USS Hector (AC-7)
 Off the Cavite Navy Yard, Philippine Islands, circa March 1915, with submarines A-3, A-5 and B-1 on deck, after transporting them out from the United States. - B-1 is on Hector 's starboard side. The two A-boats are in the center and port side cradles. | |
| Career | |
|---|---|
| Name: | USS Hector |
| Namesake: | Hector |
| Builder: | Maryland Steel Company, Sparrows Point, Maryland |
| Launched: | 3 July 1909 |
| Commissioned: | 22 October 1909 |
| Struck: | 1916 (est.) |
| Homeport: | Norfolk, Virginia |
| Fate: |
Wrecked off the Atlantic coast, 14 July 1916 Sank three days later |
| General characteristics | |
| Type: | Collier |
| Displacement: | 11,230 long tons (11,410 t) |
| Length: | 403 ft (123 m) |
| Beam: | 53 ft (16 m) |
| Draft: | 24 ft 8 in (7.52 m) |
| Propulsion: | Steam engine |
| Speed: | 12 kn (14 mph; 22 km/h) |
| Complement: | 82 officers and enlisted |
| Armament: | Unknown |
USS Hector (AC-7) was a collier acquired by the United States Navy prior to World War I. She carried coal to those ships still burning coal to build up steam for their engines, and continued that service until her wrecking and sinking in 1916. She was the sister of USS Mars.
Built at Sparrows Point, Maryland
Hector — the second ship to be so named by the U.S. Navy — was launched on 3 July 1909 by the Maryland Steel Company, Sparrows Point, Maryland; and commissioned on 22 October 1909.
Service in providing fuel
She was on special service with the Atlantic Fleet from commissioning through 1913, when she was stationed at Norfolk, Virginia. From there, Hector served as a fuel ship, ferrying freight and fuel up the U.S. East Coast and down to the Caribbean, especially Guantánamo Bay and Santo Domingo.
Sinking of Hector
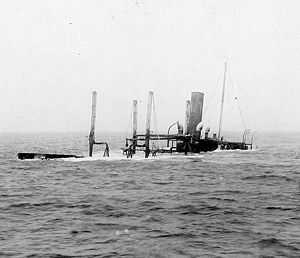
Hector was wrecked off the Atlantic coast on 14 July 1916 and sank three days later.
See also
References
- This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.