the codes changed often. For example, after 1960 a car registered in Craiova as 150-Cv would have changed its license plate to 150-OL, corresponding to the new administrative region Oltenia. Similarly, when Braşov changed its name to Oraşul Stalin in 1952, the regional code was also changed to O.S., before reverting to Bv in 1960. By the 1960s all codes were two letters long and capitalised.
Special numbers were used occasionally to denote the type of vehicles they were on. For a period in the 1930s, in Bucharest, numbers between 10,000-B and 12,999-B (the comma was used as thousands separator) were taxis; some had Tx as an additional tag, as did buses, which started with 15,000-B. In the 1950s, small commercial vehicles were given numbers over 25,000, large commercial vehicles and buses numbers over 50,000, tractors over 65,000 and motorcycles over 75,000. By 1966, when the system was changed, in Bucharest cars had reached over 23,000 and motorcycles over 90,000. Although in the interbellum period 1 was the smallest number possible (0 in Bucharest), under Communism numbers started with 101, possibly after the Soviet system, 01-01.
Interwar-period county codes
| County | Code | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Alba | Al | Alba-Iulia |
| Arad | Ar | Arad |
| Argeş | Pt | Piteşti |
| Bacǎu | Bc | Bacǎu |
| Baia | Flt | Fǎlticeni |
| Bǎlţi | Bţ | Bǎlţi |
| Bihor | Ord | Oradea |
| Brǎila | Br | Brǎila |
| Braşov | Bv | Braşov |
| Botoşani | Bt | Botoşani |
| Buzǎu | Bz | Buzǎu |
| Caliacra | Bzg | Bazargic |
| Cahul | Ch | Cahul |
| Caraş | Orv | Oraviţa |
| Câmpu-Lung | C.Lg | Câmpu-Lung |
| Ciuc | Mr.C | Miercurea-Ciuc |
| Cernǎuţi | Cţi | Cernǎuţi |
| Cetatea Albǎ | C.Al | Cetatea Albǎ |
| Cluj | Clj | Cluj |
| Constanţa | Cţa | Constanţa |
| Covurlui | Gl | Galaţi |
| Dâmboviţa | Tg | Târgovişte |
| Dolj | Cv | Craiova |
| Dorohoi | Dr | Dorohoi |
| Durostor | Sl | Silistra |
| Fǎlciu | Hş | Huşi |
| Fǎgǎraş | Fgs | Fǎgǎraş |
| Gorj | Tg.J | Târgu Jiu |
| Hotin | Ht | Hotin |
| Hunedoara | Dv | Deva |
| Ialomiţa | Cl | Cǎlǎraşi |
| Iaşi | Iş | Iaşi |
| Ilfov | B | Bucureşti |
| Ismail | Is | Ismail |
| Lǎpuşna | Chs | Chişinǎu |
| Maramureş | Sgt | Sighet |
| Mehedinţi | Tr.S | Turnu-Severin |
| Mureş | Tg.M | Târgu-Mureş |
| Muscel | Cp.L | Câmpulung-Muscel |
| Nǎsǎud | Btr | Bistriţa |
| Neamţ | Pn | Piatra-Neamţ |
| Odorhei | Odh | Odorhei |
| Olt | St | Slatina |
| Orhei | Oh | Orhei |
| Prahova | Pl | Ploeşti |
| Putna | Fş | Focşani |
| Rǎdǎuţi | Rdţ | Rǎdǎuţi |
| Râmnicu-Sǎrat | Rm.S | Râmnicu-Sǎrat |
| Roman | Ro | Roman |
| Romanaţi | Cr | Caracal |
| Satu-Mare | St.M | Satu-Mare |
| Sǎlaj | Zal | Zalǎu |
| Severin | Lgş | Lugoj |
| Sibiu | Sb | Sibiu |
| Someş | Dej | Dej |
| Soroca | Sor | Soroca |
| Storojineţ | Stj | Storojineţ |
| Suceava | Suc | Suceava |
| Târnava-Mare | Seg | Sighet |
| Târnava-Micǎ | D-in | Diciosânmartin |
| Tecuci | Tc | Tecuci |
| Teleorman | Tr.M | Turnu-Mǎgurele |
| Timiş-Torontal | Tmş | Timişoara |
| Tighina | Tgh | Tighina |
| Trei-Scaune | St.G | Sfântu-Gheorghe |
| Tulcea | Tl | Tulcea |
| Turda | Trd | Turda |
| Tutova | Bd | Bârlad |
| Vâlcea | Rm.V | Râmnicu-Vâlcea |
| Vaslui | Vs | Vaslui |
| Vlaşca | Gg | Giurgiu |

1966 - 1992
In 1966 the whole system was changed. The new plates were initially issued in the format aa-BB-ccccc:
- The numbers in front (aa) were arranged as follows:
- 1 to 19 - automobiles, since 1990 all private vehicles, regardless of type
- 20 - reserved for automobiles, but never used
- 21 to 30 - freight transport vehicles, including lorry tractor units; also buses, if modified for freight transport
- 31 to 40 - buses, coaches and utility vehicles
- 41 to 45 - road tractors
- 46 to 50 - motorcycles.
- The letters (BB) denoted the administrative regions until 1968, and after that counties (judeţe). Following the 1968 reorganisation of Romania's counties, new codes were introduced. These represented generally the same counties as the ones used today (see the county codes). However, between 1966 and 1968, some old codes were used. Thus, a registration plate for Ploiesti region would be 1-PL-1234, which would have changed after 1968 to 1-PH-1234 (for Prahova). Many codes, however, did not need to change: Bucharest (B), Cluj (CJ) and Sibiu (SB), for example, remained the same.
- The numbers after the county abbreviation (ccccc) were in groups of either three, four or five digits, and were issued in ascending order, starting from 101. The old plates were declared invalid. 101 as the first number may have come from the Soviet-style "first number" 01-01.
- Numbers with 5 digits after the county code were issued only in Bucharest. It started with 1-B-10000 to 1-B-99999, then 2-B-10000 to 59999, until the change of the system. 9-B-10000 to 9-B-39999 were issued, between the early 1980s and 1992, for Ilfov (or the Ilfov Agricultural Sector). Up until the 1980s Ilfov plates were registered IF, an abbreviation which would return in 2005.
An interesting development was the connection between the license plate and the social status of the car owner. For example, the "important" cars (i.e. those belonging to the nomenklatura) generally used 1, then the county, then three digits. Nicolae Ceauşescu's ARO sported the "1-B-111" license plate. By the mid-1970s, any plate with three digits was considered important (regardless of the number at the front), and although older cars had been initially issued with three-digit combinations, many owners were "asked" by the authorities to change their numbers. In an age where most people had the same car - the Dacia - such distinguishing features were considered important. By the 1980s, in Bucharest 1-B with 3 or 4 digits and 2-B and 3-B with three digits were also considered important numbers. Furthermore, the legend that the three-digit formula, where the middle number was the sum of the other two numbers, signified real importance sprang up. Thus, many senior Communist leaders had numbers such as 1-B-363, while the Neamţ County party secretary had 1-NT-165 on his black Volga.
Foreign citizens and organizations were issued plates with 12-B (later 12-xx in other counties). 14-B was used for rental cars, but since 1990 some official cars had such number plates too.
There were also some stylistic variations. Numbers on a yellow (rather than white) background were state property, but since all trucks, buses and other heavy vehicles were state property, those with yellow background plates belonged to ministries or other special state organizations. Numbers with white letters on a black background were issued to vehicles of the foreign organizations in Romania, but also to vehicles belonging to religious organizations.
Temporary plates had the county code and then a number beginning with 0; test drive plates had a number beginning with 0 and then the county.
In late 1977 the manufacture of plates was standardized and they were all made on a pressed steel rectangle; previously plates had been plastic, cast iron, enamel, porcelain or even plaster. In around 1982, after 19-B-9999 had been reached, it was decided to begin the series 1-B with five digits. In 1983, after a brief reorganization of the counties, IF (Ilfov County) was dropped, CL (Călăraşi County) and GR (Giurgiu County) were introduced, and the Bucharest Agricultural Sector (Sectorul Agricol Ilfov) issued plates beginning with 9-B and followed by five digits. The fonts used on the number plates changed slightly in 1988.
1992-present
The system was finally changed in 1992, when new reflective plates were introduced, with the numbering system still in use today. One reason was to please the European authorities and to make Romanian cars safer when being driven abroad; another was allegedly to hide the identities of previous Communist leaders, whose importance was visible on their bumpers. Indeed, in the weeks after the Romanian Revolution, many changed their license plates to Army plates to avoid trouble. Nevertheless, they remained valid until late 2000, and for many years 1-B-101 and 1-B-106 were seen being driven around Bucharest on cars owned by tennis player Ilie Năstase.
In the mid-1990s, urban myths circulated that the new "powerful" license plates began with B 06. However, this was quickly superseded by the rumour that they contained a W in the three-letter sequence. Although this is not strictly incorrect - many, such as the cars used by Traian Băsescu and Prince Charles, do - certainly not all such numbers are of any significance.
Special plates
The Army license plates
The license plates before around 1945 were white and had a number beginning with a zero. In front of the number was the initial of the Ministry of Defense State Undersecretaries:
- U for the Ground Forces (U for Uscat, Land)
- A for the Air Force (A for Aer, Air)
- M for the Navy (M for Marină, Navy)
- I for the Logistics (I for Înzestrare, Logistics).
This system was subsequently abolished when all military vehicles had the prefix A (for Armată, Army) in front of the registered numbers, which start at 100. This system lasted until 2005 and is still visible today. Numbers smaller than 10,000 are generally kept for cars.
Diplomatic license plates
Until 1958 these were standard plates, with "CD" prefix attached to them. In 1958 oval and square plates were introduced, oval for CD (Corps Diplomatique) and square for TC (auxiliary staff). CD or TC went above a three-digit number.
Special license plates
In the pre-1968 system, "CO" (Cetăţean de Onoare, Honorary Citizen) was occasionally seen on private cars before 1941.
Transnistria
Wartime Transnistria occupied by Romanian forces briefly had its own special plates. These began Tr-number-regional suffix. Thus, the Cadillac of the regional administrator had Tr-1-Ods (for Odessa). These numbers were very short-lived.
References
- ↑ "Numerele de inmatriculare auto din Bucuresti vor fi formate si din trei cifre". România Liberă. 30 December 2009. Retrieved 15 December 2010.
- ↑ "Numere de inmatriculare cu trei cifre, pentru Bucuresti". Ziare.com. 4 January 2010. Retrieved 25 May 2012.
- ↑ "Inmatriculari". Directia Regim Permise de Conducere si Inmatriculare a Vehiculelor. Retrieved 31 August 2013.
External links
-
 Media related to License plates of Romania at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to License plates of Romania at Wikimedia Commons
| ||||||||||||||||||