Tunicamycin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
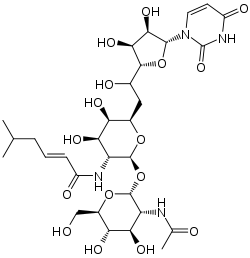
| IUPAC name
(E)-N-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6R)-2-[(2R,3R,4R,5S,6R)-
3-acetamido-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy- 6-[2-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)- 3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]-2-hydroxyethyl]-4,5-dihydroxyoxan- 3-yl]-5-methylhex-2-enamide | |
| Other names
NSC 177382 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 11089-65-9 | |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL505513 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| MeSH | Tunicamycin |
| PubChem | 6433557 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C39H64N4O16 | |
| Molar mass | N/A |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | 28 |
| S-phrases | 28-37/39-45 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Tunicamycin is a mixture of homologous nucleoside antibiotics that inhibits the UDP-HexNAc: polyprenol-P HexNAc-1-P family of enzymes. In eukaryotes, this includes the enzyme GlcNAc phosphotransferase (GPT), which catalyzes the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate from UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to dolichol phosphate in the first step of glycoprotein synthesis. Tunicamycin blocks N-linked glycosylation (N-glycans) and causes cell cycle arrest in G1 phase. It is used as an experimental tool in biology, e.g. to induce unfolded protein response.[1] Tunicamycin is produced by several bacteria, including Streptomyces clavuligerus and Streptomyces lysosuperficus.
Tunicamycin homologues have varying molecular weights owing to the variability in fatty acids side chain conjugates.[2]
See also
- Glycosylation - tunicamycin blocks all N-glycosylation of proteins
- Glycoprotein
- Streptomyces the genus
References
- ↑ Hepatitis C virus envelope proteins regulate CHOP via induction of ...
- ↑ Tunicamycin product details]
External links
- Book section of Essentials in Glycobiology (1999) Tunicamycin: Inhibition of DOL-PP-GlcNAc Assembly
- Tunicamycin data sheet prepared by a student of the Open University, UK