Trifluoromethyl hypofluorite
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 373-91-1 | |
| ChemSpider | 71322 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 78989 |
| |
| Properties | |
| OCF 4 | |
| Molar mass | 104.004012 |
| Appearance | Colourless gas |
| Melting point | −213 °C (−351.4 °F; 60.1 K) |
| Boiling point | −95 °C (−139 °F; 178 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Toxic |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
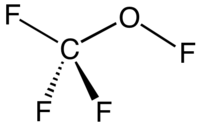
Trifluoromethyl hypofluorite is an organofluorine compound with the formula CF
3OF. It exists as a colorless gas at room temperature and is highly toxic.[1] It is a rare example of a hypofluorite (compound with an O-F bond). It is prepared by the fluorination of carbon monoxide:
- 2 F2 + CO → CF3OF
The gas hydrolyzes only slowly at neutral pH.
Use in organic chemistry
The compound is a source of electrophilic fluorine. It has been used for the preparation of α-fluoroketones from silyl enol ethers.[2] Behaving like a pseudohalogen, it adds to ethylene to give the ether:
- CF3OF + CH2CH2 → CF3OCH2CH2F
References
- ↑ Cady, G (1966). "Trifluoromethyl Hypofluorite". Inorganic Syntheses 8: 168. doi:10.1002/9780470132395.ch43.
- ↑ Middleton, W. J.; Bingham, E. M. (1980). "α-Fluorination of carbonyl compounds with trifluoromethyl hypo fluorite". Journal of the American Chemical Society 102: 4845–6. doi:10.1021/ja00534a053.