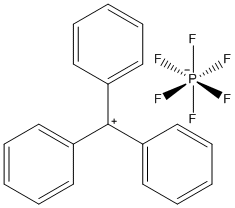
Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Trityl hexafluorophosphate Triphenylcarbenium hexafluorophosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 437-17-2 | |
| Properties | |
| C19H15F6P | |
| Molar mass | 388.31 g/mol |
| Appearance | brown powder |
| Melting point | 145 °C (293 °F; 418 K) |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | |
| R-phrases | R34, R26, R36/37, R39, R45 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate is an organic salt with the formula C(C6H5)3PF6. This compound is a brown powder that is air sensitive and changes colors when exposed to light. Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate is used as a catalyst and reagent in organic syntheses.[1]
Preparation
Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate is generated by two ways. The first method is by combining silver hexafluorophosphate with triphenylmethyl chloride:[2]
- AgPF6+C(C6H5)3Cl→C(C6H5)3PF6+AgCl
The second method of generating triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate is through the reaction of triphenylmethyl chloride with an ether complex of hexafluorophosphoric acid:[3]
- Ph3CCl+HPF6·O(C2H5)2→Ph3C+PF−6+HCl+(C2H5)2O
Triphenylmethyl chloride is afforded by combining carbon tetrachloride and benzene in a Friedel-Crafts reaction.[3]
Structure and Properties
The trityl group can exist in three oxidation states: the trityl cation, the trityl radical, and the trityl anion. The trityl cation is the form present in triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate. The triphenylmethyl cation effectively has D3h molecular symmetry.
The hexafluorophosphate of triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate readily undergoes hydrolysis.[4]
CPh3PF6+H2O→HOCPh3+HPF6
Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate combined with water in basic conditions undergo hydrolysis to form triphenylmethanol and the conjugate acid hexafluorophosphoric acid. When acidic conditions are present, the reaction will proceed in the opposite direction and triphenyl methanol will form triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate and water.
Reactions
Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate has been used for abstracting hydride from transition metal alkene and diene complexes. For example, triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate can also ionize an alkoxy substituted and cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl complexes.[1]
Triphenylmethyl perchlorate is a common substitute for triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate. However, the perchlorate is not used as widely, because, like other organic perchloriates, it is potentially explosive. Both triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate and triphenylmethyl perchlorate produce similar results and yields in most reactions.[1]
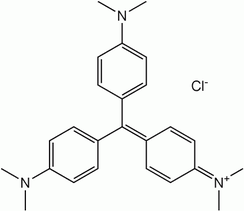
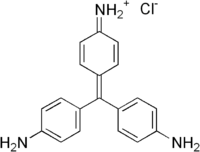
Triarylmethane dyes
Triarylmethane dyes are derivatives are stabilized version of the trityl cation, so much so that they are water soluble and are often obtained as the chloride salts. These dyes have strong electron donor groups, often amines, at the p-positions of two or three of the aryl groups.[5]
- Triarylmethane dyes
-

New fuchsine dye.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Urch, C. (2001). "Triphenylmethyl Hexafluorophosphate". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt363f.
- ↑ Sharp, D., Shepard, N. (1956). "Complex Fluorides. Part VIII". University Chemical Laboratory, Cambridge: 674–682.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Olah, G., Svoboda, J., Olah, J. (1972). "Preparative Carbocation Chemistry; IV. Improved Preparation of Triphenylcarbenium (Trityl) Salts". Synthesis: 544.
- ↑ Fernandez-Galan, R.; Manzano, B; Otero, A; Lanfranchi, M; Pellinghelli, M. (1994). "19F and 31P NMR Evidence for Silver Hexafluorophosphate Hydrolysis in Solution". Inorg. Chem 33: 2309–2312. doi:10.1021/ic00088a039.
- ↑ Thomas Gessner and Udo Mayer "Triarylmethane and Diarylmethane Dyes" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_179