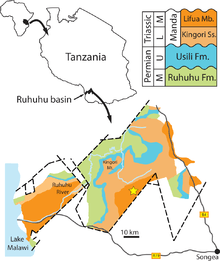
The Usili Formation is a Late Permian geologic formation in Tanzania. It preserves fossils of many terrestrial vertebrates from the Permian, including temnospondyls, pareiasaurs, therapsids and the archosauromorph Aenigmastropheus.[1][2]
History of study

Animals from locality B35 of the Usili Formation
One of the first to study rocks of the Usili Formation was British geologist G. M. Stockley. In 1932, Stockley explored the geology of the Ruhuhu Basin in Tanzania. He called a series of layers dating from the Late Carboniferous to the Middle Triassic of the Songea Series and divided it into eight units labelled K1-K8. Stockley was also the first to describe fossils from these rocks, naming an older layer the "Lower Bone Bed" and a younger layer the "Upper Bone Bed".[3]
In 1957, paleontologist Alan J. Charig described many more fossils from the upper bone beds in his Ph.D. thesis for the University of Cambridge.[4][5] Subsequently, Stockley's units were renamed, Charig (1963) calling unit K6 the Kawinga Formation, K7 the Kingori Sandstones, and K8 the Manda Formation. Fossils were identified in many strata, invalidating Stockley's division into two distinct bone beds. Since Charig's description, the Kawinga Formation has been renamed the Usili Formation, the Kingori Sandstones have become the Kingori Sandstone Member of the Manda Formation, and Charig's original Manda Formation has become a subunit of the formation called the Lifua Member.[3] Six formations and one informal unit are currently recognized in the Songea Group (Ruhuhu basin) rocks range in age from Pennsylvanian to Anisian, including the Idusi (K1), Mchuchuma (K2), Mbuyura (K3), Mhukuru (K4), Ruhuhu (K5), and Usili (K6) formations and the informal Manda Beds, which include the Kingori Sandstone (K7) and Lifua Member (K8).[6]
Recent studies have described the Usili Formation as a 260 meters thick fluviolacustrine succession made up of a lowermost conglomeratic interval that is approximately 5 meters thick, grading up into a trough cross-bedded, coarse-grained, sandstone-dominated interval that is 25–40 meters thick, overlain by massive nodular siltstone and laminated mudstone beds with minor ribbon sandstones forming the bulk of the succession. Since Parrington (1956), the Usili Formation became widely recognized as a Late Permian formation that correlates with the Teekloof and/or Balfour formations of South Africa, as well as with the Zambian Upper Madumabisa Mudstone (Cistecephalus AZ). Comparison of Usili tetrapods with those of the lower Beaufort Group has suggested a broad biostratigraphic correlation with the Cistecephalus, Dicynodon, and Tropidostoma assemblage zones. Sidor et al. (2010) recognized only one undivided tetrapod faunal assemblage in the Usili Formation, which includes Aenigmastropheus, temnospondyls, pareiasaurs, gorgonopsians, therocephalians, cynodonts, and dicynodonts, whose remains were collected from various localities. This suggests that several therapsid genera have unequal stratigraphic ranges and temporal durations in the Ruhuhu and Karoo basins.[2][6]
Sidor et al. (2010) and Sidor et al. (2013) noted that it is probable that the Chiweta Beds of Malawi and the Usili Formation of Tanzania represent the same rock unit, separated only by political boundaries and geologic faulting (being located on either side of Lake Nyasa). Except for the burnetiid MAL 240, which is unique to the Chiweta Beds, the Usili Formation hosts identical genera, including Aelurognathus, Dicynodontoides, Rhachiocephalus, Endothiodon cf. E. bathystoma, Oudenodon baini, Gorgonops? dixeyi and an indeterminate tusked dicynodont (SAM-PK-7862, SAM-PK-7863).[1][6]
Paleobiota
Tetrapods
|
|
|
Color key
| Taxon |
Reclassified taxon |
Taxon falsely reported as present |
Dubious taxon or junior synonym |
Ichnotaxon |
Ootaxon |
Morphotaxon |
|
|
Notes
Uncertain or tentative taxa are in small text; crossed out taxa are discredited. |
Temnospondyls
| Taxon | Locality | Material | Notes | Images |
| Peltobatrachus pustulatus | | | A stereospondyl, endemic to this formation. | |
|
Parareptiles
| Taxon | Locality | Material | Notes | Images |
| Anthodon serrarius | | | A pareiasaur. Originally named Anthodon minisculus, but it was considered a junior synonym of A. serrarius by Lee (1997). | |
| Pareiasaurus serridens | | | A pareiasaur. | |
| Unnamed | | GPIT K72, six or seven dorsal vertebrae with articulated osteoderms | A pareiasaur originally described by von Huene (1944), endemic to this formation. | |
|
Eureptiles
| Taxon | Locality | Material | Notes | Images |
| Aenigmastropheus parringtoni | B35 | UMZC T836, a partial postcranial skeleton including five posterior cervical and anterior dorsal vertebrae, the distal half of the right humerus, a fragment of probable left humeral shaft, the proximal end of the right ulna, and three indeterminate fragments of bone, one of which may represent a partial radius. | A protorosaurid archosauromorph, endemic to this formation. | |
|
Therapsids
Anomodonts
| Taxon | Locality | Material | Notes | Images |
| Daptocephalus leoniceps | | | A dicynodontoid dicynodont, previously considered to be a species of Dicynodon. | |
| "Dicynodon" huenei | B2 (Kingori) | SAM-PK-10630, fragmentary skull and postcrania; 7 additional skulls | A dicynodontoid dicynodont, possibly a species of Dicynodon. | |
| Dicynodon lacerticeps | | | A dicynodontoid dicynodont, known only from South Africa. | |
| Dicynodon robertsi | | | Originally considered to be a species of Dicynodon, but it is a junior synonym of Oudenodon bainii. | |
| "Dicynodon" tealei | B32 | SAM-PK-10631, fragmentary skull roof | An indeterminate dicynodont, a nomen dubium. | |
| Dicynodontoides nowacki | Kingori | GPIT/RE/7174, a nearly complete skull; other skulls and skeletons | A kingoriid dicynodont, previously considered to be a species of Dicynodon. | |
| Endothiodon cf. bathystoma | | | Basal dicynodont, endothiodontid. | |
| Endothiodon sp. nov. | | | A new, yet unnamed species. | |
| Endothiodon uniseries | | | Basal dicynodont, endothiodontid. Originally placed in its own genus Esoterodon. | |
| Euptychognathus bathyrhynchus | Kingori | GPIT/RE/7104 (UT K 19), well preserved partial skull | Basal lystrosaurid dicynodont, previously considered to be a species of Dicynodon. | |
| Geikia locusticeps | | GPIT K87/UT von HUENE 1942 Abb.3, juvenile partial skull and dentary; GPIT K114, skull and dentary | A geikiine cryptodont, previously considered to be a species of Dicynodon. | |
| Katumbia parringtoni | B19 (Kingori); B4 (Katumbi); Usili-Berges | GPIT K120/UT Huene 1942 S.155, fragmentary skull; UMZC T761, UMZC T791, incomplete skulls; A dentary | Basal dicynodontoid, endemic to this formation. | |
| Kawingasaurus fossilis | Kingori | UT K 52, skull and dentary; UT K 56, skull; UT K 55, 5 skulls and postcrania | A cistecephalid dicynodont, endemic to this formation. | |
| Oudenodon bainii | | Many skulls | Basal oudenodontid cryptodont. | |
| Pachytegos stockleyi | B32 | SAM 10639, SAM 10642, fragmentary skull elements | Basal dicynodont, endothiodontid, endemic to this formation. | |
| Pristerodon mackayi | | NMT RB38 | Basal dicynodont, eumantellid. Previous reports by King (1988, 1992), King and Rubidge (1993), and Gay and Cruickshank (1999) were based on the holotype specimen of Katumbia parringtoni. In 2008, the first diagnostic specimen of Pristerodon mackayi from this formation, NMT RB38, was discovered. | |
| Rhachiocephalus behemoth | | GPIT K 15, nearly complete skull; GPIT K 15B, fragmentary skull | A rhachiocephalid cryptodont. | |
| Rhachiocephalus magnus | | Many specimens | A rhachiocephalid cryptodont. | |
| Unnamed | | NMT RB22, a partial maxilla of an adult. NMT RB156, a nearly complete skull, mandible, and associated postcrania of a subadult. | A new genus and species of a cryptodontian dicynodont. Endemic to this formation. | |
|
Biarmosuchians
| Taxon | Locality | Material | Notes | Images |
| Burnetiidae indet. | | NMT RB4, partial isolated skull roof; NMT RB36, fragmentary right dorsal margin of the orbit | A burnetiid most closely related to Burnetia mirabilis from the Dicynodon AZ of South Africa. Too fragmentary to be assigned to a new taxon, its morphology is unique among Cistecephalus AZ taxa. | |
|
Cynodonts
| Taxon | Locality | Material | Notes | Images |
| Procynosuchus delaharpeae | | IGP K 92, fragmentary skull | A procynosuchid | |
|
Therocephalians
| Taxon | Locality | Material | Notes | Images |
| Silphictidoides ruhuhuensis | Kingori | K 70, nearly complete skull and dentary; K 125, nearly complete skull, dentary and right humerus | A baurioid, endemic to this formation. | |
| Theriognathus microps | Kingori | K 107 and K 84, two fragmentary skulls | A whaitsiid | |
|
Gorgonopsians
| Taxon | Locality | Material | Notes | Images |
| Aelurognathus? parringtoni | Usili-Berges | IGP U 28, complete skull and dentary and fragmentary skeleton | A gorgonopsid, endemic to this formation. | |
| Aloposaurus? broomianus | | | A gorgonopsian | |
| Arctognathus? nasutus | | IGP K 52, nearly complete skull; IGP K 96, fragmentary skull; 6 more skulls | A gorgonopsid reassigned to the new genus, "Njalila", unofficially by Gebauer (2007). Endemic to this formation. | |
| Dinogorgon quinquemolaris | Kingori | IGP K 16, nearly complete skull and dentary | A gorgonopsid, endemic to this formation. | |
| Gorgonops sp. | | | A gorgonopsid | |
| Leontocephalus intactuse | Kingori | MZC T878/FRP 41, skull | A gorgonopsid, endemic to this formation. | |
| Leontocephalus haughtoni | Kingori | IGP K 46 b, nearly complete skull | A gorgonopsid, endemic to this formation. | |
| Lycaenops sp. | | | A gorgonopsid | |
| Ruhuhucerberus terror | Katumbi, B4 | MZC T891, nearly complete skull | A gorgonopsid, endemic to this formation. | |
| Scylacops capensis | Kingori, B19 | MZC T885/FRP 93, skull and cervical vertebrae | A gorgonopsid | |
| Sycosaurus? kingoriensis | Kingori | IGP K 47, nearly complete skull | A gorgonopsid, endemic to this formation. | |
| Titanogorgon maximus | | IGP K 46, fragmentary skull | A gorgonopsid, endemic to this formation. | |
|
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sidor, C. A.; Vilhena, D. A.; Angielczyk, K. D.; Huttenlocker, A. K.; Nesbitt, S. J.; Peecook, B. R.; Steyer, J. S.; Smith, R. M. H.; Tsuji, L. A. (2013). "Provincialization of terrestrial faunas following the end-Permian mass extinction". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 110 (20): 8129. doi:10.1073/pnas.1302323110.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Ezcurra, M. N. D.; Scheyer, T. M.; Butler, R. J. (2014). "The Origin and Early Evolution of Sauria: Reassessing the Permian Saurian Fossil Record and the Timing of the Crocodile-Lizard Divergence". PLoS ONE 9 (2): e89165. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0089165.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Butler, R. J.; Barrett, P. M.; Abel, R. L.; Gower, D. J. (2009). "A possible ctenosauriscid archosaur from the Middle Triassic Manda Beds of Tanzania". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 29 (4): 1022. doi:10.1671/039.029.0404.
- ↑ Charig, A. J. (1957). New Triassic archosaurs from Tanganyika, including Mandasuchus and Teleocrater: Dissertation Abstracts. Cambridge University.
- ↑ Nesbitt, S. J.; Butler, R. J. (2012). "Redescription of the archosaur Parringtonia gracilis from the Middle Triassic Manda beds of Tanzania, and the antiquity of Erpetosuchidae". Geological Magazine: 1. doi:10.1017/S0016756812000362.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Sidor, C. A.; Angielczyk, K. D.; Weide †, D. M.; Smith, R. M. H.; Nesbitt, S. J.; Tsuji, L. A. (2010). "Tetrapod fauna of the lowermost Usili Formation (Songea Group, Ruhuhu Basin) of southern Tanzania, with a new burnetiid record". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 30 (3): 696. doi:10.1080/02724631003758086.