VESA Digital Flat Panel
| Type | Digital video connector | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Superseded | VGA connector | ||
| Superseded by | Digital Visual Interface | ||
| General specifications | |||
| Pins | 20 | ||
| Data | |||
| Data signal | PanelLink protocol Transition Minimized Differential Signaling | ||
| Width | 3 bits plus clock | ||
| Max. devices | 1 | ||
| Protocol | PanelLink (Serial) | ||
| Pin out | |||
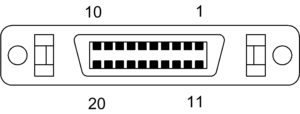 | |||
| Pin 1 | TMDS data 1 + | ||
| Pin 2 | TMDS data 1 – | ||
| Pin 3 | GND | ||
| Pin 4 | GND | ||
| Pin 5 | TMDS data C + | ||
| Pin 6 | TMDS data C – | ||
| Pin 7 | GND | ||
| Pin 8 | + 5V | ||
| Pin 9 | Reserved | ||
| Pin 10 | Reserved | ||
| Pin 11 | TMDS data 2 + | ||
| Pin 12 | TMDS data 2 – | ||
| Pin 13 | GND | ||
| Pin 14 | GND | ||
| Pin 15 | TMDS data 0 + | ||
| Pin 16 | TMDS data 0 – | ||
| Pin 17 | Reserved | ||
| Pin 18 | Reserved | ||
| Pin 19 | DDC data | ||
| Pin 20 | DDC clock | ||
The VESA Digital Flat Panel (DFP) interface standard specifies a video connector and signaling for flat-panel displays.[1] It features 20 pins and uses the PanelLink protocol.
Unlike DVI, DFP never achieved widespread implementation. The connector was used by displays such as the Compaq Presario FP400, FP500, FP700, Fp720, 5204, and 5280. It was offered on graphics cards such as the Xpert LCD, and Rage LT Pro by ATI Technologies Inc.
DFP was superseded by DVI because of a low maximum resolution of 1280 × 1024 (SXGA), whereas DVI supports much higher resolutions.
DFP monitors can generally be used with a DVI graphics card with a passive adaptor.
-

male DFP connector
-

female DFP connector
-

DVI-DFP adapter
References
- ↑ Gary Manchester (1999), The VESA Digital Flat Panel (DFP) Standard: A White Paper VESA Marketing Committee.
External links
- DFP diagram and description of pin layout
- DFP is mentioned in ATI's description of the Xpert LCD Archive copy at the Wayback Machine
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||