Uranium mining by country
Africa
Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
Uranium is being mined in the DRC. The uranium for the nuclear bombs which were used to bomb Japan at the end of the Second World War came from this region, known then as the Belgian Congo. The mining occurs in the mineral rich province of Katanga, for example in Shinkolobwe,[1] Mindigi, Kalongwe, Kasompi, Samboa[2] and the Emmanuel Depot in Kolwezi.[3] Major player is Gécamines, the state mining company.
The French conglomerate Areva has an undisclosed contract with Gecamines which is reportedly allows the company to mine unlimited amounts of uranium in the region[4]
Gabon
In Gabon, mining used to occur in Oklo, but the deposits are reported to be exhausted. In 1972, remains of a natural nuclear fission reactor were found at the Oklo deposits.
Malawi
Uranium is produced at Kayelekera mine near Karonga. The mine owned and operated by Australian company, Paladin Energy. As of 2014, the mine is under 'care and maintenance' due to weak uranium prices.
Namibia
Namibia produces uranium at Rossing deposit, where an igneous deposit is mined from one of the world's largest open pit mines. The mine is owned by a subsidiary of the Rio Tinto Group.[5] The Langer Heinrich calcrete uranium deposit was discovered in 1973 and the open pit mine was officially opened in 2007.[6] The Husab Uranium Project currently under development is expected to be completed towards the end of 2015. As of 2013 the cost of uranium production in Namibia is among the highest of major producers due to the remote desert location of deposits.[7]
Niger
Niger is Africa's leading uranium-producing nation. Uranium is produced from mines at Arlit owned by Areva NC.[8]
In 2007, production in Niger had a total output of 3,720 tonnes U3O8 (8.2 million pounds) coming mainly from the Akouta (Cominak) and the Arlit (Somair) mines.[9]
Niger's uranium came to world attention before the US invasion of Iraq, when it was asserted that Iraq had attempted to buy uranium from Niger (see Niger uranium forgeries).
South Africa
South Africa produces uranium from deposits in Precambrian quartz-pebble conglomerates of the Witwatersrand Basin, at Brakpan and Krugersdorp, Gauteng.
Asia
China
China mined in 2007 636 tonnes of U3O8, a decrease of 17% of its production in 2006.[9]
India
In Nalgonda District, the Rajiv Gandhi Tiger Reserve (the only tiger project in Andhra Pradesh) has been forced to surrender over 3,000 sq. kilometres to uranium mining, following a directive from the Central Ministry of Environment and Forests.[10]
In 2007, India was able to extract 229 tonnes of U3O8 from its soil.[9]
On July 19, 2011, Indian officials announced that the Tumalapalli mine in Andhra Pradesh state of India could provide more than 170,000 tonnes of uranium, making it as the world's largest uranium mine. Production of the ore is slated to begin in 2012.[11]
The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) recently discovered that the upcoming mine in Tumalapalli has close to 49,000 tonne of uranium reserves. This could just be a shot in the arm for India's nuclear power aspirations as it is three times the original estimate of the area's deposits.[12]
Jordan
Jordan, the only Middle East country with confirmed uranium, is estimated to have around 140,000 tonnes in its uranium reserves plus a further 59,000 tonnes in phosphate deposits. Although no uranium has been mined yet, it was announced in 2008 that the Jordanian government signed an agreement with the French company AREVA to explore for uranium. This will benefit them on building a future nuclear plant in Jordan.[13] [14]
CIS
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan produced some 7847 tU3O8 (17.3 million pounds) in 2007, much more than in 2006. Kazatomprom's four 100%-owned ISR mining groups (LLP Kazatomprom) combined produced half of the total output.[9]
Russia
The World Nuclear Association[15][16] states that Russia has known uranium deposits of 500,000 tonnes and planned to mine 11,000 to 12,000 tonnes per year from deposits in the South Urals, Western Siberia, and Siberia east of Lake Baikal, by 2010.
The Russian nuclear industry underwent an overall restructuring process during 2007. The production was high as almost 4,000 tU3O8 (8.8 million pounds) from three operating mines in 2007. Atomredmetzoloto reported that the Priargunsky mine yielded 7.8 million pounds in 2007, a slight decline from the 8.2 million pounds reported by TVEL in 2006. At the Dalur (Dolmatovskoye) and Khiagda ISR mines, production of 910,000 pounds and 68,000 pounds, respectively, was reached in 2007. Both ISR projects are expected to increase production steadily through 2015.[9]
Uzbekistan
In Uzbekistan, the Navoi Mining & Metallurgy Combinat reportedly produced 2,721 tonnes U3O8 or tU3O8 (6 million pounds) from its Nurabad, Uchkuduk and Zafarabad in-situ recovery facilities.[9]
Europe
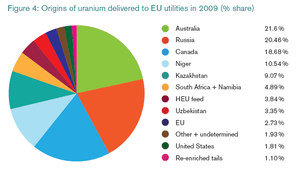
European uranium mining supplied just below 3% of the total EU needs, coming from the Czech Republic and Romania (a total of 526 tU). Production in the Rožná mine was to be terminated in 2008, but the Czech government decided in May 2007 to continue mining and extended the lifetime without time limit as long as it remains profitable.[9]
Bulgaria
Bulgaria shut down its facilities for environmental reasons in 1992; terrains were recultivated but recently, there has been certain interest in resuming activities. Industrial mining first started in 1938 and was resumed after 1944 by a joint Soviet–Bulgarian mining company, reorganized in 1956 into the Redki Metali (Rare Metals) government-owned concern. At its peak, it had 13,000 employees, operated 48 uranium mines and two enrichment plants at Buhovo outside Sofia and Eleshnitsa near Bansko. Yearly production was estimated at 645 t that met about 55% of the needs of Kozloduy Nuclear Power Plant, which had six reactors with a total output of over 3600 MWe at its peak.[17]
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is the birthplace of industrial scale uranium mining. Uranium mining at Jáchymov (at that time named Joachimsthal and belonging to Austria-Hungary) started in the 1890s on an industrial scale, after the silver and cobalt production of the deposit declined. Uranium was first utilised to produce mainly yellow colours for glass and porcelain manufacture. After the Curies in France discovered the polonium and radium in tailings from Jáchymov, the town became the first place in the world for commercial radium production from uranium ore. Radioactive water from the mines was also used to set up a health resort still existing today for radon-treatments. Pre–Cold War production is estimated to be around 1,000 t of uranium. From 1947 on the Czech Republic started producing uranium for the Soviet Union. Early mining sites, such as Jáchymov, Horní Slavkov and Příbram, became known as parts of the "Czech Gulag".[18] In the whole, the Czech Republic produced 110,000 t of uranium to 1992 from 64 uranium deposits. The largest deposit Příbram (vein style) produced about 50,000 t of uranium and was mined to a depth of over 1,800 m.
Today, the Rožná underground facility 55 km northwest of Brno is Europe's only operating uranium mine, continuously operating since 1957. It produces about 300 t of uranium annually. Since 2007, the Australian company Uran Ltd. is interested in participating in the operations at Rožná, as well as seeking permits with the Czech Ministry of Trade and Resources to open mines in the Czech Republic at other known locations, such as Brzkov, Jamné, Polná and Věžnice, through its Czech partner Timex Zdice and since 2008 through its subsidiary Urania Mining.[19][20][21]
Estonia
During 1946–1952, the Dictyonema argillite (claystone) was mined and used for uranium production in Sillamäe.[22][23][24]
Finland

In Uusimaa, Karelia and Lapland in Finland, presently (2009) uranium deposits are investigated.[25]
In addition, Talvivaara Mining Company plc has announced in early 2010 the commencement of uranium recovery as a by-product out of its mine producing mainly nickel, copper, zinc and cobalt in Sotkamo, eastern Finland. Production is expected to be approximately 350 tons of yellowcake annually, making Finland almost self-sufficient in uranium, accounting for approximately 80% of annual demand. However, as Finland lacks the required reprocessing facilities to convert yellowcake into nuclear fuel, the mine's output will need to be sent abroad for reprocessing and enrichment.[26]
Germany
The search for uranium ore intensified during the cold war, but only in East Germany was an extensive uranium mining industry established. Uranium was mined from 1947 to 1990 from mines in Saxony and Thuringia by the SDAG Wismut. All the uranium mines were closed after the German reunification for economic and environmental reasons. Total production in East Germany was 230,400 t of uranium, making it the third largest producer in history behind the USA and Canada. Minor production still takes place at the Königstein mine southeast of Dresden from cleaning of mine water. This production has been 38 t of uranium in 2007.[27]
Hungary
In Hungary, uranium mining began in the 1950s around Pécs to supply the country's first atomic plant in Paks. A whole district was built for the mining industry on the outskirt of Pécs, for which the name Uránváros (Uranium city) was given. After the fall of communism, uranium mining was gradually given up because of the high production costs. That caused serious economic problems and a rise of unemployment in Pécs. Recently an Australian company took up the challenge to search for uranium in the Mecsek.[28]
Portugal
Portugal has some uranium exploration around the Northern Alentejo town of Nisa, although further exploration of this area is subject to resistance from environmental groups [29]
Romania
Romania produced in 2008 around 250 tonnes of uranium.,[30] see SovRoms, Crucea - Botusana mine and Băiţa mine.
At the village Ciudanoviţa in the Banat region in the south west of Romania there are closed down mines which provided ore for 50 years but are now closed.[31]
Slovakia
Uranium was formerly mined in the Novoveská Huta near Spišská Nová Ves from stratiform deposits. Currently there are plans to open a mine for the extraction of uranium ore in the hills of Jahodna near the city of Košice.[32] European Uranium Resources (earlier known as Tournigan Energy) is planning to mine uranium at the Kuriskova mine, near Košice,[33] however, the plan is strongly opposed by local inhabitants.[34] Several other uranium deposits are found in the Považský Inovec Mts. near Kálnica, in the area of Petrova Hora near Krompachy and in the Vikartovský chrbát in Kozie chrbty Mts..[35] None of them is extracted.
Spain
The Australian Berkeley Resources Ltd. and Korea Electric Power mine uranium in Salamanca Province, near the city of Ciudad Rodrigo.[36] Berkeley Resources is also active in the Cáceres (province), the Barcelona Province and the Guadualajara Province.[37]
Sweden
In Sweden, uranium production took place at Ranstadsverket between 1965 and 1969 by mining of alum shale (kind of oil shale) deposits. The goal was to make Sweden self-supplying with uranium. The high operating costs of the pilot plant (heap leaching) due to the low concentration of uranium in the shale and the availability at that time of comparatively cheap uranium on the world market caused the mine to be closed, although a much cheaper and more efficient leaching process, using sulfur-consuming bacteria, had by then been developed. Since 2005 there have been investigations on opening new uranium mines in Sweden.
Ukraine
Ukraine's VostGOK produced almost 1,000 tU3O8 (2.2 million pounds) from the Zhovti Vody mill in 2007, which was similar to the 2.1 million pounds produced in 2006.[9]
United Kingdom
The South Terras Mine in Cornwall was mined for uranium from 1873 to 1903.[38]
Substantial uranium deposits were found on Orkney in the 1970s.[39] When Margaret Thatcher proposed a uranium mine on Orkney a campaign followed which successfully argued that uranium mining would mean irreversible environmental, social and psychological damage.[40]
Oceania
Australia


Production in Australia rose significantly to 10,115 tU3O8 (22.3 million pounds) in 2007 from 19.7 million pounds in 2006, securing its position as the second largest uranium producing country, most of the production gain coming from increased operational performance and an increase in the grade of the ore mined.[9]
Australia has the world's largest uranium reserves, 24% of the planet's known reserves. The majority of these reserves are located in South Australia with other important deposits in Queensland, Western Australia and the Northern Territory.
The Olympic Dam operation run by BHP Billiton in South Australia is combined with mining of copper, gold, and silver, and has reserves of global significance. There are currently three operating uranium mines in Australia, and several more have been proposed. The expansion of Australia's uranium mines was supported by the Federal Australian Labor Party (ALP) Government headed by Prime Minister Julia Gillard. The ALP abandoned its long-standing and controversial "no new uranium mines" policy in April 2007. One of the more controversial proposals was Jabiluka, to be built surrounded by the World Heritage listed Kakadu National Park. The existing Ranger Uranium Mine is also surrounded by the National Park, as the mine area was not included in the original listing of the Park.
Uranium mining and export and related nuclear issues have often been the subject of public debate, and the anti-nuclear movement in Australia has a long history.[41]
New Zealand
There are some uranium deposits in New Zealand but they have never been mined on a commercial scale.
North America
Canada
For many years Canada was the largest exporter of uranium ore; however, in 2009 the top spot was taken over by Kazakhstan.[42] The largest Canadian mines are located in the Athabasca Basin of northern Saskatchewan.
Canada's first uranium discovery was in the Alona Bay area, south of Lake Superior Provincial Park in Ontario, by Dr. John Le Conte in 1847.[43] The Canadian uranium industry, however, really began with the 1932 discovery of pitchblende at Port Radium, Northwest Territories. The deposit was mined from 1933 to 1940, for radium, silver, copper, and cobalt. The mine shut down in 1940, but was reopened in 1942 by Eldorado Mining and Refining Limited to supply uranium to the Manhattan Project. The Canadian government expropriated the Port Radium mine and banned private claimstaking and mining of radioactive minerals.[44]
In 1947, the government lifted the ban on private uranium mining, and the industry boomed through the 1950s, spurred by high prices due to the nuclear weapons programs. Production peaked in 1959, when 23 mines in five different districts made uranium Canada's number-one export. That same year, however, the United Kingdom and the United States announced their intention to halt uranium purchases in 1963. By 1963, seven mines were left operating, a number that shrank to only three in 1972.
A price rise caused uranium to boom again in 1975 and 2005.
United States
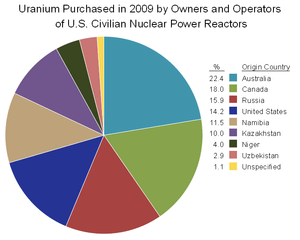
2009 Sources of Uranium
Most uranium ore in the United States comes from deposits in sandstone, which tend to be of lower grade than those of Australia and Canada. Because of the lower grade, many uranium deposits in the United States became uneconomic when the price of uranium declined sharply in the 1980s. Today nearly all uranium operations in the United States are In-situ leach.
Regular production of uranium-bearing ore in the United States began in 1898 with the mining of carnotite-bearing sandstones of the Colorado Plateau in Colorado and Utah, for their vanadium content. The discovery of radium by Marie Curie, also in 1898, soon made the ore also valuable for radium. Uranium was a byproduct. By 1913, the Colorado Plateau uranium-vanadium province was supplying about half of the world supply of radium. Production declined sharply after 1923, when low-cost competition from radium from the Belgian Congo and vanadium from Peru made the Colorado Plateau ores uneconomic.[45]
Mining revived in the 1930s with higher prices for vanadium. American uranium ores were in very high demand by the Manhattan Project during World War II, although the mining companies did not know that the by-product uranium was suddenly valuable. The late 1940s and early 1950s saw a boom in uranium mining in the western US, spurred by the fortunes made by prospectors such as Charlie Steen.
Uranium mining declined with the last open pit mine (Shirley Basin, Wyoming) shutting down in 1992. United States production occurred in the following states (in descending order): New Mexico, Wyoming, Colorado, Utah, Texas, Arizona, Florida, Washington, and South Dakota. The collapse of uranium prices caused all conventional mining to cease by 1992. In-situ leach mining has continued primarily in Wyoming and adjacent Nebraska as well has recently restarted in Texas. Rising uranium prices since 2003 have increased interest in uranium mining in the United States.
Arizona
On Wednesday, 25 June 2008, the House Natural Resources Committee voted overwhelmingly to enact emergency protections from uranium mining for 1,000,000 acres (4,000 km2) of public lands around Grand Canyon National Park. This will mean the Secretary of the Interior has an obligation to protect public lands near the Grand Canyon from uranium extraction for three years. The Center for Biological Diversity, Sierra Club, and the Grand Canyon Trust recently won a court order against the Kaibab National Forest stopping uranium drilling near the national park until a thorough environmental analysis is conducted.[46]
The Grand Canyon Watersheds Protection Act has been proposed. This bill would permanently ban uranium mining in the area. The impacts of uranium development have raised concerns of scientists and government officials alike. Due to increasing demand, uranium projects have been on the increase, raising concerns about water, public health, and fragile desert ecosystems.
Virginia
In February 2010, the Commonwealth of Virginia contracted the National Research Council and Virginia Polytechnic Institute to oversee a National Research Council study of potential environmental and economic effects of uranium mining in Virginia. The National Research Council study, funded indirectly by a $1.4 million grant from Virginia Uranium to the Commonwealth, resulted in a report released in December 2011.[47] Uranium mining and processing carries with it a range of potential health risks to the people who work in or live near uranium mining and processing facilities. Some of these health risks apply to any type of hard rock mining or other large-scale industrial activity, but others are linked to exposure to radioactive materials. In addition, uranium mining has the potential to impact water, soil, and air quality, with the degree of impact depending on site-specific conditions, how early a contaminant release is detected by monitoring systems, and the effectiveness of mitigation steps.[48]
Some of the worker and public health risks could be mitigated or better controlled through modern internationally accepted best practices, the report says. In addition, if uranium mining, processing, and reclamation were designed, constructed, operated, and monitored according to best practices, near- to moderate-term environmental effects should be substantially reduced, the report found.[49]
However, the report noted that Virginia’s high water table and heavy rainfall differed from other parts of the United States — typically dry, Western states — where uranium mining has taken place. Consequently, federal agencies have little experience developing and applying laws and regulations in locations with abundant rainfall and groundwater, such as Virginia. Because of Virginia’s moratorium on uranium mining, it has not been necessary for the Commonwealth’s agencies to develop a regulatory program that is applicable to uranium mining, processing, and reclamation.
The report also noted the long-term environmental risks of uranium tailings, the solid waste left after processing. Tailings disposal sites represent potential sources of contamination for thousands of years. While it is likely that tailings impoundment sites would be safe for at least 200 years if designed and built according to modern best practices, the long-term risks of radioactive contaminant release are unknown.
The report’s authoring committee was not asked to recommend whether uranium mining should be permitted, or to consider the potential benefits to the state were uranium mining to be pursued. It also was not asked to compare the relative risks of uranium mining to the mining of other fuels such as coal.[50]

Texas
Uranium Energy Corp. began in-situ leach mining at its Palangana deposit (grading .135% U3O8) in Duval County in 2010. Uranium loaded resin beads from that ion exchange facility are processed into yellowcake at the company's Hobson processing plant, one of only three operating processing plants in the United States. The company has three more South Texas deposits permitted or under development.[51]
South America
Argentina
Blue Sky Uranium Corp. of Canada, together with an Argentinian partner, announced a 2012 exploration program in Rio Negro Province, and Chubut Province. The company's mining concessions cover 500,000 hectares. The near surface resource is believed to be recoverable through conventional open-pit mining. Other Canadian miners, however, have withdrawn from Argentina in the wake of recent legislation, considered to be unfriendly to the industry.[52]
Paraguay
Uranium exploration has only recently been undertaken in Paraguay, starting in 2006 by CUE Resources, Ltd. of Canada. Uranium Energy Corporation acquired CUE in 2012. The company's Yuty and Oviedo mining concessions, in the Parana Basin cover 230,650 hectares, roughly 5% of the country. Still in the exploration stage, the resource (grading roughly .05% U3O8) is thought to be favorable to In-situ leach recovery.[53]
References
- ↑ "DR Congo uranium mine collapses". BBC News. 2004-07-12.
- ↑ "Areva and Congo to cooperate in uranium mining". World-nuclear-news.org. 2009-03-27. Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ http://raid-uk.org/docs/ChinaAfrica/DRCCHINA%20report.pdf
- ↑ http://www.oenz.de/fileadmin/users/oenz/PDF/Studie/Uranium_Mining_in_the_DRC_OENZ_June_2011.pdf
- ↑ George J. Coakley (2004) Namibia, in Minerals Yearbook, Area Reports: International 2002, Africa and the Middle East, U.S. Geological Survey, p. 24.2.
- ↑ "Global Mining Market Intelligence". InfoMine.
- ↑ Miller, John W. (March 12, 2013). "Nuclear Fallout: Less Demand For Uranium Roils Miners". The Wall Street Journal (paper). pp. B1–2.
- ↑ Thomas R. Yager (2004) Burkina Faso, Mauritania, and Niger, in Minerals Yearbook, Area Reports: International 2002, Africa and the Middle East, U.S. Geological Survey, p. 6.2.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 9.8 2007 Annual report of the Euratom Supply Agency
- ↑ "Tiger reserve in Andhra made to shrink legally". Wildlifewatch.in. January 7, 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-22.
- ↑ "India reveals 'world's biggest' uranium discovery". AFP. July 19, 2011.
- ↑ url: http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-south-asia-14196372, title:India: 'Massive' uranium find in Andhra Pradesh , Source: BBC
- ↑ "Google Translate". google.com.
- ↑ "Jordan, France sign uranium exploration deal". Petra News Agency.
- ↑ "An overview of the Uranium Institute's 22nd Annual Symposium". Uranium Institute. 3–5 September 1997. Retrieved 2008-05-10.
- ↑ "World Nuclear Association". Retrieved 2008-05-10.
- ↑ "Урановото производство в България". DarikNews.bg. 2011-10-23. Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ See article in Czech: cs:Koncentrační tábory při československých uranových dolech.
- ↑ Uran stumbles in wooing towns. Victor Velek, The Prague Post. 7 May 2008.
- ↑ Uran Limited wants to open a new uranium mine in Havlickuv Brod district. Advantage Austria, Commercial Section of the Austrian Embassy in Prague. 17 April 2008.
- ↑ Negotiations with government of Czech Republic regarding Rozna uranium mine (PDF). Uran Ltd. 29 January 2007.
- ↑ Dyni, John R. (2006). "Geology and resources of some world oil-shale deposits. Scientific Investigations Report 2005–5294" (PDF). U.S. Department of the Interior. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved 2008-10-25.
- ↑ Lippmaa, E.; Maremäe, E. (2000). "Uranium production from the local Dictyonema shale in North-East Estonia". Oil Shale. A Scientific-Technical Journal (Estonian Academy Publishers) 17 (4): 387–394. ISSN 0208-189X.
- ↑ Maremäe, E. (2001). "Extraction of uranium from local Dictyonema shale at Sillamäe in 1948–1952". Oil Shale. A Scientific-Technical Journal (Estonian Academy Publishers) 18 (3): 259–271. ISSN 0208-189X.
- ↑ Uranium Mining in Finland: Fighting Prospectors in the Nuclear Age - URANIUM MINING IN FINLAND By Renate Nimtz-Köster(05/29/2007)SPIEGEL ONLINE
- ↑ - Talvivaara to recover uranium as a by-product (09.02.2010)
- ↑ "World uranium mining". World Nuclear Association. Retrieved 2008-12-08.
- ↑ "A baranyai falvak nem tiltakoznak uránkitermelés ellen". BAMA.
- ↑ "Últimas notícias de Portugal e do mundo > TVI24". Diario.iol.pt. Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ About Us Uranium National Company S.A.
- ↑ http://www.nipne.ro/events/conferences/seminar_sck-cen/docs/CNUiulie009.pdf
- ↑ Košice does not want uranium mines(27 February 2006) - The Slovak Spectator
- ↑ "European Uranium Resources Ltd. - Home - Tue Oct 16, 2012". Tournigan.com. Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ Košice: Activists protest against uranium mining in Jahodná again(26 February 2013) - The Slovak Spectator
- ↑ Daniel, J., Mašlárová, I., Maslár, E., Daniel, V., Danielová, K., Miháľ, F., 2006, Záverečná správa Zhodnotenie geologických prác na U rudy vo vybraných oblastiach Západných Karpát na území Slovenska. Manuskript, Spišská Nová Ves, Archív URANPRES, 122 s.
- ↑ "RSS Feed Detailed News". Platts. 1999-02-22. Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ "Projects Overview - Berkeley Resources Ltd". Berkeleyresources.com.au. Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ Cornwall Calling: South Terras Mine, Cornwall
- ↑ "Official Report 10 November 2005". Scottish Parliament. Retrieved 2008-05-10.
- ↑ "Peter Maxwell Davies". The Chamber Opera of Memphis. Retrieved 2008-05-10.
- ↑ Australia's anti-nuclear movement: a short history (26 August 1998) by Jim Green, Green Left
- ↑ "Uranium in Canada". World Nuclear Association. August 2010. Retrieved 2010-09-04.
- ↑ Nuffield, E. W., 1955, Geology of the Montreal River Area; Ontario Department of Mines, Volume LXIV, Part 3, Sixty-Fourth Annual Report.
- ↑ Carlie F. Banks (1976) Uranium and the Uranium Industry in Canada, Richardson, Tex.: Suntech Inc., p. 36–37.
- ↑ Robert J. Wright and Donald L. Everhart (1960) Uranium, in Mineral Resources of Colorado First Sequel, Denver: Colorado Mineral Resources Board, p. 329–365.
- ↑ New uranium mining halted at Canyon - Interior Dept. questions order issued by House committee Ginger D. Richardson, The Arizona Republic(Jun. 26, 2008)
- ↑ : Free National Research Council report PDF
- ↑ "Uranium Mining in Virginia: Scientific, Technical, Environmental, Human Health and Safety, and Regulatory Aspects of Uranium Mining and Processing in Virginia (2011) : Division on Earth and Life Studies". Dels.nas.edu. Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ : Report Public Summary
- ↑ "Division on Earth and Life Studies". Dels.nas.edu. Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ "Uranium production begins," Mining Engineering, December 2010.
- ↑ "Major Canadian uranium mining company leaves Argentina fearful of populist policies — MercoPress". En.mercopress.com. Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- ↑ "Yuty ISR Project | Uranium Energy Corp". Uraniumenergy.com. Retrieved 2012-10-16.