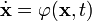Variable structure system
A variable structure system, or VSS, is a discontinuous nonlinear system of the form
where ![\mathbf{x} \triangleq [x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n]^{\operatorname{T}} \in \mathbb{R}^n](../I/m/0564f5cf9b731c9c350f909163de4011.png) is the state vector,
is the state vector, 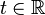 is the time variable, and
is the time variable, and ![\varphi(\mathbf{x},t) \triangleq [ \varphi_1(\mathbf{x},t), \varphi_2(\mathbf{x},t), \ldots, \varphi_n(\mathbf{x},t) ]^{\operatorname{T}} : \mathbb{R}^{n+1} \mapsto \mathbb{R}^n](../I/m/6dbae6f94f5d1a72a81d5ef7b828107f.png) is a piecewise continuous function.[1] Due to the piecewise continuity of these systems, they behave like different continuous nonlinear systems in different regions of their state space. At the boundaries of these regions, their dynamics switch abruptly. Hence, their structure varies over different parts of their state space.
is a piecewise continuous function.[1] Due to the piecewise continuity of these systems, they behave like different continuous nonlinear systems in different regions of their state space. At the boundaries of these regions, their dynamics switch abruptly. Hence, their structure varies over different parts of their state space.
The development of variable structure control depends upon methods of analyzing variable structure systems, which are special cases of hybrid dynamical systems.
See also
- Variable structure control
- Sliding mode control
- Hybrid system
- Nonlinear control
- Robust control
- Optimal control
- H-bridge – A topology that combines four switches forming the four legs of an "H". Can be used to drive a motor (or other electrical device) forward or backward when only a single supply is available. Often used in actuator sliding-mode control systems.
- Switching amplifier – Uses switching-mode control to drive continuous outputs
- Delta-sigma modulation – Another (feedback) method of encoding a continuous range of values in a signal that rapidly switches between two states (i.e., a kind of specialized sliding-mode control)
- Pulse density modulation – A generalized form of delta-sigma modulation
- Pulse-width modulation – Another modulation scheme that produces continuous motion through discontinuous switching
References
Further reading
- Khalil, H.K. (2002). Nonlinear Systems (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-067389-7.
- Utkin, V.I. (1992). Sliding Modes in Control and Optimization. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-387-53516-6.
- Zinober, A.S.I., ed. (1990). Deterministic control of uncertain systems. London: Peter Peregrinus Press. ISBN 978-0-86341-170-0.
- Zinober, Alan S.I., ed. (1994). Variable Structure and Lyapunov Control. London: Springer-Verlag. doi:10.1007/BFb0033675. ISBN 978-3-540-19869-7.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||