Trisquel
 | |
|
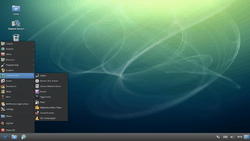
Trisquel 7.0 desktop | |
| Developer | Trisquel community and Sognus, S.L.U. |
|---|---|
| OS family | Unix-like |
| Working state | Current[1] |
| Initial release | January 30, 2007 |
| Latest release | 7.0[2] / November 3, 2014 |
| Update method | APT |
| Package manager | dpkg |
| Platforms | x86, AMD64 |
| Kernel type | Monolithic (Linux-libre) |
| Userland | GNU Core Utilities |
| Default user interface | GNOME |
| License | Exclusively free licenses per GNU Free System Distribution Guidelines (GNU FSDG)[3] |
| Official website |
trisquel |
Trisquel (officially known as Trisquel GNU/Linux[4]) is a Linux-based operating system derived from Ubuntu.[5] The project aims for a fully free software system without proprietary software or firmware and uses Linux-libre, a version of the Linux kernel with the non-free code (binary blobs) removed.[6] Trisquel relies on user donations.[7] Its logo is a triskelion.[8] Trisquel is listed by the Free Software Foundation as a distribution that contains only free software.[9]
Overview
Three basic versions are available.
Trisquel
The standard Trisquel distribution includes the GNOME desktop environment and GUI as well as English, Spanish and many other localizations on a 1.5GB DVD image.
Trisquel Mini
Trisquel Mini is an alternative to the mainline Trisquel, designed to run well on netbooks and aging hardware. It uses the low-resource environment LXDE and lightweight GTK+ and X Window System alternatives to GNOME and Qt/KDE applications.[10] The LXDE desktop also includes English and Spanish localizations, and it can be installed from a 500 MB CD image.
If an Internet connection has been enabled during the installation of either Trisquel or Trisquel Mini, the operating system will download and install itself (including user menus and all available documentation) in any one or more of the 51 languages that Trisquel has been localized in.
Internationalization
The full installation includes 51 languages (Albanian, Arabic, Aranese, Asturian, Basque, Bulgarian, Catalan, Central Khmer, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Esperanto, Estonian, Finnish, French, Galician, German, Greek, Hebrew, Hindi, Hungarian, Indonesian, Irish, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Latvian, Lithuanian, Low German, Norwegian Bokmål, Norwegian Nynorsk, Occitan, Punjabi, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Russian, Serbian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish, Swedish, Tamil, Thai, Turkish, Valencian and Vietnamese) pre-installed in a downloadable 1.2-gigabyte DVD image.
Full source code for the entire Trisquel installation is also available in a downloadable 3-gigabyte DVD image.
History
The project began in 2004 with sponsorship of the University of Vigo for Galician language support in educational software and was officially presented in April 2005 with Richard Stallman, founder of the GNU Project, as a special guest.[11] According to project director Rubén Rodríguez, the support for Galician has created interest in South American and Mexican communities of emigrants from the Province of Ourense.[12]
By December 2008, Trisquel was included by the FSF in its list of Linux distributions endorsed by the Free Software Foundation.[13]
Release history
| Legend: | Old version | Older version, still supported | Current version |
|---|
| Version | Code name | Release date | Supported until | Kernel | Desktop environment | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old version, no longer supported: 1.0 | Arianrhod | 2007-01-30[14] | N/A | Linux 2.6.18.6 | GNOME 2.14 | Debian 4.0 (Etch) |
| Old version, no longer supported: 2.0 LTS | Robur | 2008-07-24[15] | 2014-03-02[16][17] | Linux 2.6.24 | GNOME 2.22 | Ubuntu 8.04 LTS (Hardy Heron) |
| Old version, no longer supported: 3.0 STS | Dwyn | 2009-09-08[18] | 2011-05-11[16][19] | Linux-libre 2.6.28 | GNOME 2.26 | Ubuntu 9.04 (Jaunty Jackalope) |
| Old version, no longer supported: 3.5 STS | Awen | 2010-03-22[20] | 2011-07-14[16][21] | Linux-libre 2.6.31 | GNOME 2.28 | Ubuntu 9.10 (Karmic Koala) |
| Older version, yet still supported: 4.0 LTS | Taranis | 2010-09-18[22] | 2015[23] | Linux-libre 2.6.32 | GNOME 2.30 | Ubuntu 10.04 LTS (Lucid Lynx) |
| Old version, no longer supported: 4.5 STS | Slaine | 2011-03-24[24] | 2012-09-15[16][25] | Linux-libre 2.6.35 | GNOME 2.32 | Ubuntu 10.10 (Maverick Meerkat) |
| Old version, no longer supported: 5.0 STS | Dagda | 2011-09-17[26] | 2014-03-02[16][17] | Linux-libre 2.6.38 | GNOME 2.32 | Ubuntu 11.04 (Natty Narwhal) |
| Old version, no longer supported: 5.5 STS | Brigantia | 2012-04-16[27] | 2014-03-02[16][17] | Linux-libre 3.0 | GNOME 3.2 | Ubuntu 11.10 (Oneiric Ocelot) |
| Older version, yet still supported: 6.0 LTS | Toutatis | 2013-03-09[28] | 2017[28] | Linux-libre 3.2 | GNOME 3.4 | Ubuntu 12.04 LTS (Precise Pangolin) |
| Current stable version: 7.0 LTS | Belenos | 2014-11-03[29] | 2019[29] | Linux-libre 3.13 | GNOME 3.12 | Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty Tahr) |
The releases that use GNOME 3.x use GNOME Classic/Flashback, rather than the default GNOME Shell. All Trisquel releases starting with version 6 are only based on Ubuntu LTS releases.[30]
Current versions include this common software:
- A rebranded version of Firefox called "Abrowser" that never suggests non-free add-ons, and includes no trademarked art or names. Abrowser is rebranded because the Mozilla Trademark Policy forbids modifications that include their trademark without consent.[31] As Adobe Flash Player is proprietary software, Trisquel does not provide it, instead offering the Gnash SWF Viewer.[32]
Previous editions:
- Trisquel Pro
- Trisquel Pro was a small business oriented operating system. It was part of the Trisquel 2.0 LTS Robur (2008), but no further releases have been made since.[33]
- Trisquel Edu
- Trisquel Edu was another Trisquel spin focused on providing educational packages for schools and universities. Like Trisquel Pro, no further releases have been made since Trisquel 2.0 Robur (2008).[34]
- Trisquel on Sugar
- Trisquel on Sugar was based on the Sugar desktop environment for interactive learning for children. It was released at the same time as Trisquel 7.
- Trisquel Gamer
- Trisquel Gamer was an independent edition maintained by David Zaragoza. It came with 55 free software games and could be booted from a LiveDVD or USB drive. It was released along with Trisquel 3.5 (2010), which is no longer supported.[35]
Reception

Jesse Smith of DistroWatch reviewed the 4.0 release, Taranis, and described it as refined and dependable. He portrayed difficulty with removing software as his main problem with the release. Smith complimented Trisquel as an operating system that showcased utility instead of mere compliance with free software criteria.[5]
Jim Lynch of Desktop Linux Reviews reviewed the 5.5 release, Brigantia, and described it as "well-ordered and well developed" and recommended it to users whether they care about only using free software or not. Lynch stated that the release was suitable for beginners and advanced users.[36]
Chris Fisher and Matt Hartley of the The Linux Action Show! praised the design, ease of use, and hardware support of Trisquel 5.5 and Trisquel 5.5 Mini, but found that the Linux-libre kernel found in Trisquel impedes functionality of proprietary wireless devices. They argued that the distribution was targeting power users and that new users should use a different distribution.[37]
Richard Stallman announced in January 2015 that he is using Trisquel on a Thinkpad X60 instead of his former computer the Lemote Yeeloong.[38]
Hardware
ThinkPenguin hardware is supported since Trisquel 5.5, that includes free software compatible chipsets.[39]
See also
- Comparison of Linux distributions
- List of Linux distributions based on Ubuntu
- GNU/Linux naming controversy
References
- ↑ https://trisquel.info/en/download
- ↑ https://trisquel.info/en/trisquel-70-lts-belenos
- ↑ https://www.gnu.org/distros/free-distros.html
- ↑ "Download". Trisquel website. Retrieved December 27, 2013.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Smith, Jesse (October 4, 2010). "Trisquel GNU/Linux - a free distribution". DistroWatch. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ↑ Huber, Mathias (September 9, 2011). "Trisquel GNU/Linux 5.0 verfügbar" [Trisquel GNU/Linux 5.0 available] (in German). Linux-Magazin. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ↑ "Siete factores antes de usar 'software'" (in Spanish). El Comercio. April 14, 2012. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ↑ "How is "Trisquel" pronounced?". The Trisquel Project. Retrieved September 14, 2012.
- ↑ "List of Free GNU/Linux Distributions". Retrieved 13 May 2014.
- ↑ "Trisquel Mini". The Trisquel Project. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ↑ "Richard Stallman, defensor del software libre, sorprendió a los universitarios" (in Spanish). La Voz de Galicia. April 28, 2005. Retrieved November 26, 2008.
- ↑ García, Ana (May 17, 2007). "Software libre da terra, compartindo cultura" (in Galician). El Progreso. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ↑ "Free GNU/Linux distributions". Free Software Foundation. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ↑ Trisquel (January 30, 2007). "Publicación de Trisguel 1.0" (in Galician). Archived from the original on February 3, 2007. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "Proxecto Trisquel" (in Galician). July 24, 2008. Archived from the original on July 24, 2008. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 "Index of /trisquel/dists". Retrieved August 4, 2014.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 "[Trisquel-announce] [Trisquel-devel] Robur, Dagda and Brigantia moved to oldarchive". March 2, 2014. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "Trisquel 3.0 STS "Dwyn" has landed!". The Trisquel Project. September 8, 2009. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "[Trisquel-announce] Trisquel 3.0 STS Dwyn reaches end of life, 3.5 soon to follow.". May 11, 2011. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "Trisquel 3.5 Awen release announcement". The Trisquel Project. March 22, 2010. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "[Trisquel-devel] Trisquel 5.0 development repository up, 3.5 reaches end of life". July 15, 2011. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "Trisquel 4.0 LTS "Taranis" strikes!". The Trisquel Project. September 18, 2010. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "Versions". Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "Trisquel 4.5 "Slaine" released". The Trisquel Project. March 24, 2011. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "[Trisquel-announce] Trisquel 4.5 Slaine reached end of life". September 15, 2012. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "Trisquel 5.0 Release announcement". The Trisquel Project. September 17, 2011. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "Trisquel 5.5 STS Brigantia release announcement". The Trisquel Project. April 16, 2012. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "Trisquel 6.0 LTS "Toutatis" has arrived!". The Trisquel Project. March 9, 2013. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Trisquel 7.0 LTS Belenos". The Trisquel Project. November 3, 2014. Retrieved November 3, 2014.
- ↑ "2013-03-05 Meeting". Trisquel. March 5, 2013. Retrieved November 29, 2014.
- ↑ "Mozilla Trademark Policy". Mozilla. October 30, 2009. Retrieved December 19, 2012.
- ↑ Baader, Hans-Joachim (September 20, 2011). "Trisquel 5.0 veröffentlicht" [Trisquel 5.0 published] (in German). Pro-Linux. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ↑ "Trisquel Pro". The Trisquel Project. Retrieved December 19, 2012.
- ↑ "Trisquel Edu". The Trisquel Project. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ↑ Zaragoza, David. "Trisquel Gamer". The Trisquel Project. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ↑ Lynch, Jim (April 24, 2012). "Trisquel 5.5". Desktop Linux Reviews. Retrieved April 28, 2012.
- ↑ Fisher, Chris; Hartley, Matt (September 2, 2012). "Trisquel GNU/Linux Review - LAS - s23e05". Jupiter Broadcasting. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ↑ Stallman, Richard. "Richard Stallman's personal site - How I do my computing". Retrieved January 6, 2015.
- ↑ Will ThinkPenguin hardware work with Trisquel?
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Trisquel. |
| ||||||
| ||||||||||