Tryptophan 7-halogenase
| Tryptophan 7-halogenase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 1.14.14.7 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Tryptophan 7-halogenase (EC 1.14.14.7, PrnA, RebH) is an enzyme with system name L-tryptophan:FADH2 oxidoreductase (7-halogenating).[1][2][3][4][5] This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
- tryptophan + FADH2 + Cl− + O2 + H+
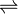 7-chloro-L-tryptophan + FAD + 2 H2O
7-chloro-L-tryptophan + FAD + 2 H2O
In Lechevalieria aerocolonigenes the enzyme catalyses the initial step in the biosynthesis of rebeccamycin.
References
- ↑ Dong, C., Kotzsch, A., Dorward, M., van Pee, K.H. and Naismith, J.H. (2004). "Crystallization and X-ray diffraction of a halogenating enzyme, tryptophan 7-halogenase, from Pseudomonas fluorescens". Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60 (Pt 8): 1438–1440. doi:10.1107/S0907444904012521. PMID 15272170.
- ↑ Yeh, E., Garneau, S. and Walsh, C.T. (2005). "Robust in vitro activity of RebF and RebH, a two-component reductase/halogenase, generating 7-chlorotryptophan during rebeccamycin biosynthesis". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102 (11): 3960–3965. doi:10.1073/pnas.0500755102. PMC 554827. PMID 15743914.
- ↑ Bitto, E., Huang, Y., Bingman, C.A., Singh, S., Thorson, J.S. and Phillips Jr., G.N. (2008). "The structure of flavin-dependent tryptophan 7-halogenase RebH". Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 70: 289–293.
- ↑ Dong, C; Kotzsch, A; Dorward, M; Van Pée, K. H.; Naismith, J. H. (2004). "Crystallization and X-ray diffraction of a halogenating enzyme, tryptophan 7-halogenase, from Pseudomonas fluorescens". Acta crystallographica. Section D, Biological crystallography 60 (Pt 8): 1438–40. doi:10.1107/S0907444904012521. PMID 15272170.
- ↑ Dong, C; Flecks, S; Unversucht, S; Haupt, C; Van Pée, K. H.; Naismith, J. H. (2005). "Tryptophan 7-halogenase (PrnA) structure suggests a mechanism for regioselective chlorination". Science 309 (5744): 2216–9. doi:10.1126/science.1116510. PMC 3315827. PMID 16195462.
External links
- Tryptophan 7-halogenase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)