United States of Indonesia
| Republic of the United States of Indonesia | ||||||
| Republik Indonesia Serikat | ||||||
| Autonomous republic of the Netherlands | ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| Anthem Indonesia Raya | ||||||
 | ||||||
| Capital | Djakarta | |||||
| Languages | Indonesian | |||||
| Government | Federal parliamentary republic | |||||
| President | Sukarno Assaat Datuk Mudo (provisional) | |||||
| Prime Minister | Mohammad Hatta | |||||
| Historical era | Cold War | |||||
| - | Established | 27 December 1949 | ||||
| - | Independence from the Netherlands | 17 August 1950 | ||||
| Currency | Rupiah (IDR) | |||||
The Republic of the United States of Indonesia[1] (Indonesian: Republik Indonesia Serikat, RIS), abbreviated as RUSI,[1] was a federal state to which the Netherlands formally transferred sovereignty of the Dutch East Indies on 27 December 1949 following the Dutch-Indonesian Round Table Conference. This transfer ended the four-year conflict between Indonesian nationalists and the Netherlands that was fought over for control of Indonesia. At the same time, the Federal Constitution of 1949 came into effect.
The RUSI comprised sixteen state entities: a "Republic of Indonesia" consisting of territories in Java and Sumatra (a combined population of over 31 million); and the fifteen states established by the Dutch, which had populations between 100,000 and 11 million.
The RUSI had a bicameral legislature. The People's Representative Council consisted of 50 representatives from the Republic of Indonesia and 100 from the various states according to their populations. The Senate had two members from each constituent part of the RUSI regardless of population.
Over the first half of 1950, the non-Republic states gradually dissolved themselves into the Republic. The United States of Indonesia was officially dissolved by President Sukarno on 17 August 1950 – the fifth anniversary of his proclamation of independence – and replaced by a unitary Republic of Indonesia.
Component states
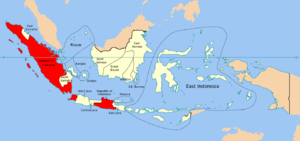
 Bandjar
Bandjar Banka
Banka Billiton
Billiton Central Java
Central Java East Indonesia
East Indonesia East Borneo (not including for former territory of Pasir Kingdom)
East Borneo (not including for former territory of Pasir Kingdom) East Java
East Java East Sumatra
East Sumatra Groot Dajak (Dajak Besar)
Groot Dajak (Dajak Besar) Madoera
Madoera Pasundan
Pasundan Republic of Indonesia (Negara Repoeblik Indonesia)
Republic of Indonesia (Negara Repoeblik Indonesia) Riouw
Riouw South East Borneo Federation
South East Borneo Federation South Sumatra
South Sumatra West Borneo (Special Region)
West Borneo (Special Region)
See also
- History of Indonesia
- Indonesian National Revolution
- Indonesian regions
- State of East Indonesia
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Frederick, William H.; Worden, Robert L ., eds. (1993), Indonesia: A Country Study, Washington: Library of Congress.
References
- Friend, Theodore (2003), Indonesian Destinies, Cambridge: Harvard University Press, ISBN 0-674-01834-6.
- Kahin, George McTurnan (1970), Nationalism and Revolution in Indonesia, Cornell University Press, ISBN 0-8014-9108-8.
- Ricklefs, M.C. (2001), A History of Modern Indonesia Since c. 1200 (3rd ed.), Stanford: Stanford University Press, ISBN 0-8047-4480-7.
- Frederick, William H.; Worden, Robert L ., eds. (1993), Indonesia: A Country Study, Washington: Library of Congress.
_COA_4.jpg)